Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2024; 16(10): 1188-1198
Published online Oct 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i10.1188
Published online Oct 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i10.1188
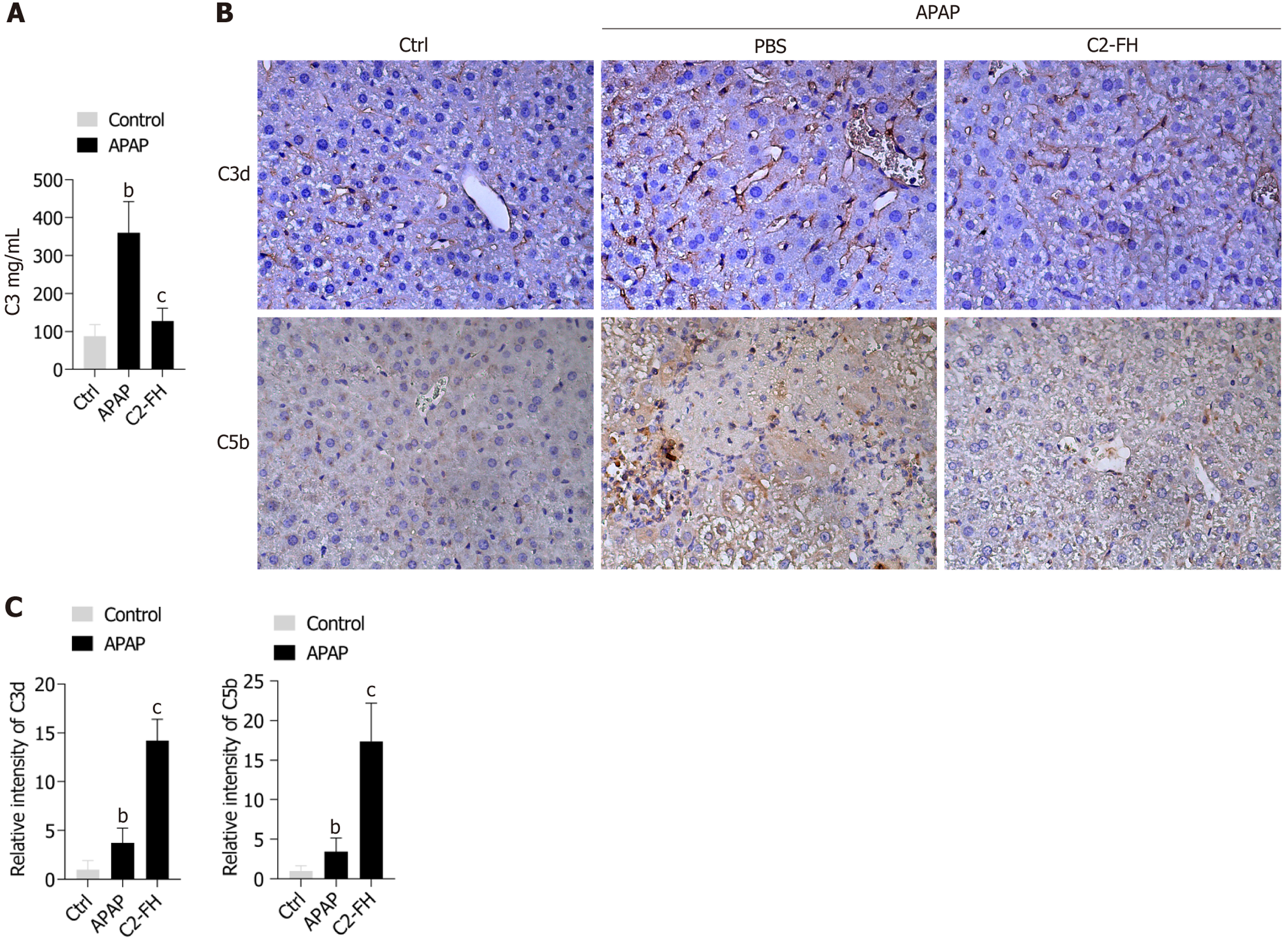
Figure 3 Impact of C2-FH on activation of complement in liver injury induced by acetaminophen.
A: Serum C3 concentration; B: Immunohistochemical analysis to detect C3d and C5b deposition at 24 hours post-acetaminophen treatment; C: Relative intensity of C3d and C5b quantified using Image J software. n = 4/5 per group, magnification, 400 ×, scale bars 25 µm. bP < 0.05 Ctrl vs APAP group. cP < 0.01 APAP vs C2-FH group. APAP: Acetaminophen.
- Citation: Li CM, Sun T, Yang MJ, Yang Z, Li Q, Shi JL, Zhang C, Jin JF. Complement activation targeted inhibitor C2-FH ameliorates acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(10): 1188-1198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i10/1188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i10.1188