Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2022; 14(7): 1291-1306
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1291
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1291
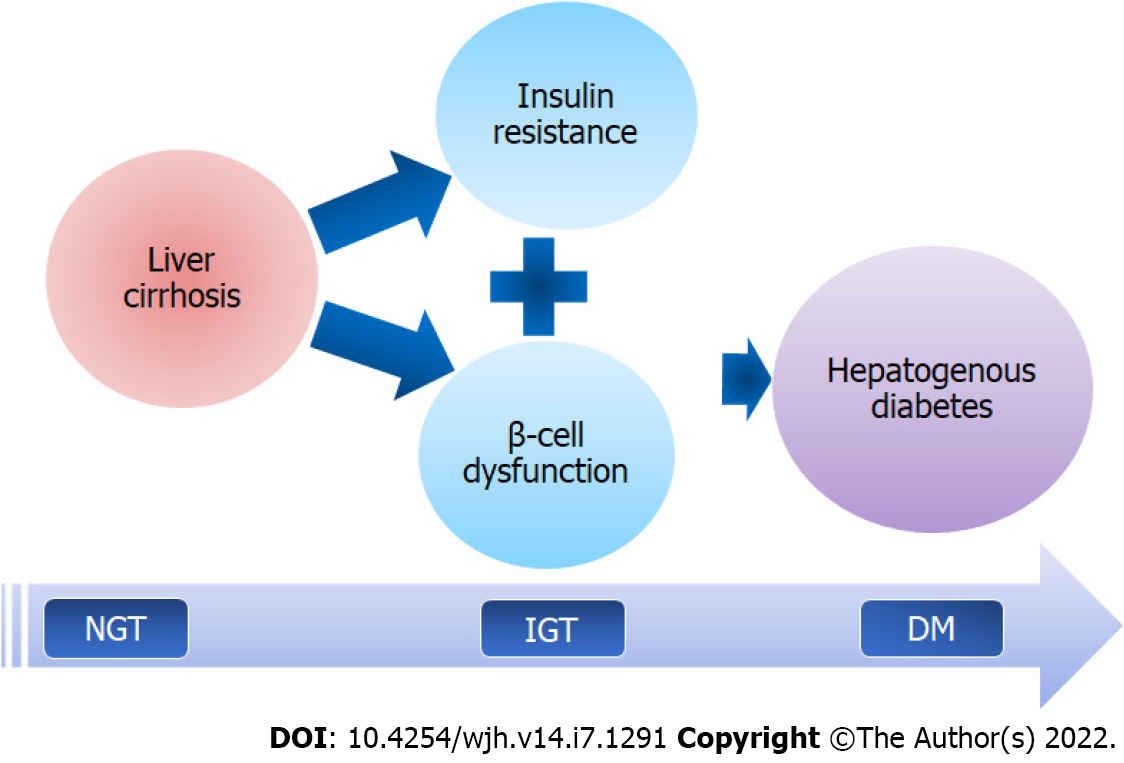
Figure 1 Key events leading to development of hepatogenous diabetes in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Insulin resistance, followed by β-cell dysfunction, occurs as a result of liver cirrhosis, culminating in a progressive worsening of glucose tolerance and the onset of hepatogenous diabetes. Both of these occurrences are linked to the pathophysiological changes in the body caused by liver cirrhosis. NGT: Normal glucose tolerance; IGT: Impaired glucose tolerance; DM: Diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Kumar R, García-Compeán D, Maji T. Hepatogenous diabetes: Knowledge, evidence, and skepticism. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(7): 1291-1306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i7/1291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1291