Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2022; 14(1): 98-118
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i1.98
Published online Jan 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i1.98
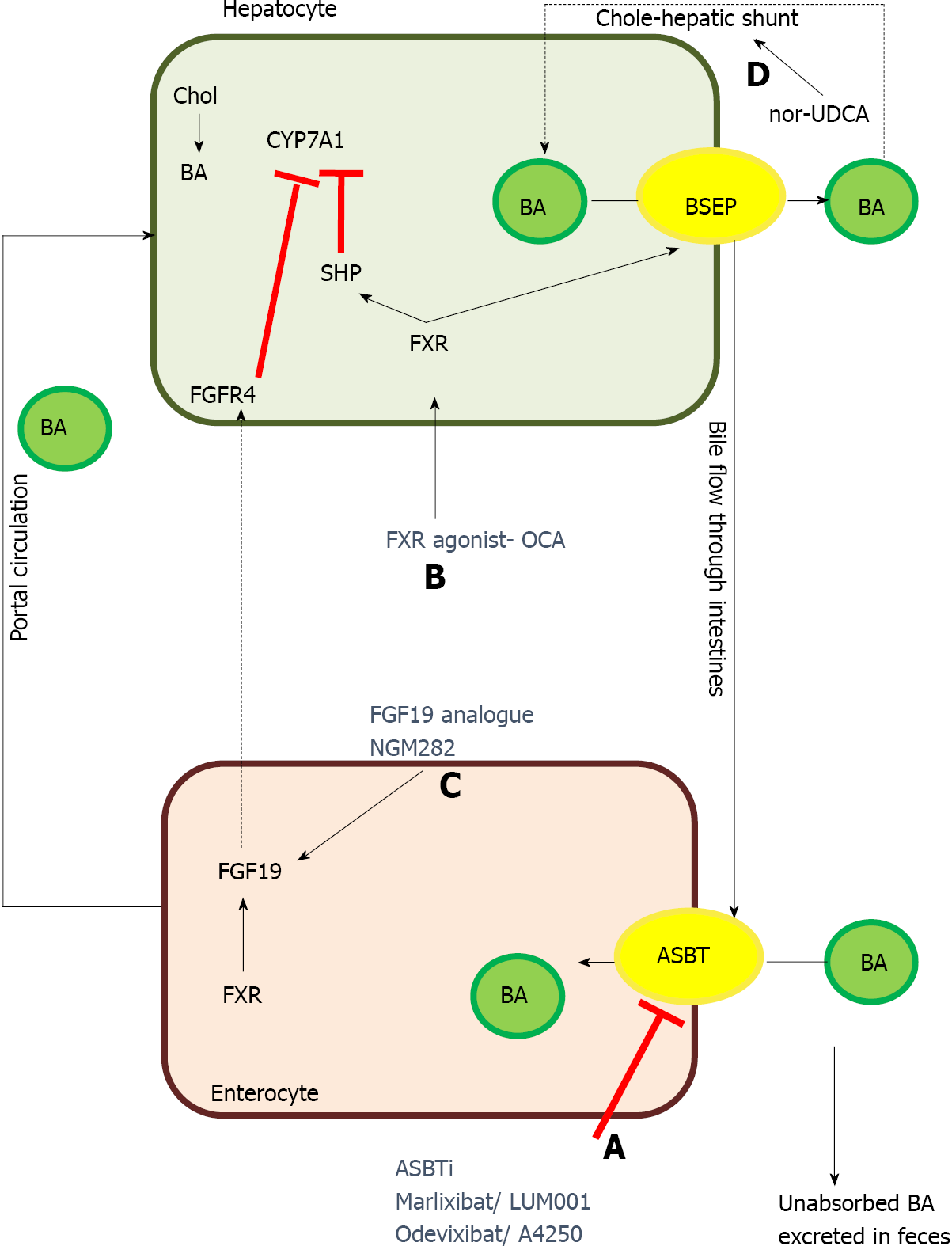
Figure 5 Therapeutic targets of some of the newer drugs for treatment of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
A: Apical sodium-dependent bile salt transporter inhibitors prevent the absorption of bile acids in the terminal ileum resulting in significant decrease in enterohepatic circulation of bile acids, ultimately resulting in decreased serum bile acids; B:Farnesoid X receptor agonist acts by increasing bile salt exporter pump expression as well as by inhibiting CYP7A1, the rate limiting step in synthesis of bile acids in hepatocytes; C: Fibroblast growth factor 19 analogue act via fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 and inhibit CYP7A1; D:Nor-ursodeoxycholic acid increases the bile-acid dependent bile flow by increasing the cholehepatic shunt. ASBT: Apical sodium-dependent bile salt transporter; BA: Bile acid; BSEP: Bile salt exporter pump; Chol: Cholesterol; CYP7A1: Cholesterol 7-α hydroxylase; FGFR4: Fibroblast growth factor receptor-4; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; FGF19: Fibroblast growth factor 19; nor-UDCA: Nor-ursodeoxycholic acid; OCA: Obeticholic acid; SHP: Small heterodimer partner-1.
- Citation: Alam S, Lal BB. Recent updates on progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis types 1, 2 and 3: Outcome and therapeutic strategies. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(1): 98-118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i1/98.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i1.98