Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2022; 14(11): 1964-1976
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1964
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1964
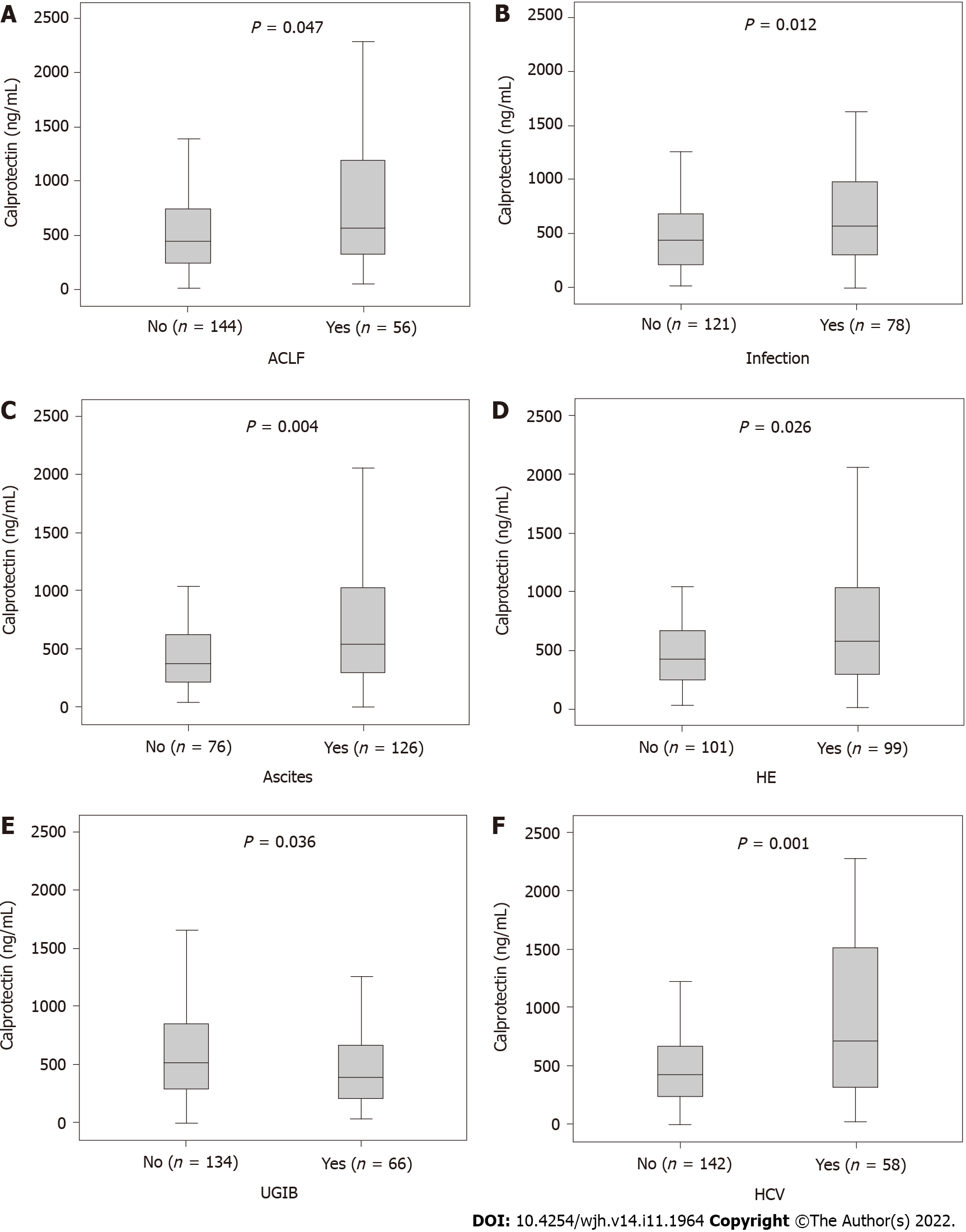
Figure 2 Box plot of serum calprotectin levels in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis according to the presence of specific complications.
The line across the box indicates the median value; the box contains the 25% to 75% interquartile range; and the whiskers represent the highest and the lower values. A-D: Significantly higher calprotectin levels were observed among patients with (A) acute-on-chronic liver failure (P = 0.047), (B) infection (P = 0.012), (C) ascites (P = 0.004), and (D) hepatic encephalopathy (HE) (P = 0.026); E: Lower levels of calprotectin were observed among patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) (P = 0.036); F: Higher levels in patients with hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) (P = 0.001).
- Citation: Matiollo C, Rateke ECM, Moura EQA, Andrigueti M, Augustinho FC, Zocche TL, Silva TE, Gomes LO, Farias MR, Narciso-Schiavon JL, Schiavon LL. Elevated calprotectin levels are associated with mortality in patients with acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(11): 1964-1976
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i11/1964.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1964