Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2021; 13(10): 1378-1393
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378
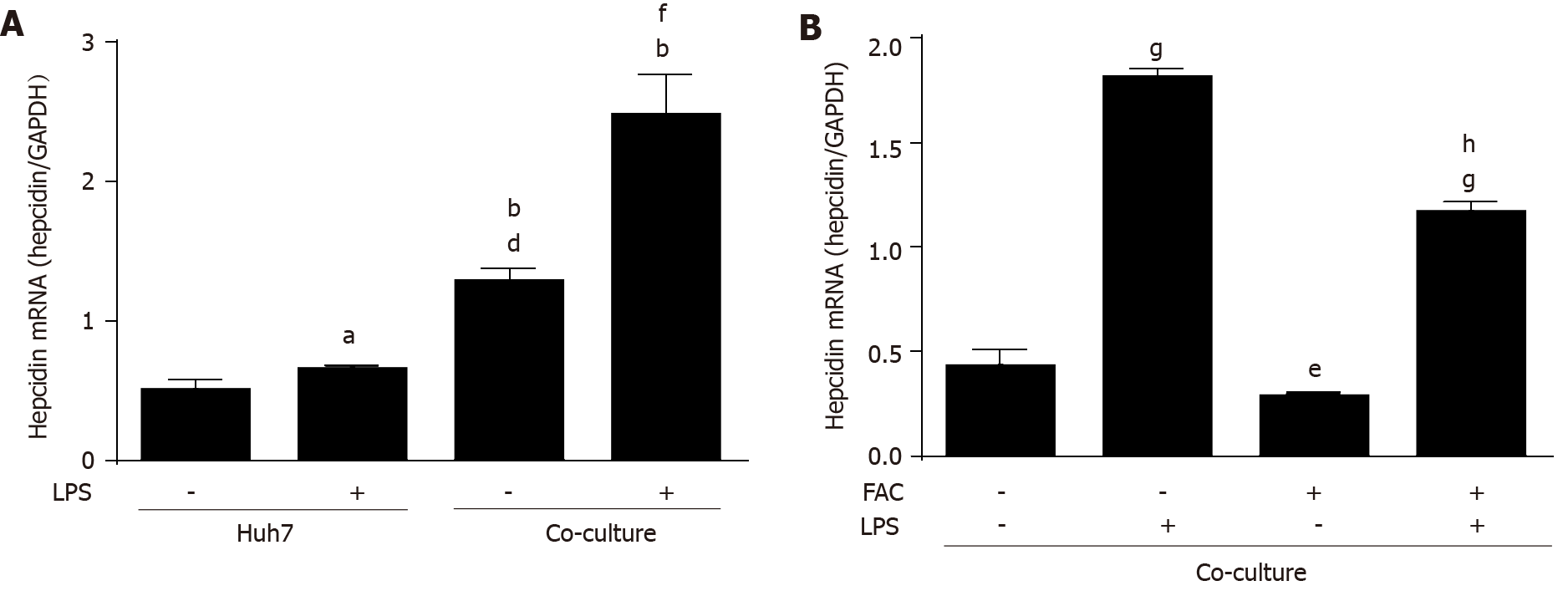
Figure 6 Ferric ammonium citrate decreases hepatic hepcidin expression induced by lipopolysaccharide in a macrophage-hepatocyte co-culture model.
Huh7 cells were treated with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (500 ng/mL) for 24 h. Huh7 cells were directly co-cultured with THP-1 macrophages according to pathophysiological macrophage/hepatocyte cell ratio (1:4) and then treated with or without LPS (500 ng/mL) for 24 h in the presence or absence of ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) (50 μmol/L). Total RNA was extracted from Huh7 cells or Huh7 cells and THP-1 macrophages. A: Hepcidin mRNA levels were slightly increased by LPS in monoculture of Huh7 cells, and macrophages increased hepcidin mRNA levels compared with monoculture control and the presence of LPS further markedly increased hepcidin mRNA levels; B: FAC decreased the basal and LPS-induced hepcidin mRNA levels in the co-culture model. Hepcidin mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR, normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs Huh7 control; dP < 0.001 vs Huh7 LPS group; eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01, gP < 0.001 vs co-culture control; hP < 0.001 vs co-culture LPS group. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; FAC: Ferric ammonium citrate.
- Citation: Yu LN, Wang SJ, Chen C, Rausch V, Elshaarawy O, Mueller S. Direct modulation of hepatocyte hepcidin signaling by iron. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(10): 1378-1393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i10/1378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378