Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2023; 15(6): 786-796
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
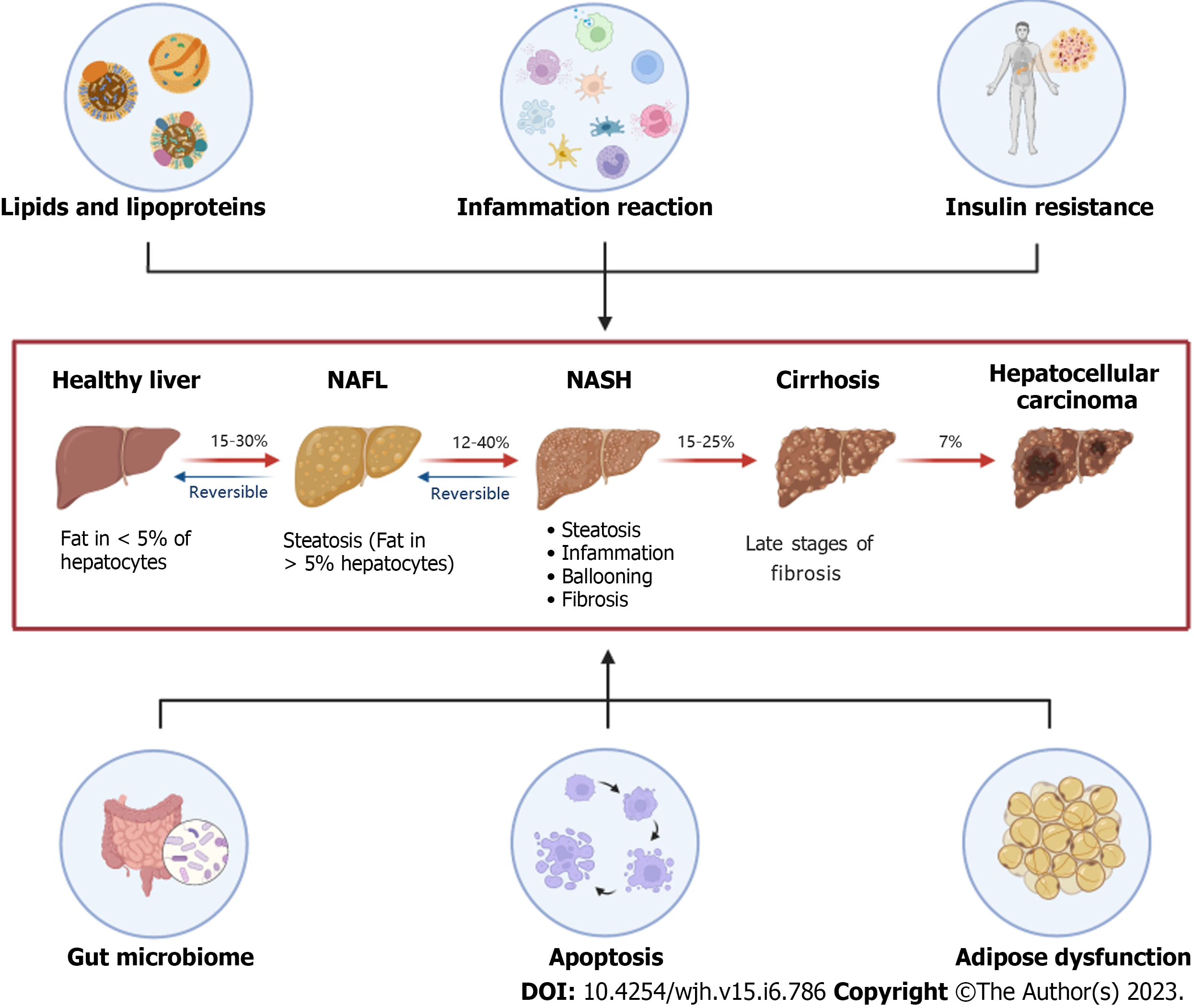
Figure 1 The “multiple-hit” theories are involved in the progress of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Lipids and lipoproteins represent the “first-hit”, while the inflammation reaction illustrates the “second-hit” in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Six aspects including lipids and lipoproteins, inflammation reaction, insulin resistance, gut microbiome, apoptosis, and adipose dysfunction have a common influence on the pathophysiological mechanism of NAFLD. NAFL: Non-alcoholic fatty liver; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Li YQ, Xin L, Zhao YC, Li SQ, Li YN. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor B in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its potential value. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(6): 786-796
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i6/786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786