Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2024; 16(12): 1395-1406
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1395
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1395
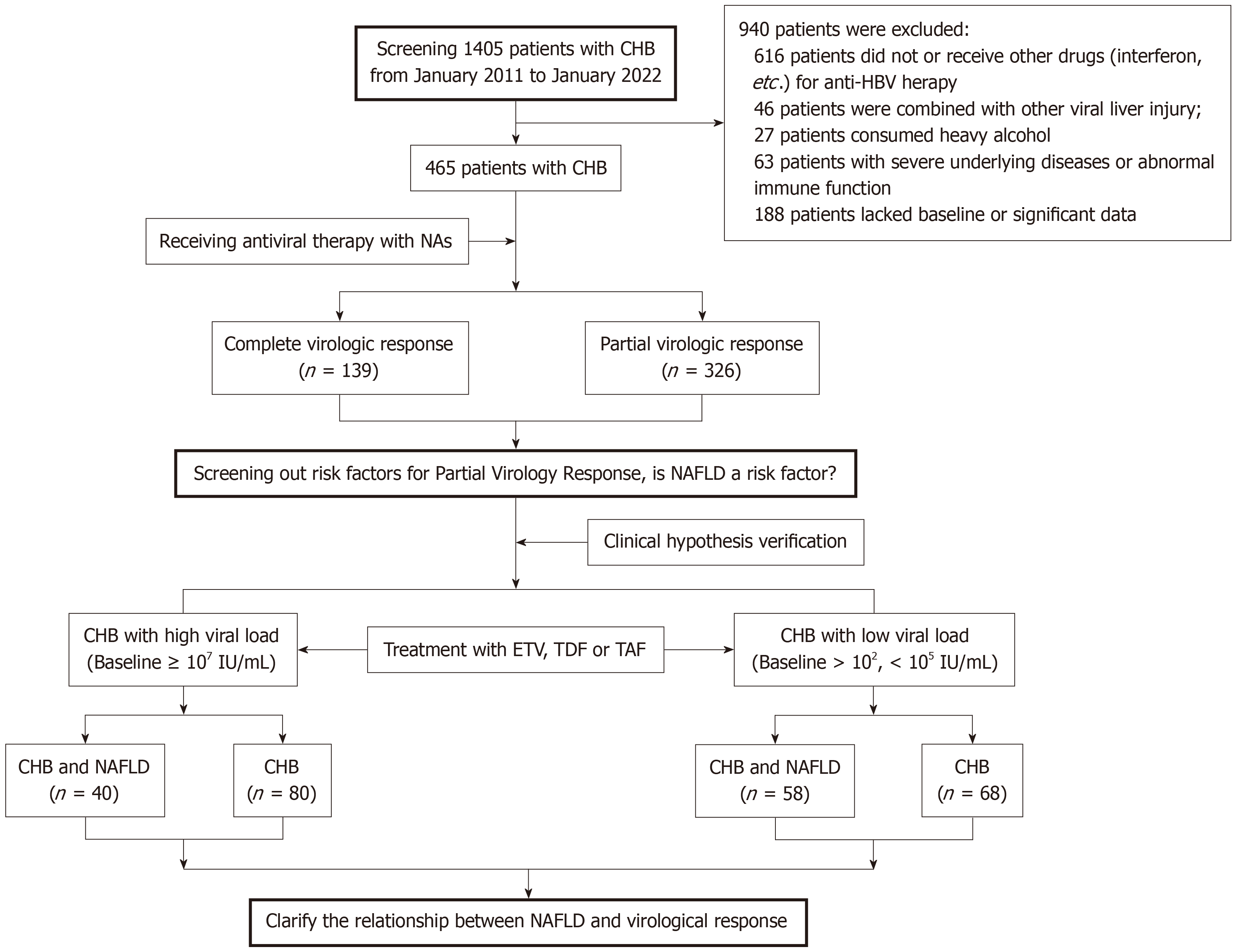
Figure 1 Flow chart of the chronic hepatitis B subjects enrolled in the study.
A total of 1405 adults with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) were assessed during the study period, and 465 met the inclusion criteria. Among those who received antiviral therapy with NAs, 139 subjects obtained complete virological response, 326 subjects got partial virological response (PVR), and the risk factors of PVR were observed. Subsequently, to verify the relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease coexisting with CHB and virological response, we conducted a dynamic analysis of viral response to NAs antiviral treatment from patients with hepatitis B virus DNA high viral load and low viral load. CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; NAs: Nucleos(t)ide analogues; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; ETV: Entecavir; TDF: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate; TAF: Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate.
- Citation: Li HD, Liu YN, Wu S, Quan XF, Wang XY, Xiang TD, Li SM, Xu L, Wang T, Wang H, Zheng X. Influence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on the therapeutic effect of nucleoside (acid) analogs for hepatitis B virus. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(12): 1395-1406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i12/1395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1395