Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 1294-1306
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294
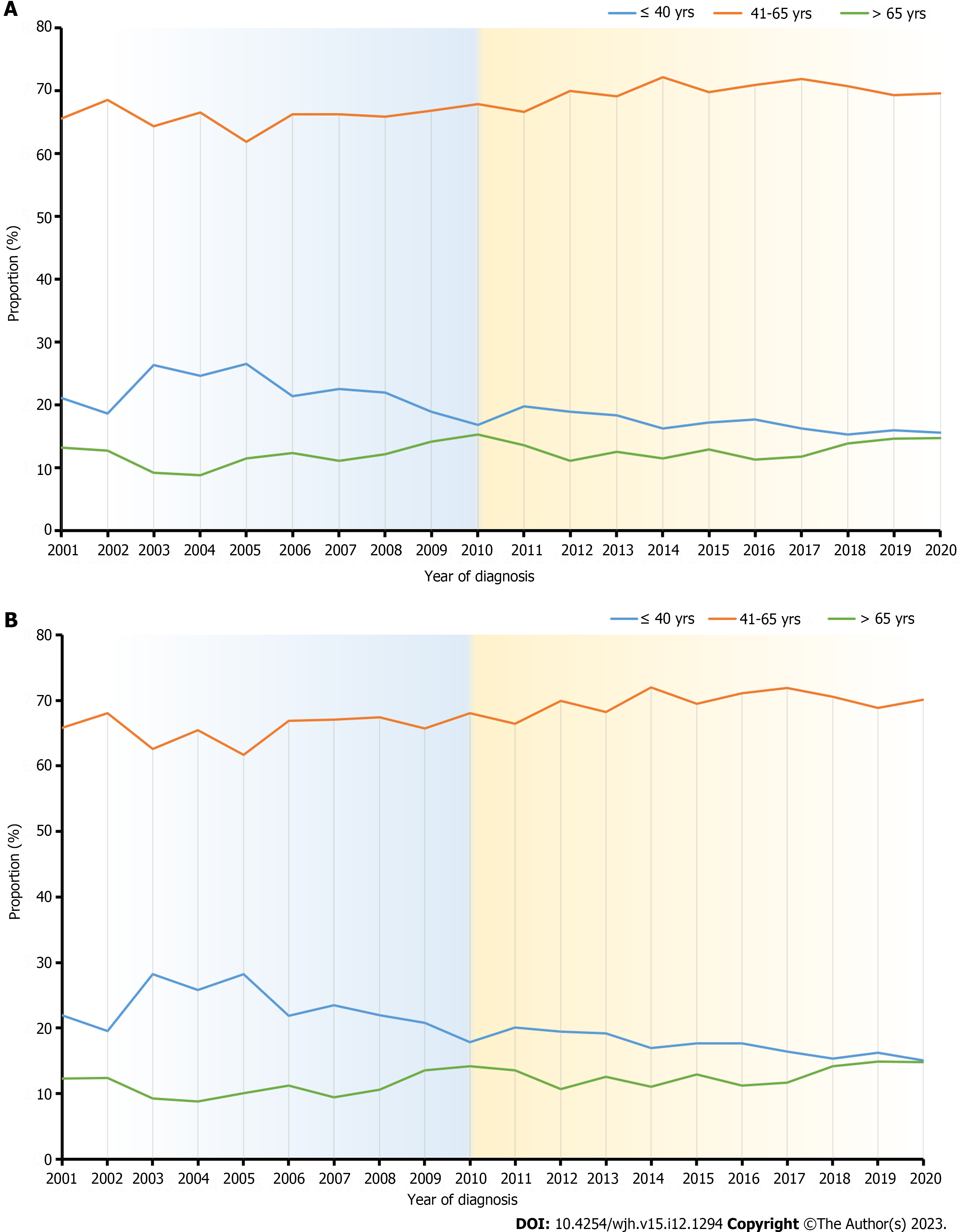
Figure 4 Temporal trends in different age groups of the study population.
A: In the whole population, the proportion of patients ≤ 40 years was decreasing (21.2% in 2001 to 15.7% in 2020), and those aged 41-65 years and > 65 years were increasing (65.6% in 2001 to 69.6% in 2020, and 13.3% in 2001 to 14.7% in 2020, respectively) during the 20-year study period; B: In patients with hepatitis B virus-liver cirrhosis, the proportion ≤ 40 years decreased (22.0% in 2001 to 15.1% in 2020), and those aged 41-65 years and > 65 years increased (65.8% in 2001 to 70.1% in 2020, and 12.3% in 2001 to 14.8% in 2020, respectively) during the 20-year study period.
- Citation: Wang X, Luo JN, Wu XY, Zhang QX, Wu B. Study of liver cirrhosis over twenty consecutive years in adults in Southern China. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(12): 1294-1306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i12/1294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294