Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2024; 16(2): 264-278
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i2.264
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i2.264
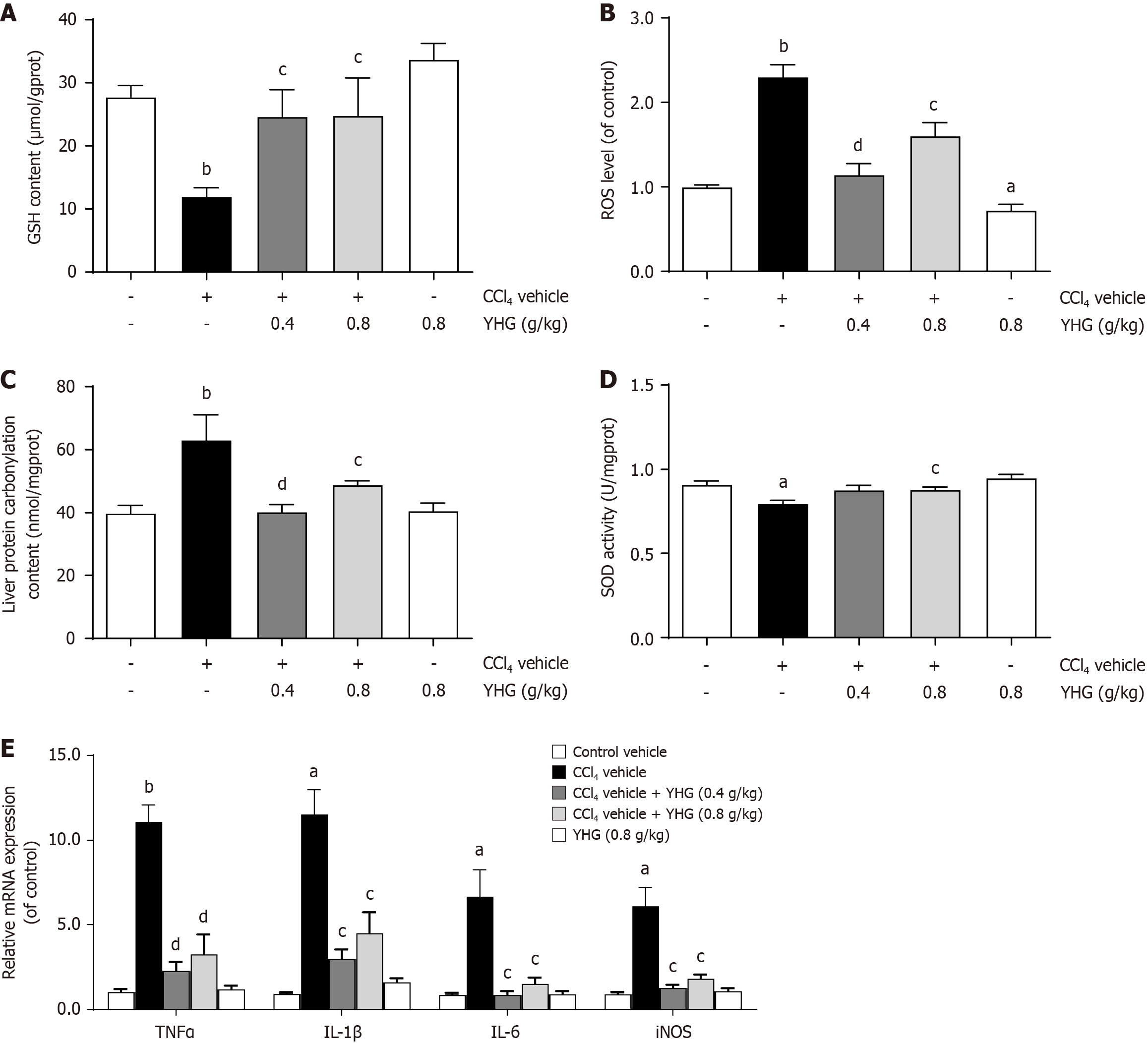
Figure 4 Yinhuang granule ameliorated hepatic oxidative stress damage and inflammation induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice.
A: Liver glutathione content (n = 6); B: Liver reactive oxygen species level (n = 6); C: Liver protein carbonylation content (n = 6); D: Liver superoxide dismutase activity (n = 5); E: Hepatic mRNA expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL)-1b, IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (n = 4-5). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control vehicle; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs carbon tetrachloride vehicle. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; YHG: Yinhuang granule; GSH: Liver glutathione; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
- Citation: Ouyang H, Miao H, Li Z, Wu D, Gao SC, Dai YY, Gao XD, Chai HS, Hu WY, Zhu JF. Yinhuang granule alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice and its mechanism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(2): 264-278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i2/264.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i2.264