Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2023; 15(6): 786-796
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
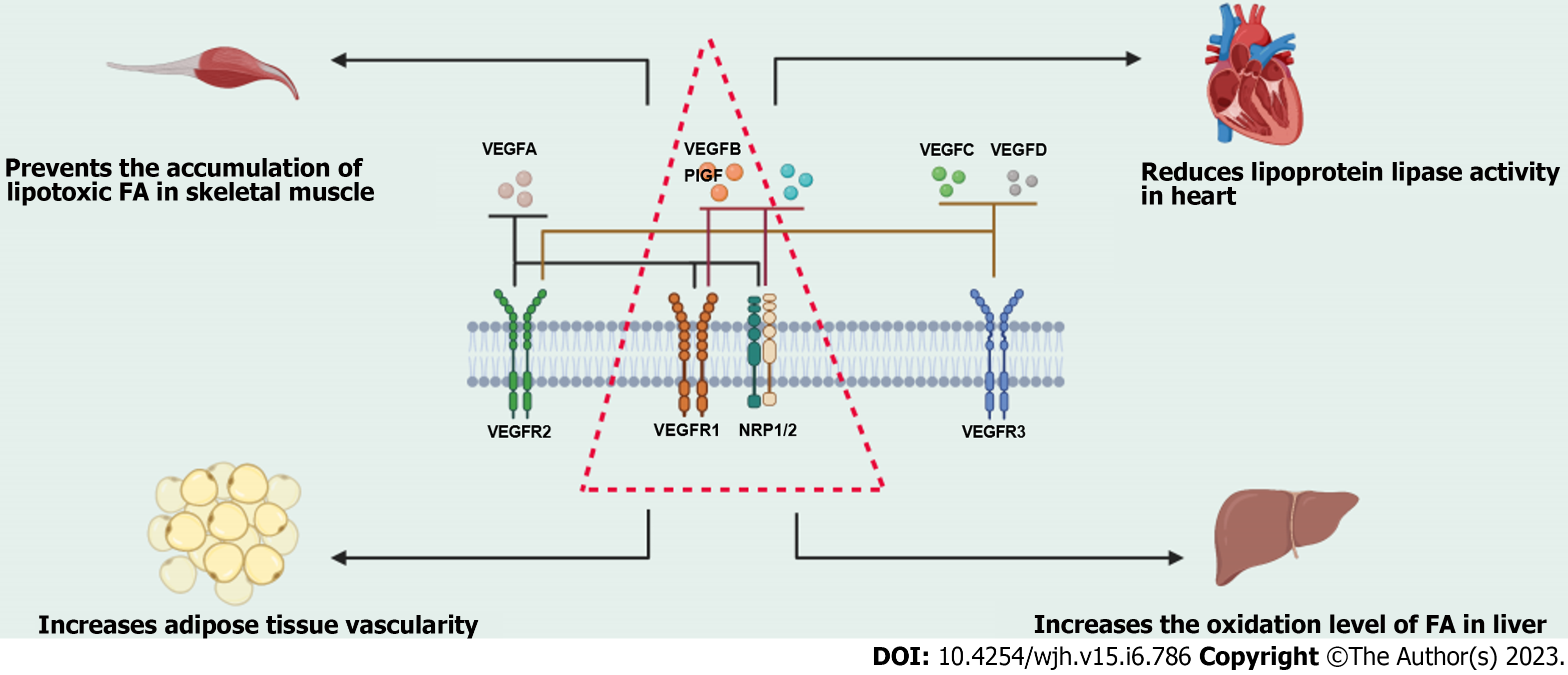
Figure 2 The vascular endothelial growth factor family and its receptors, and the biological function of vascular endothelial growth factor B.
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family includes VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB), VEGFC, VEGFD, and so on. The VEGF receptor family includes VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, and neuropilin 1/2 (NRP1/2). VEGFA combines with VEGFR1, VEGFR2, or NRP1/2. VEGFB and placental growth factor combine with VEGFR1 or NRP1/2. VEGFC and VEGFD combine with VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 to exert their biological functions. VEGFB can prevent the accumulation of lipotoxic free fatty acid (FFA) in skeletal muscle, reduce lipoprotein activity in the heart, increase adipose tissue vascularity, and increase the oxidation level of FFA in the liver. PIGF: Placental growth factor; FA: Fatty acid; NRP1/2: Neuropilin 1/2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFB: Vascular endothelial growth factor B.
- Citation: Li YQ, Xin L, Zhao YC, Li SQ, Li YN. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor B in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its potential value. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(6): 786-796
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i6/786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786