Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2022; 14(4): 729-743
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.729
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.729
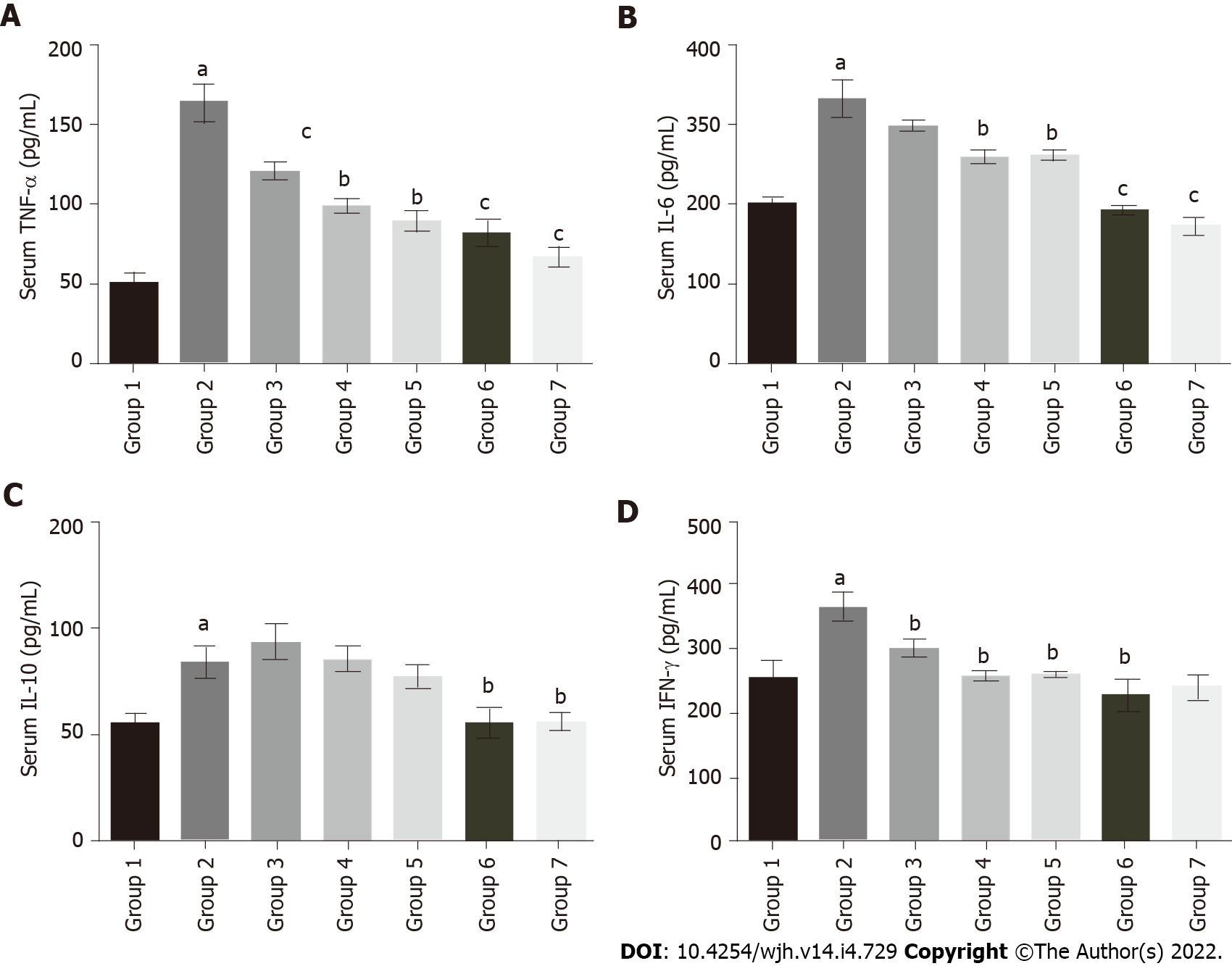
Figure 5 Effect of baicalin on serum inflammatory markers in fluoxetine treated rats.
A: Tumor necrosis factor-α; B: Interleukin (IL)-6; C: IL-10; D: Interferon-γ. The values are expressed in pg/mL. Group 1: Control rats; group 2: Fluoxetine treated rats (10 mg/kg); group 3: Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) + baicalin (50 mg/kg); group 4: Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) + baicalin (100 mg/kg); group 5: Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) + silymarin (100 mg/kg); group 6: Baicalin (100 mg/kg); group 7: Silymarin (100 mg/kg). Data represent mean ± SD, n = 6. aRepresents a significant difference compared with group 1, P < 0.05; brepresents a significant difference compared with group 2, P < 0.05; crepresents a significant difference compared with group 2, P < 0.005; drepresents a significant difference compared with group 2, P < 0.0001. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon.
- Citation: Ganguly R, Kumar R, Pandey AK. Baicalin provides protection against fluoxetine-induced hepatotoxicity by modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(4): 729-743
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i4/729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.729