Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2022; 14(3): 504-515
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.504
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.504
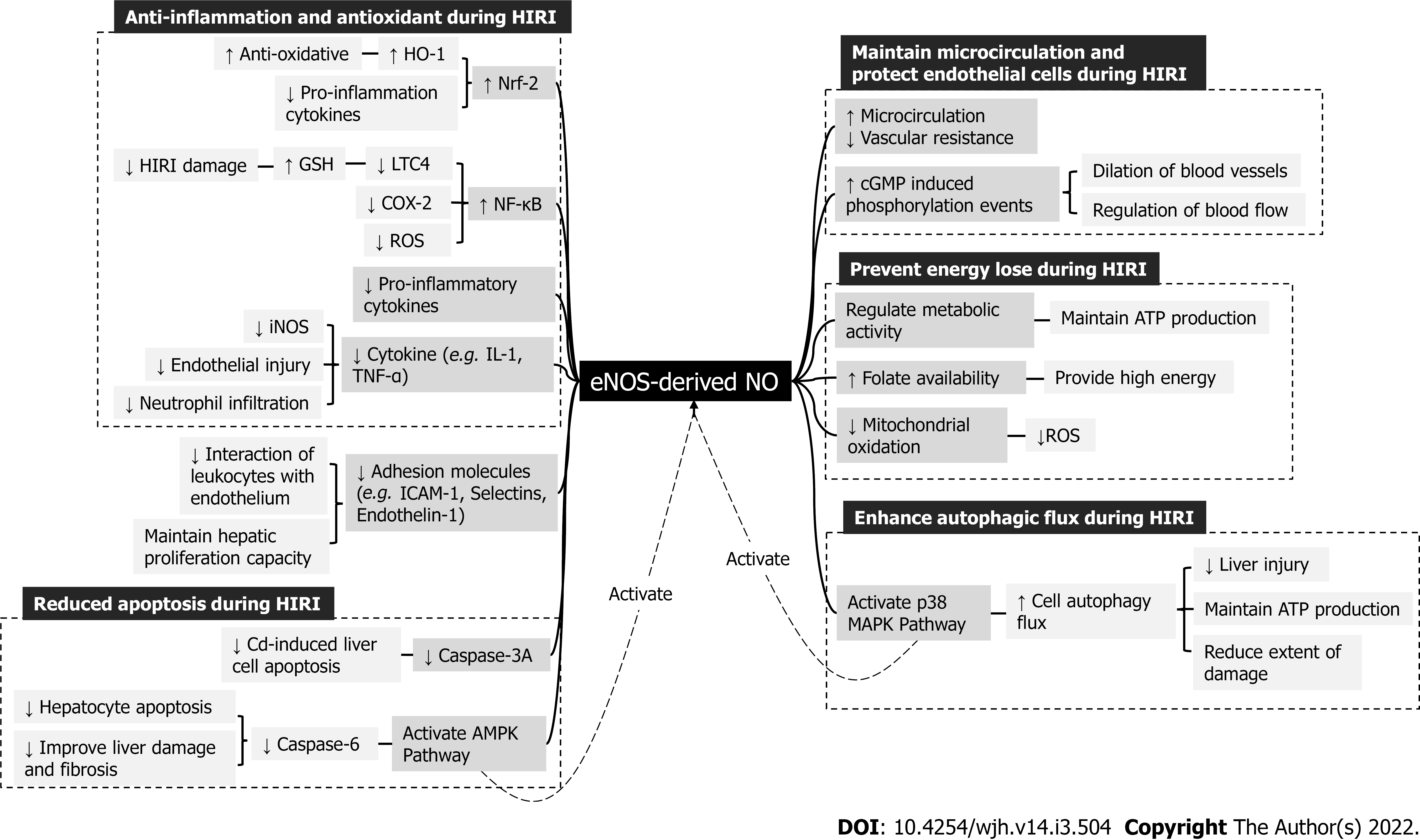
Figure 1 Hepatoprotective effects of endothelial nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and underlying mechanisms.
Nrf2: Nuclear erythroid-related factor; HO-1: Heme oxygenate-1; IL-1: Interleukin-1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κ-gene binding; LTC4: Leukotriene C4; GSH: Glutathione; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ICAM-1: Intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
- Citation: Zhang YP, Liu XR, Yang MW, Yang SL, Hong FF. New progress in understanding roles of nitric oxide during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(3): 504-515
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i3/504.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.504