Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2021; 13(3): 270-290
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.270
Published online Mar 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.270
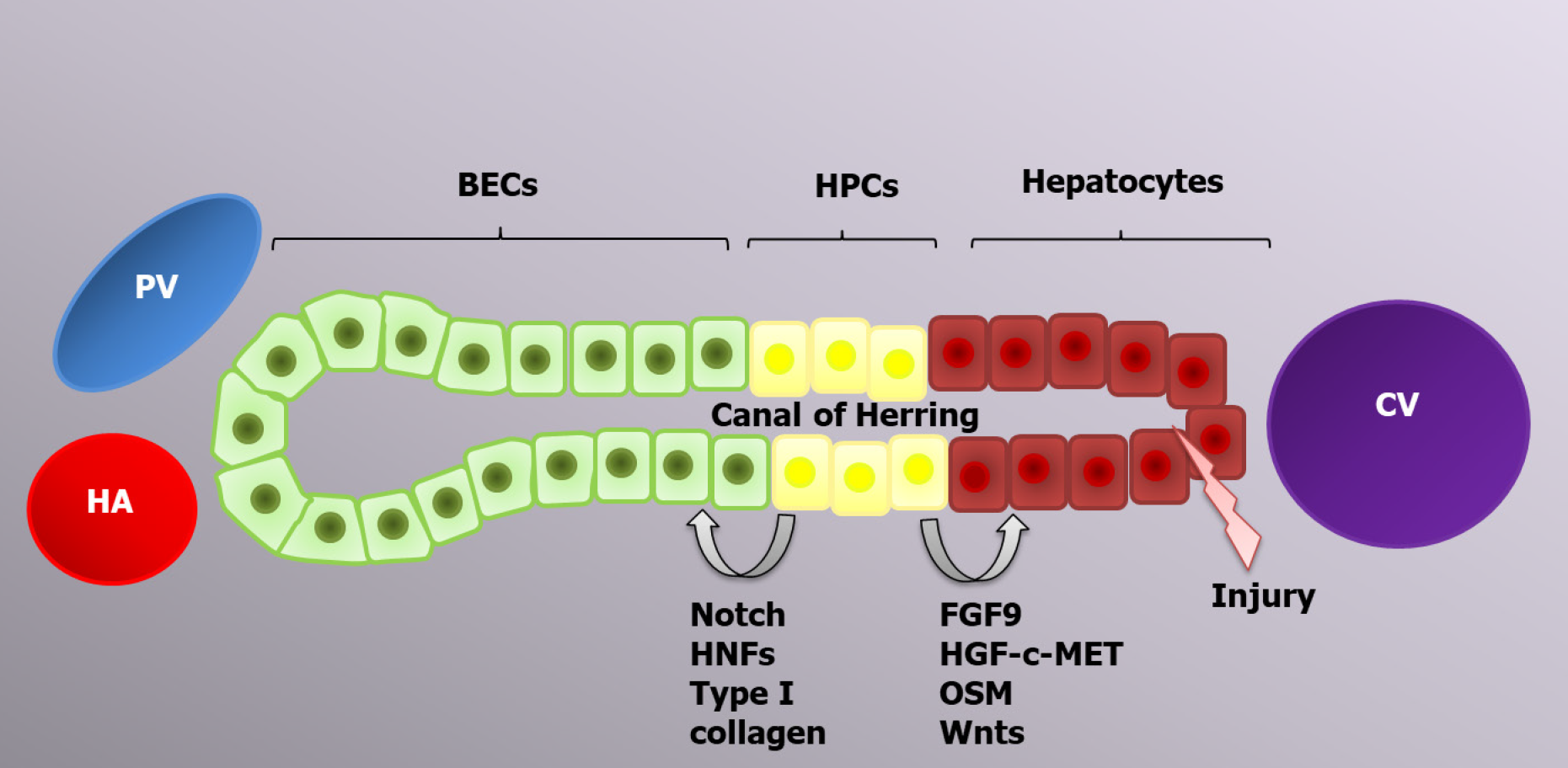
Figure 2 Progenitor-dependent liver regeneration.
In case of excessive acute injury or chronic liver diseases, hepatic progenitor cell activation occurs in response to different inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis. Depending on the type of stimulus, hepatic progenitor cells can differentiate into biliary epithelial cells or hepatocytes to restore the liver mass. PV: Portal vein; HA: Hepatic artery; CV: Central vein; BECs: Biliary epithelial cells; HPCs: Hepatic progenitor cells; HNFs: Hepatocyte nuclear factors.
- Citation: Kiseleva YV, Antonyan SZ, Zharikova TS, Tupikin KA, Kalinin DV, Zharikov YO. Molecular pathways of liver regeneration: A comprehensive review. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(3): 270-290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i3/270.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.270