Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2023; 15(3): 364-376
Published online Mar 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.364
Published online Mar 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.364
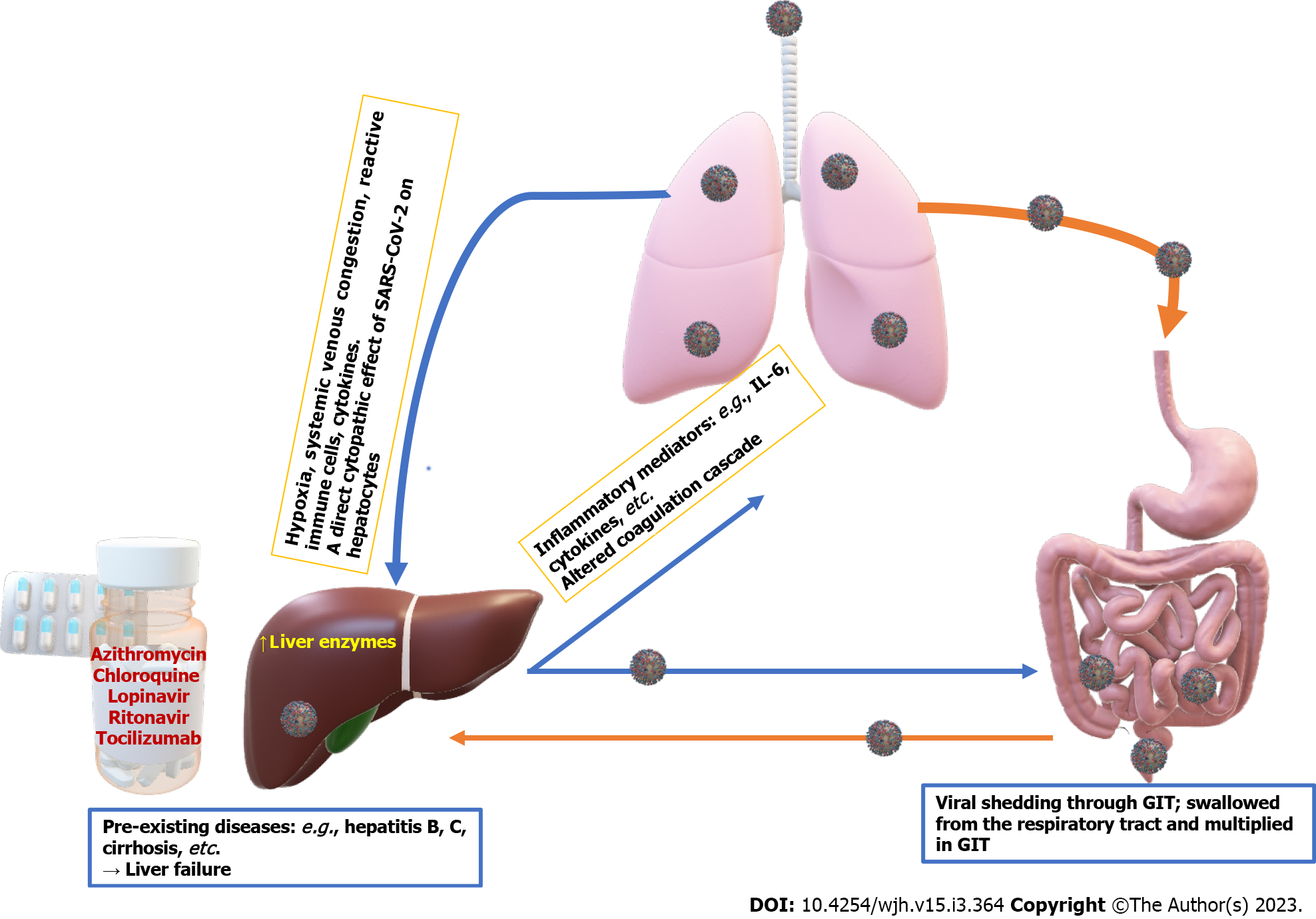
Figure 4 Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 infection on the liver as indicated by increased liver enzymes.
The virus reaches the liver from the gut-liver-lung axis and may be re-shed back to the gut through the bile. These effects are mediated through the impact of hypoxia, systemic venous congestion, immune-mediated hepatic damage by inflammatory mediators induced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection (SARS-CoV-2), the direct hepatic cytopathic effect of SARS-CoV-2, and the hepatotoxic effects of some medications used to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection such as azithromycin, chloroquine, lopinavir, ritonavir, and tocilizumab. GIT: Gastrointestinal tract; IL-6: Interleukin 6.
- Citation: Elbeltagi R, Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, Toema O. May 2022 acute hepatitis outbreak, is there a role for COVID-19 and other viruses? World J Hepatol 2023; 15(3): 364-376
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i3/364.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i3.364