Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2022; 14(7): 1365-1381
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1365
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1365
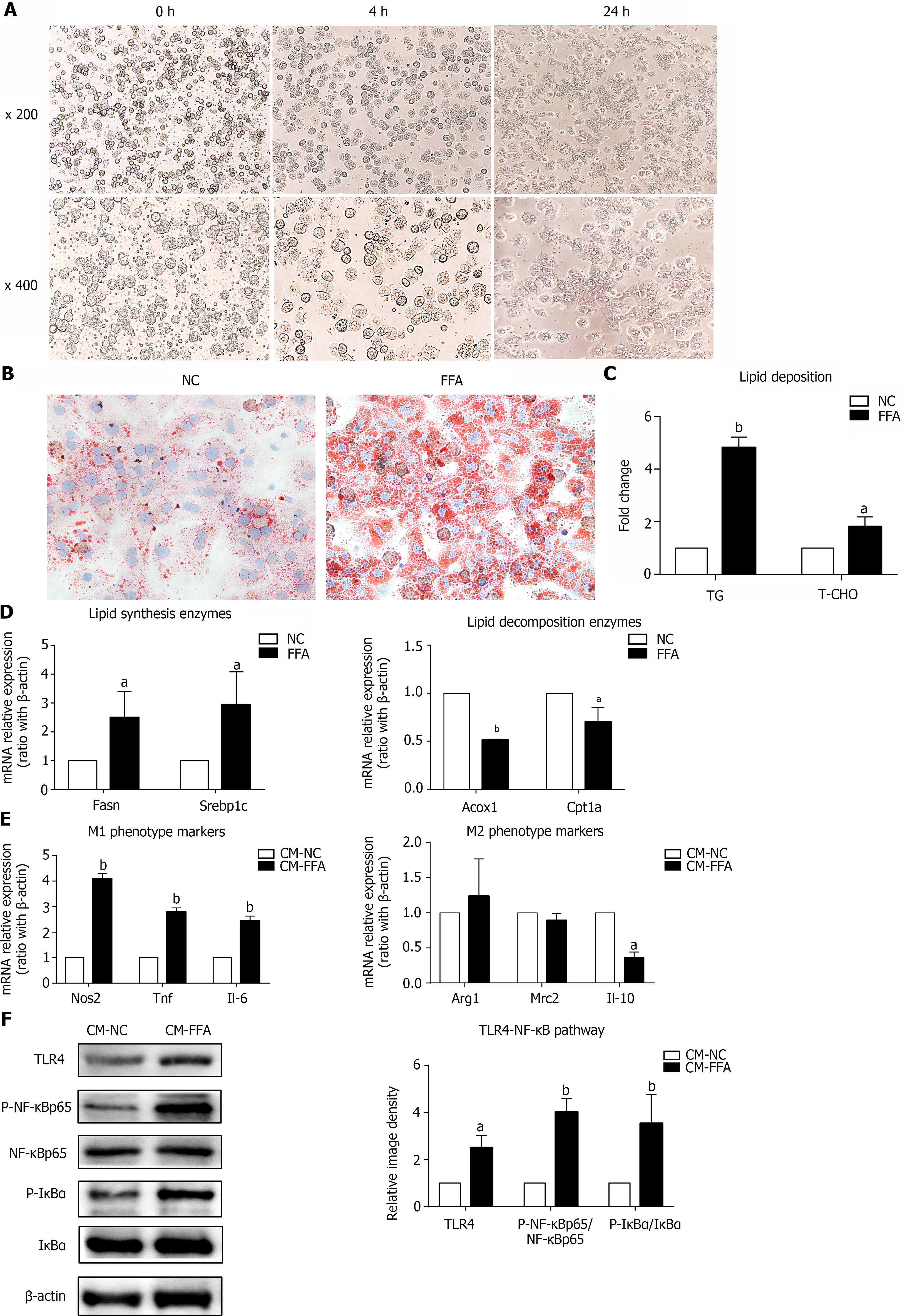
Figure 1 Lipid-laden primary hepatocytes have direct effects on macrophage M1/M2 polarization and inflammation.
Primary hepatocytes were incubated with free fatty acids for 24 h to induce the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease hepatocyte model. Cell culture supernatants of hepatocytes were collected and prepared for different conditioned mediums (CMs). RAW264.7 macrophages were treated with different CMs for 6 h for RT–PCR or 24 h for western blotting. A: Primary hepatocytes isolated by in situ perfusion of collagenase (inverted microscope, × 200, × 400); B: Lipid accumulation in hepatocytes measured by Oil Red O staining (× 400); C: Triglyceride and total cholesterol contents in primary hepatocytes; D: mRNA expression of lipid-related genes in primary hepatocytes; E: mRNA expression of M1/M2 markers in macrophages treated with CM; F: Protein expression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in macrophages treated with CM. Values are expressed as the mean ± SE of the mean, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs normal control (NC) or CM-NC, n = 3 experiments. NC: Normal control; CM: Conditioned medium; Fasn: Fatty acid synthase; Srebp1c: Sterol-regulatory element-binding protein 1C; Acox1: Acyl-CoA oxidase 1; Cpt1a: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; Nos: Nitric oxide synthase; Tnf: Tumor necrosis factor; Il: Interleukin; Arg1: Arginine-1; Mrc2: Mannose receptor 2; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B.
- Citation: Li XY, Ji PX, Ni XX, Chen YX, Sheng L, Lian M, Guo CJ, Hua J. Regulation of PPAR-γ activity in lipid-laden hepatocytes affects macrophage polarization and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(7): 1365-1381
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i7/1365.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1365