Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2023; 15(9): 1043-1059
Published online Sep 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1043
Published online Sep 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1043
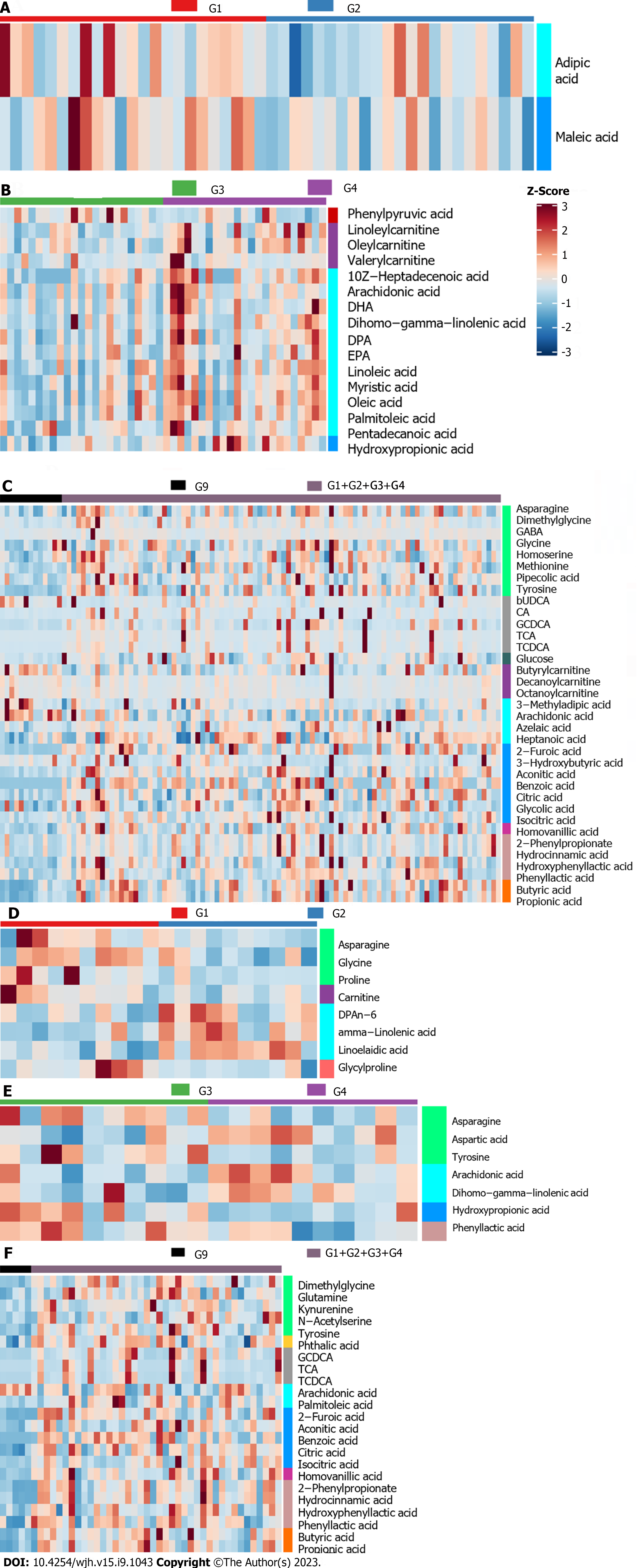
Figure 3 Heatmap of all the selected potential metabolites.
A: Heatmap of entecavir responders (E-R) vs entecavir no-responders (E-N) (training set); B: Heatmap of FuzhengHuayu tablet (FZHY) + entecavir responders (F-R) vs FZHY + entecavir no-responders (F-N) (training set); C: Heatmap of patients vs volunteers (training set); D: Heatmap of E-R vs E-N (validation set); E: Heatmap of F-R vs F-N (validation set); F: Heatmap of patients vs volunteers (validation set). CA: Citric acid; GCDCA: Glycochenodeoxycholic acid; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; TCDCA: Aurochenodeoxycholic acid; DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; DPA: Docosapentaenoic acid; EPA: Eicosapentaenoic acid.
- Citation: Dai YK, Fan HN, Huang K, Sun X, Zhao ZM, Liu CH. Baseline metabolites could predict responders with hepatitis B virus-related liver fibrosis for entecavir or combined with FuzhengHuayu tablet. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(9): 1043-1059
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i9/1043.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1043