Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2022; 14(6): 1074-1086
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1074
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1074
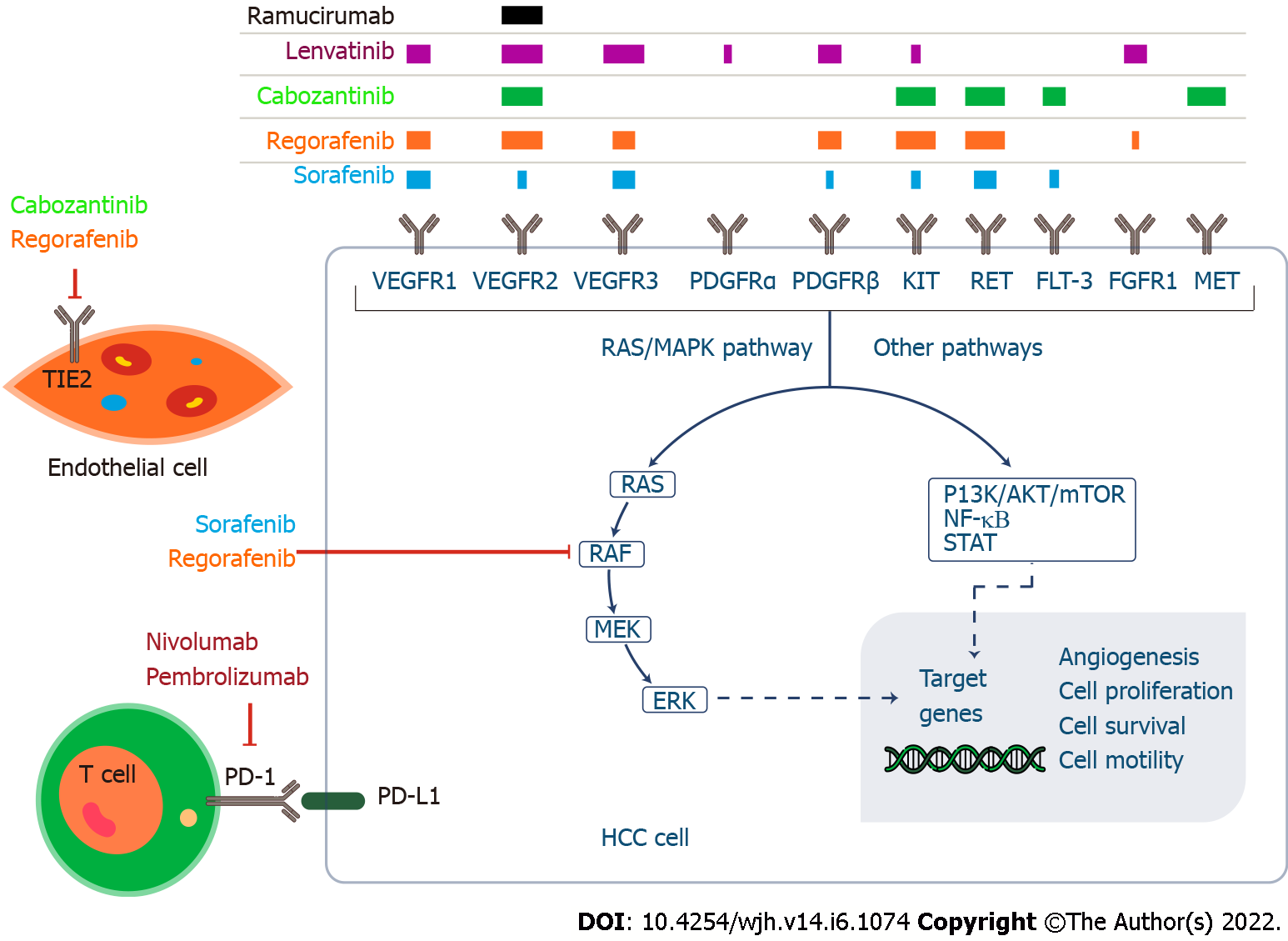
Figure 1 Graphical abstract.
ERK: Extracellular receptor kinase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; FLT-3: Cytokine Flt3 ligand; KIT: Tyrosine-protein kinase; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MET: Mesenchymal epithelial transition factor; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PD-1: Programmed cell death 1; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptors; PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; RAS: Rat sarcoma virus; RET: Rearranged during transfection; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Rajappa S, Rau KM, Dattatreya PS, Ramaswamy A, Fernandes P, Pruthi A, Cheng R, Lukanowski M, Huang YH. Second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Time for more individualized treatment options? World J Hepatol 2022; 14(6): 1074-1086
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i6/1074.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1074