Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1584-1610
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584
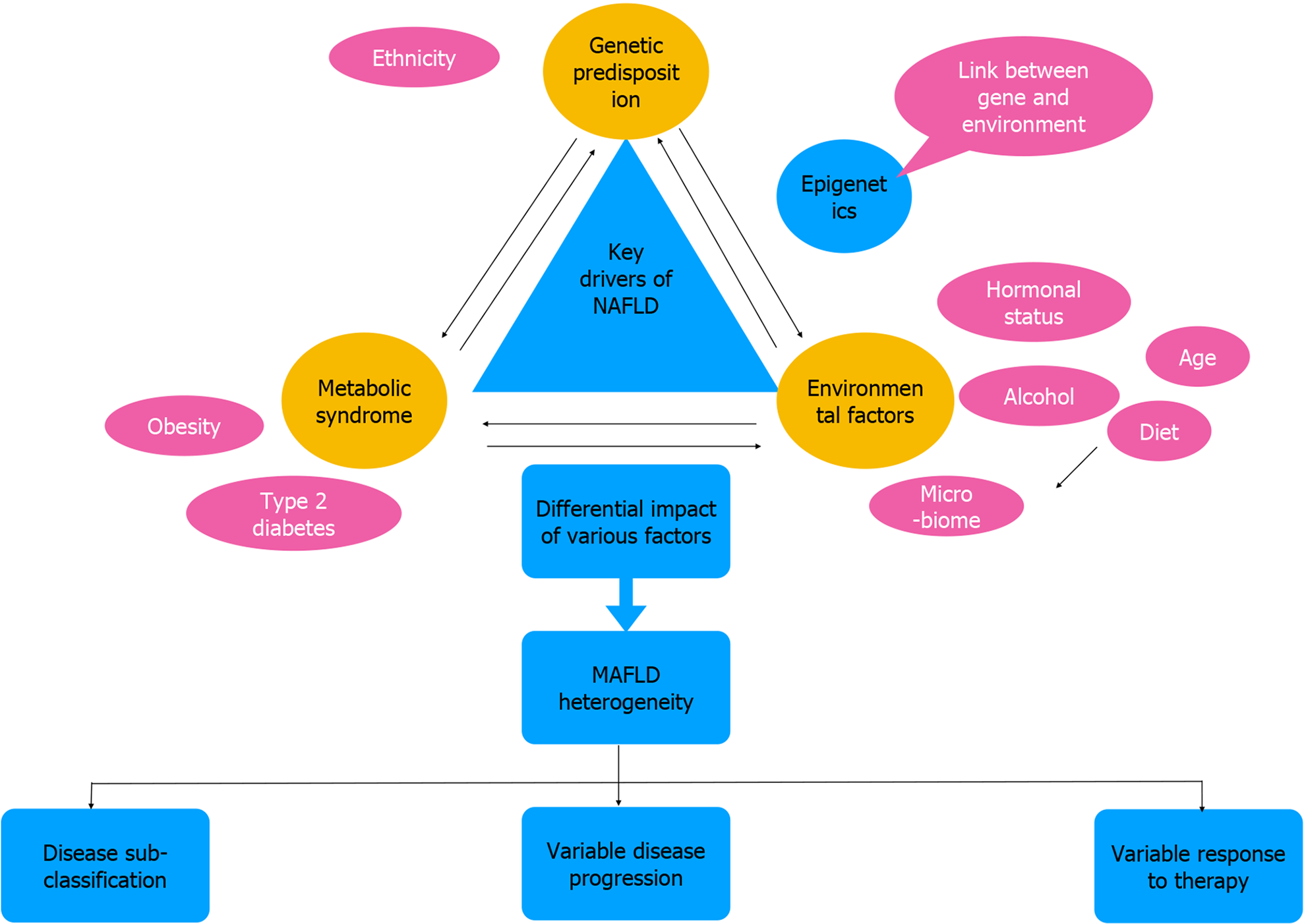
Figure 2 Key drivers of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, resulting in disease heterogeneity and its clinical implications.
Genetic predisposition, metabolic health, and environmental factors influence molecular and phenotypical heterogeneity of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease leading to various disease subtypes, variable disease progression, and response to therapy. MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Pal P, Palui R, Ray S. Heterogeneity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for clinical practice and research activity. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1584-1610
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1584