Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2021; 13(3): 343-361
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.343
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.343
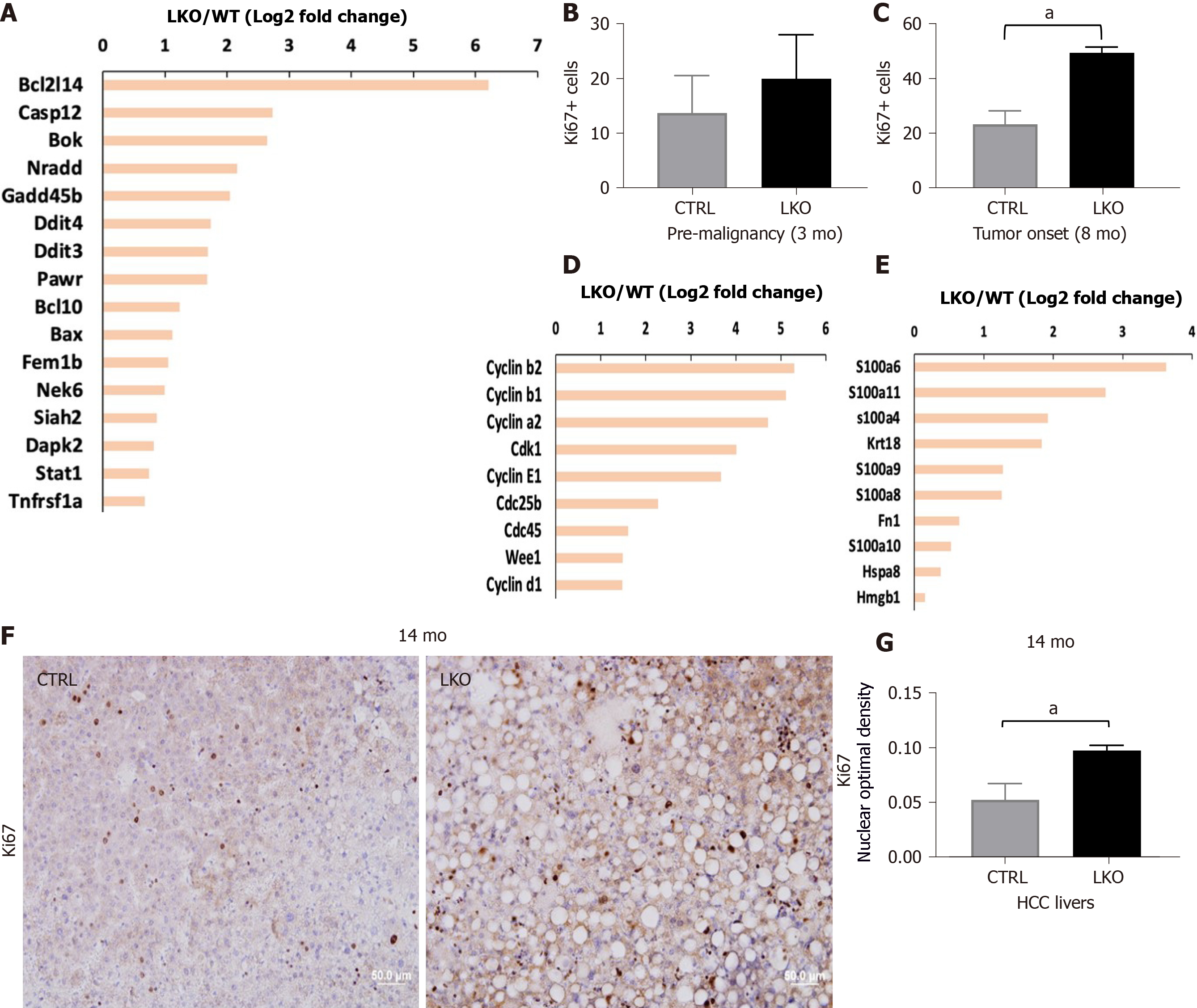
Figure 2 BRUCE deficiency increases diethylnitrosamine-induced liver injury and hepatic proliferation.
A: Apoptotic gene expression is increased in liver-specific BRUCE KO livers at the time of tumor onset; B: Hepatic proliferation was measured by immunohistochemistry staining of the livers against Ki67. Livers exposed to diethylnitrosamine for 3 mo have an increase of Ki67+ cells; C: At the time of tumor onset in LKO livers there is an increase of Ki67+ positive cells; D: At the time of tumor onset, RNA-seq analysis reveals an increase of known cell cycle markers; E: Damage associated molecular patterns in the LKO livers; F and G: Ki67 staining by immunohistochemistry in 14 mo hepatocellular carcinoma livers, as well as quantification, show an increase of proliferation in LKO livers. aP< 0.05. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; LKO: Liver-specific knockout; CTRL: Control.
- Citation: Vilfranc CL, Che LX, Patra KC, Niu L, Olowokure O, Wang J, Shah SA, Du CY. BIR repeat-containing ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (BRUCE) regulation of β-catenin signaling in the progression of drug-induced hepatic fibrosis and carcinogenesis. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(3): 343-361
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i3/343.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.343