Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2024; 16(4): 566-600
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.566
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.566
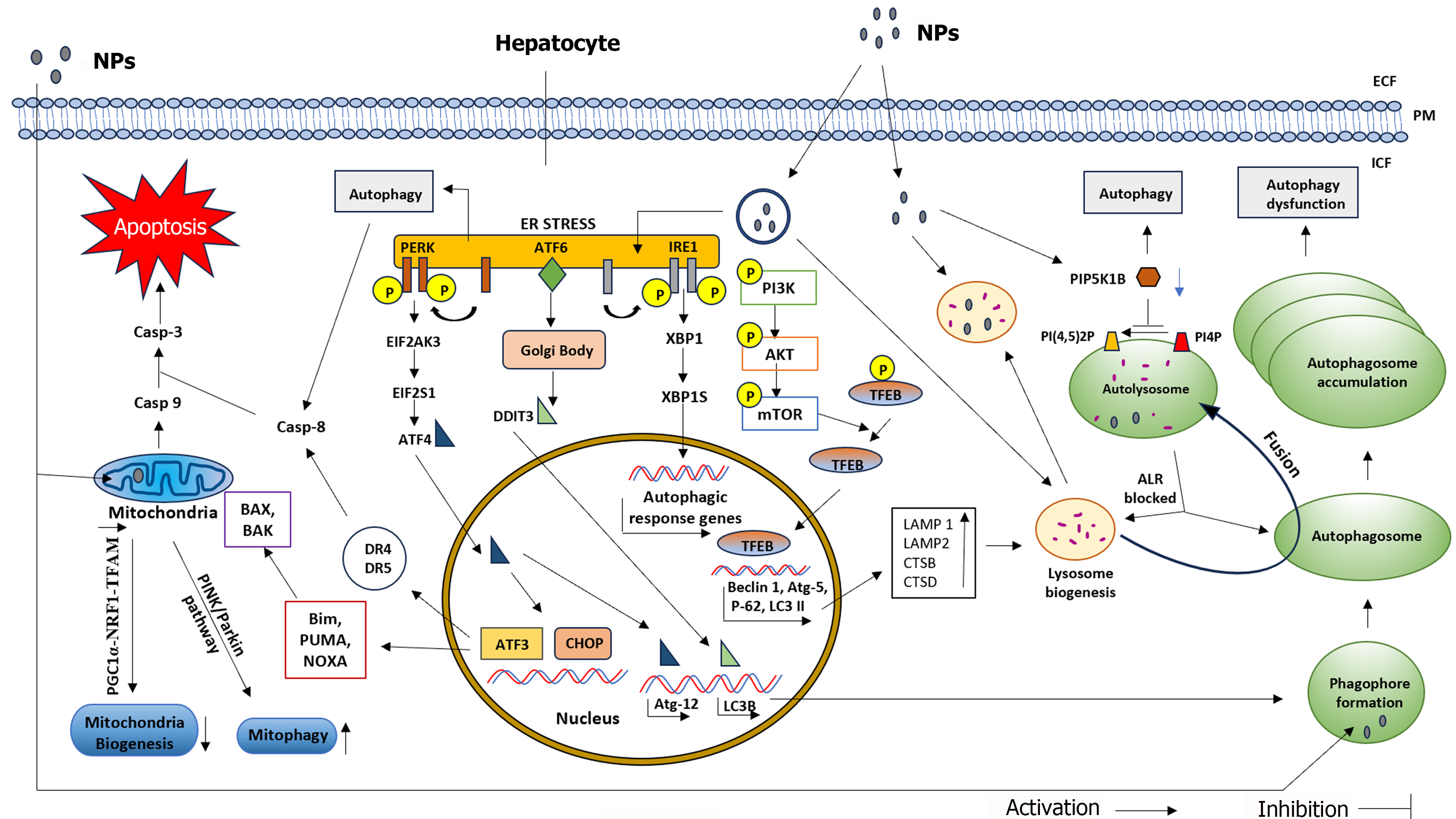
Figure 1 Diagram showing NPs induced hepatotoxicity through crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, autophagic and apoptotic pathways.
AKT: Protein kinase B; ALR: Autophagic lysosome reformation; ATF 3/4/6: Activating transcription factor 3/4/6; Atg 5/12: Autophagy related gene 5/12; BAK: Bcl-2 homologues antagonist/killer; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X-protein; Bim: Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death; Casp 3/8/9: Caspase 3/8/9; CHOP: C/EBP Homologous Protein; CTSB: Cathepsin B; CTSD: Cathepsin D; DDIT3: DNA damage inducible transcript 3; DR: Death receptor; ECF-Extra cellular fluid; EIF2AK3: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3; EIF2S1: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1; ICF-Intra cellular fluid; IRE1: Inositol-requiring enzyme type-1; LAMP1/2: Lysosome-associated membrane protein 1/2; LC3B-Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B; LC3II: LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NOXA: Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1; NPs- Nanoparticles; NRF1: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 1; P 62-Ubiquitin-binding protein p62; P: Phosphate; Parkin-Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase; PERK: Protein kinase RNA like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PGC1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha; PI(4,5)2P: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PI4P: Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate;PINK: PTEN induced kinase; PIP5K1B: Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5 kinase type 1 beta; PM: Plasma membrane; PUMA- p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis; TFAM: Mitochondrial transcription factor A; TFEB: Transcription factor EB; XBP1/1S: X box binding protein-1/1S.
- Citation: Das SK, Sen K, Ghosh B, Ghosh N, Sinha K, Sil PC. Molecular mechanism of nanomaterials induced liver injury: A review. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(4): 566-600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i4/566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.566