Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 1294-1306
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294
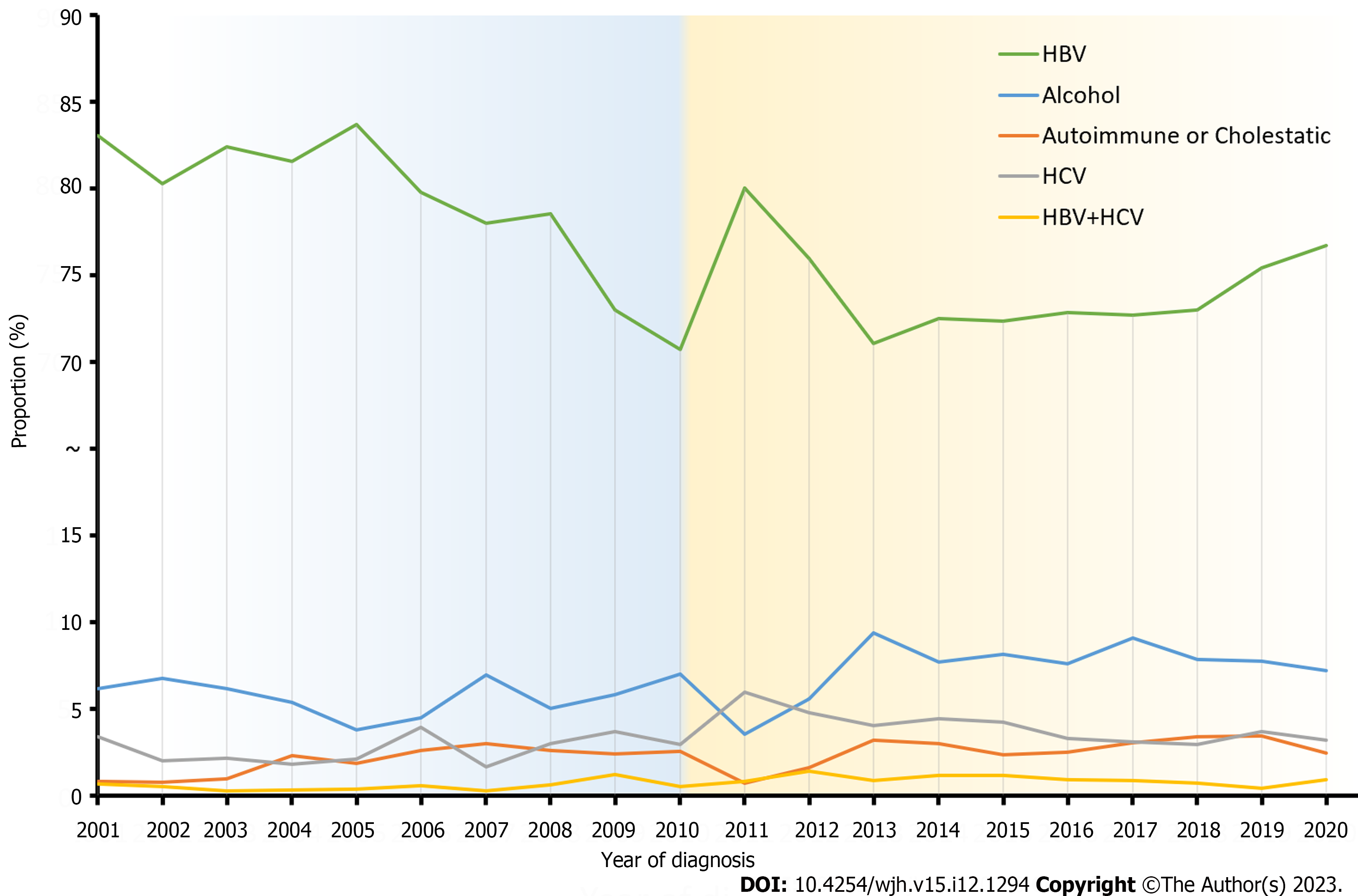
Figure 3 Temporal trends of viral hepatitis and other major etiologies in 2001-2020.
The proportion of hepatitis B virus-liver cirrhosis (HBV-LC) decreased dramatically during the 2001-2010 period but fluctuated and decreased slightly during the 2011-2020 period. Meanwhile, proportions of alcoholic-LC and autoimmune or cholestatic-LC have increased during the 20-year period. Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-LC and (HBV + HCV)-LC have not shown explicit trends. The Cochran-Armitage test for P trend found no statistical significance (P > 0.05) when comparing proportions in separated years (P > 0.05). HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Wang X, Luo JN, Wu XY, Zhang QX, Wu B. Study of liver cirrhosis over twenty consecutive years in adults in Southern China. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(12): 1294-1306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i12/1294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1294