Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 932-950
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932
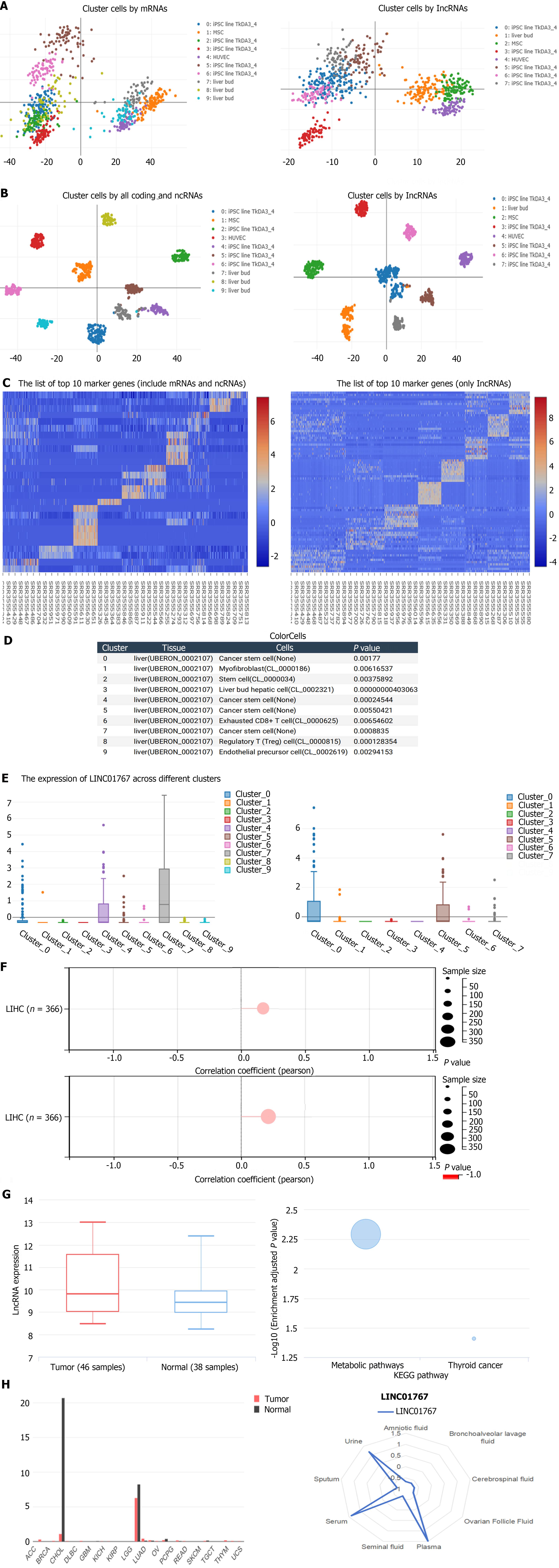
Figure 1 Single-cell sequencing analysis via the color cell web based on GSE81252 and validation.
A: The principal components analysis results showed that the 9-cluster cell by all coding and non-coding RNAs and 7-cluster cell by noncoding RNAs solely were identified; B: The t-SNE Nonlinear dimensionality reduction showed the corresponding dimensionality reduction; C: The differential genes among different cell-cluster; D: The 9-clusters cell subgroups; E: The expression of LINC01767 was upregulated in cluster 7 which was classified into cancer stem cell; F: DNAss (up) and RNAss (down) is associated in LIHC (n = 366, P < 0.001); G: GSE78160 (serum long noncoding RNAs) data showed that the serum LINC01767 was up regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a log fold change 0.699, P = 0.026524; LINC01767 is associated with the metabolic; H: LINC01767 was expressed in liver and bile duct with a significantly high level high level than other tissues LINC01767 demonstrate a high level in serum, urine, and plasma. ncRNA: Non-coding RNA; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA.
- Citation: Zhang L, Cui TX, Li XZ, Liu C, Wang WQ. Diagnostic and prognostic role of LINC01767 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(6): 932-950
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i6/932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932