Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2022; 14(3): 535-550
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.535
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.535
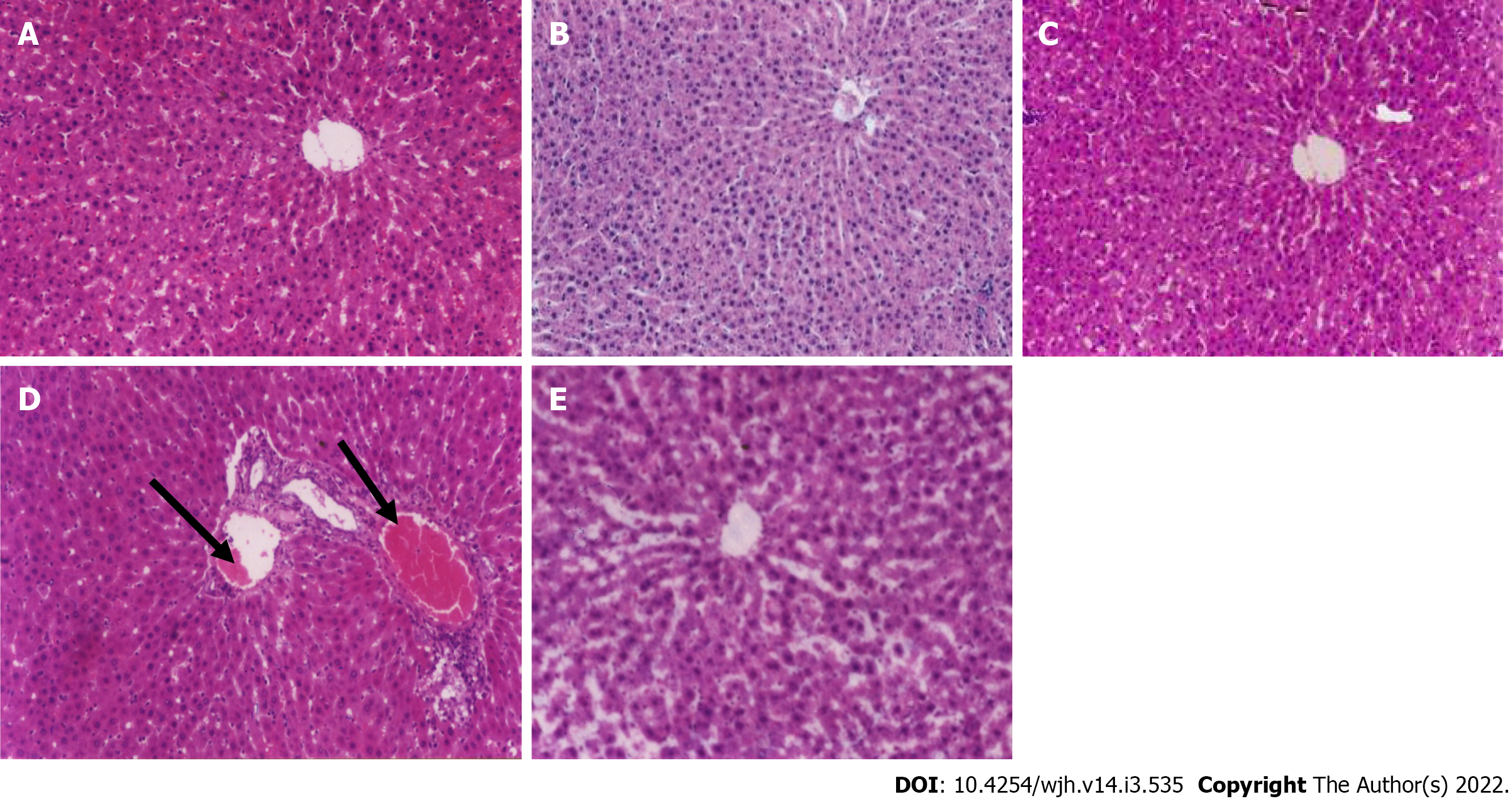
Figure 1 Pathological changes in the liver after treatment.
A: Control group; B: Paraffin oil-treated group; C: Fertaric acid (FA)-treated group; D: Bisphenol A (BPA)-treated group; E: FA + BPA-treated group. The control, paraffin oil, and FA-treated rats (A, B, and C; H&E staining, 200 ×) showed a normal hepatic architecture with preserved hepatic architecture. On the contrary, in BPA-treated rats (D), there was rim edema in the periportal area (black arrows) which compressed the surrounding hepatocytes. Intra-cytoplasm vacuolation was noted. FA + BPA-treated rats (E) had a preserved hepatic lobular architecture.
- Citation: Koriem KMM. Fertaric acid amends bisphenol A-induced toxicity, DNA breakdown, and histopathological changes in the liver, kidney, and testis. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(3): 535-550
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i3/535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.535