Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2021; 13(3): 315-327
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.315
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.315
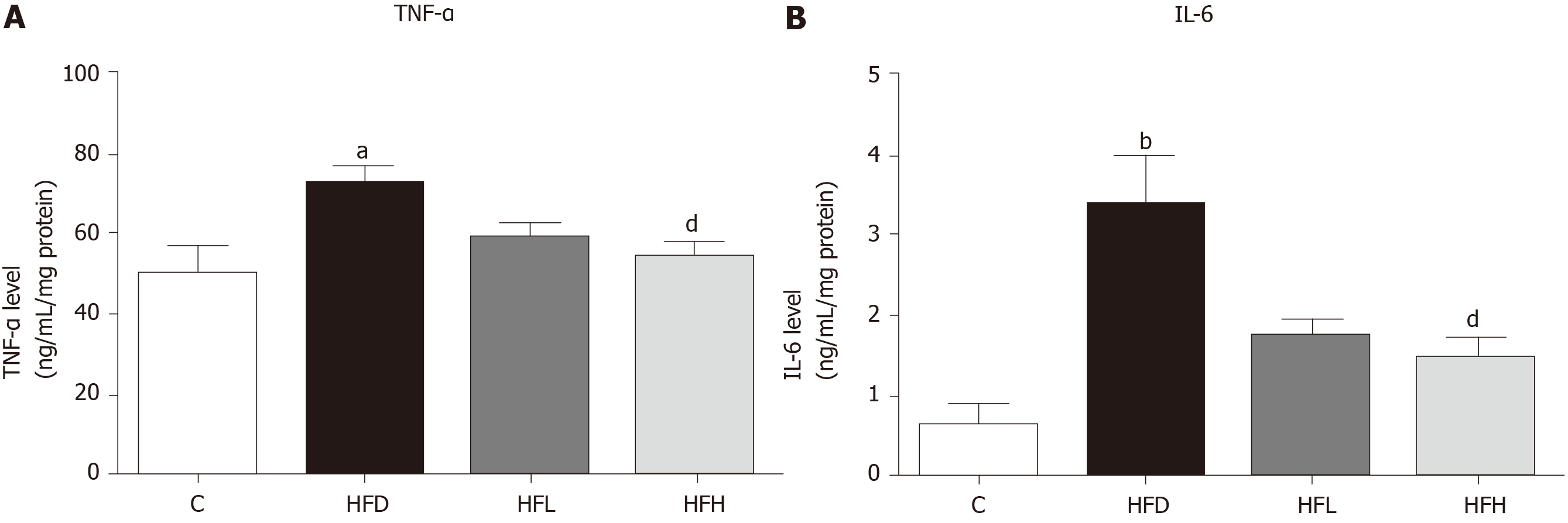
Figure 3 Effects of papaya on proinflammatory cytokines in liver tissue.
A: Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the liver; B: Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in the liver. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of the mean (n = 6-7). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control (C), and dP < 0.05 vs high fat diet (HFD) group. HFH: High fat diet treated with 1 mL of papaya juice/100 g body weight; HFL: High fat diet treated with 0.5 mL of papaya juice/100 g body weight.
- Citation: Deenin W, Malakul W, Boonsong T, Phoungpetchara I, Tunsophon S. Papaya improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and lipogenic gene expression. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(3): 315-327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i3/315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.315