Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2024; 16(4): 601-611
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.601
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.601
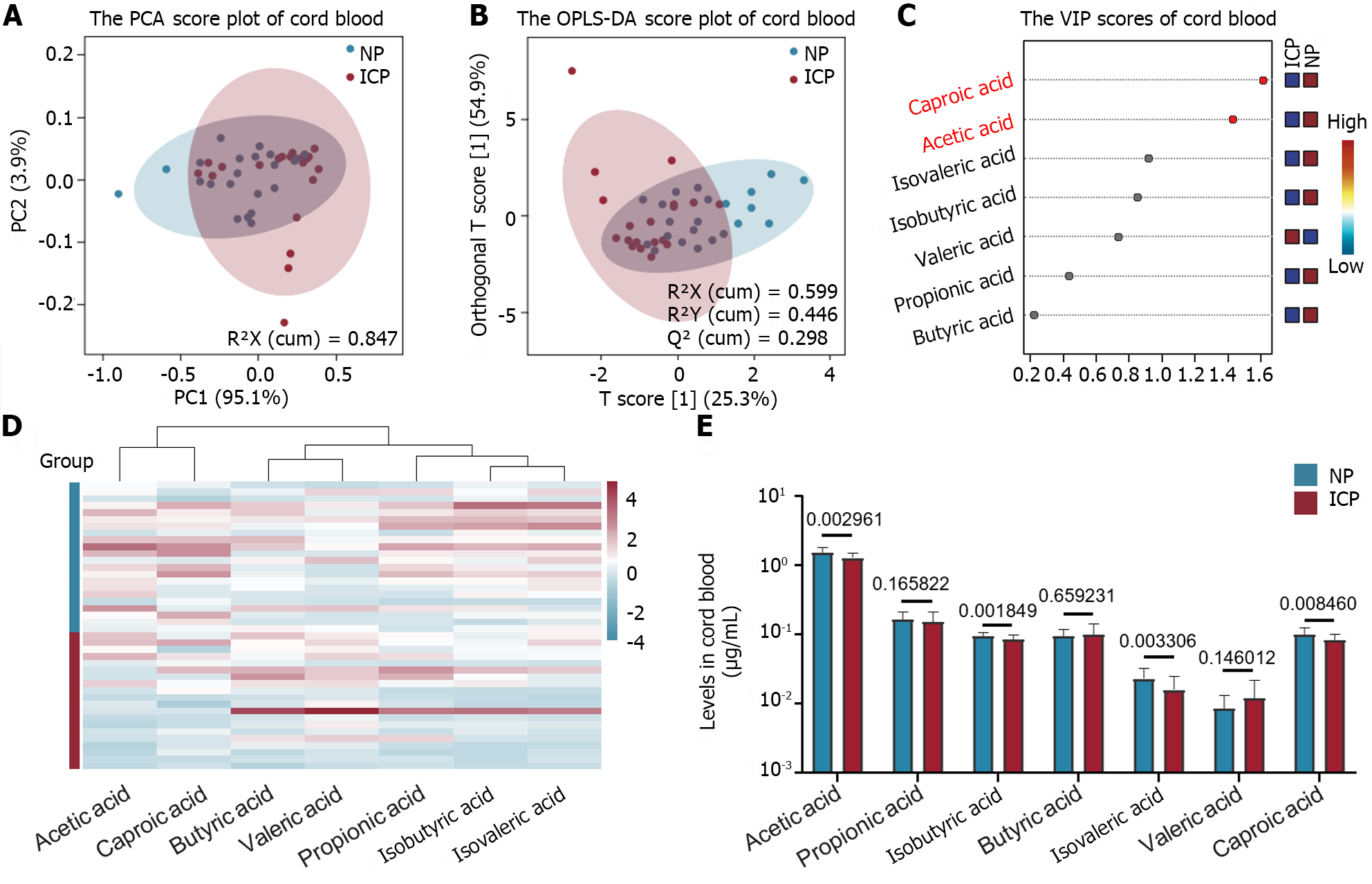
Figure 2 Characteristics of short-chain fatty acids metabolic spectrum changes in the cord blood of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy patients.
A: Principal Component Analysis score chart: intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) patients experience inadequate separation from the normal pregnant women; B: Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis score chart: A partial overlap was observed between patients with ICP and normal pregnant women; C: Variable importance for the projection diagram: Acetic acid and caproic acid were identified as important metabolites that induced differences in short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the cord blood between the two groups; D: Heat map: Except for valeric acid, other SCFAs displayed a decreasing trend in the cord blood of ICP patients; E: Quantitative analysis bar chart: Acetic acid demonstrated the highest content in the cord blood. The isobutyric acid content was lower in ICP patients. NP: n = 22; ICP: n = 20. PCA: Principal Component Analysis; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids; OPLS-DA: Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis; VIP: Variable Importance for the Projection.
- Citation: Ren SJ, Feng JT, Xiang T, Liao CL, Zhou YP, Xuan RR. Expression and clinical significance of short-chain fatty acids in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(4): 601-611
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i4/601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.601