Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2024; 16(5): 688-702
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i5.688
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i5.688
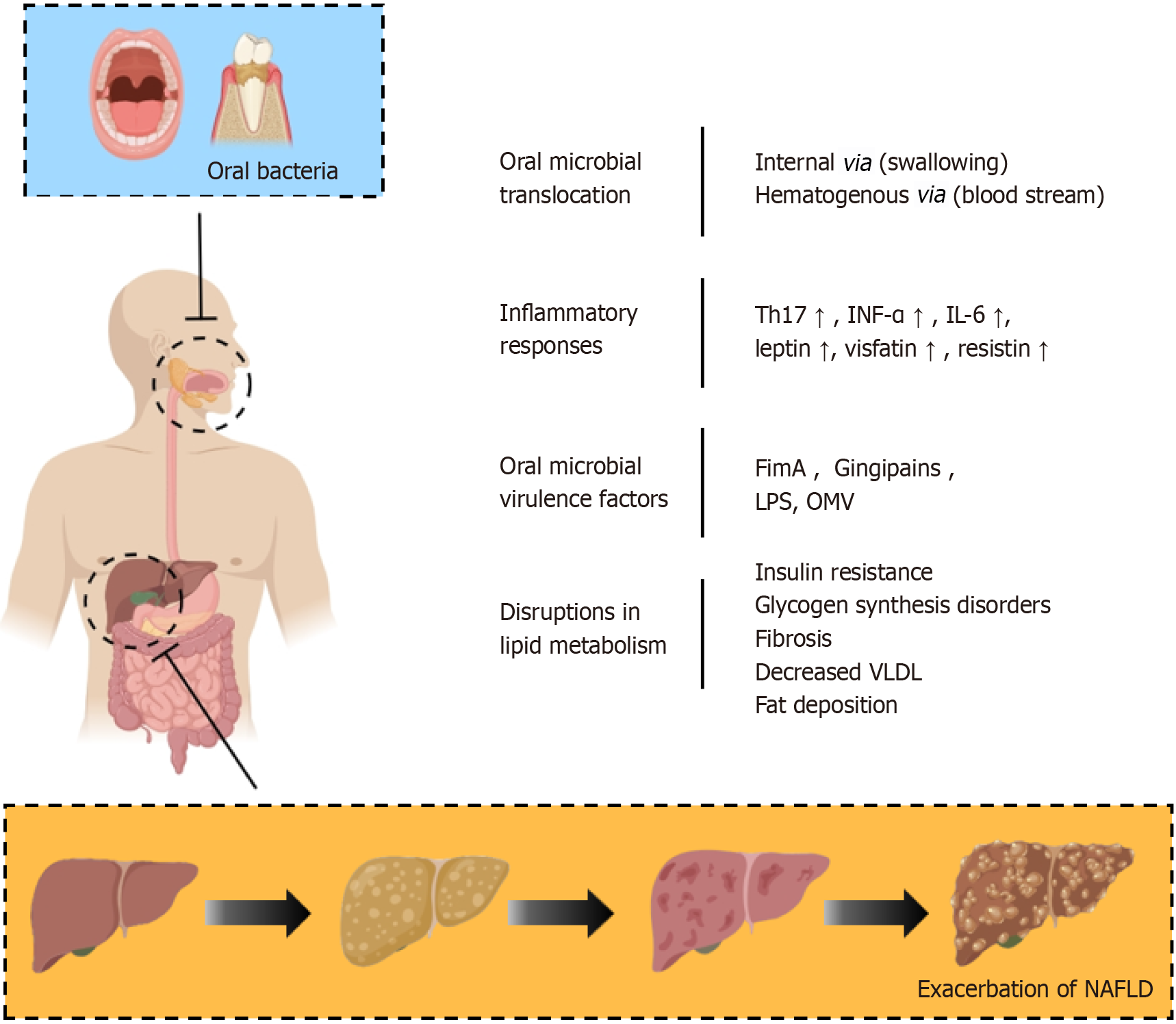
Figure 3 The connection between oral microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Oral microbiota plays a significant role in advancing liver fat deposition, inflammatory responses, and fibrosis, thus expediting the progression from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This effect is mediated through four principal mechanisms: Translocation of oral microbes, inflammatory responses, virulence factors of oral microbes, and disruptions in lipid metabolism. OMV: Outer membrane vesicles; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; INF-α: Interferon alpha; IL: Interleukin; VLDL: Very-low-density lipoprotein; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Mei EH, Yao C, Chen YN, Nan SX, Qi SC. Multifunctional role of oral bacteria in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(5): 688-702
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i5/688.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i5.688