Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2021; 13(9): 969-978
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.969
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.969
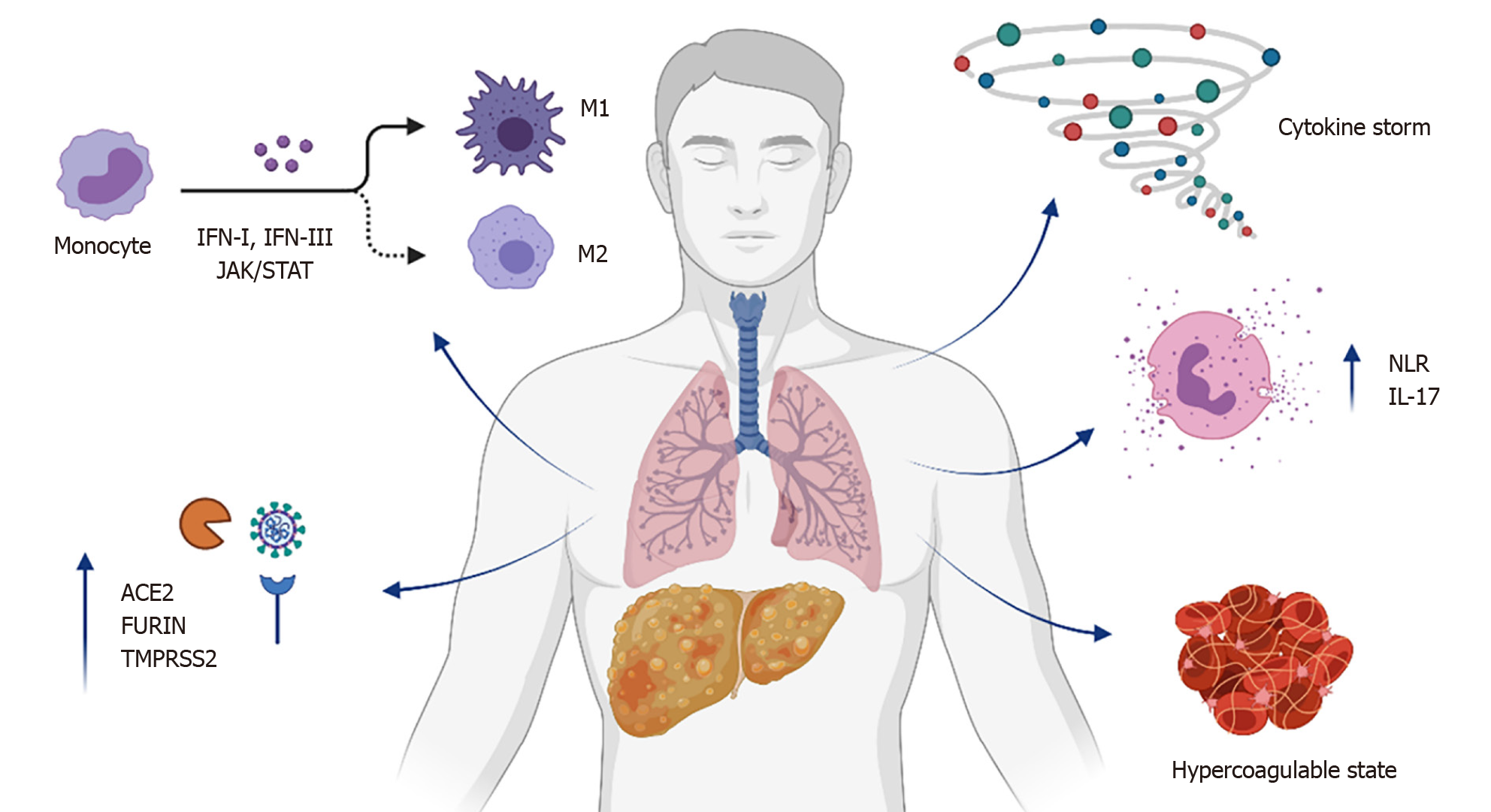
Figure 1 Mechanisms supporting severe coronavirus disease 2019 in non-alcoholic (or metabolic-associated) fatty liver disease.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic-associated fatty liver disease may present with systemic overexpression of genes involved in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 entry and cleavage (such as angiotensin I converting enzyme 2, FURIN, and transmembrane serine protease 2), interferon-mediated polarization of macrophages toward a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, elevated circulating levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with activation of the pro- interleukin-17 axis, and enhanced production of pro-coagulant molecules. Taken together, these pathways increase susceptibility of severe coronavirus disease 2019 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic-associated fatty liver disease patients. ACE2: Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2; IFN: Interferon; IL-17: Interleukin-17; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease 2.
- Citation: Bellanti F, Vendemiale G. Coronavirus disease 2019 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(9): 969-978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i9/969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.969