Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2021; 13(10): 1378-1393
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378
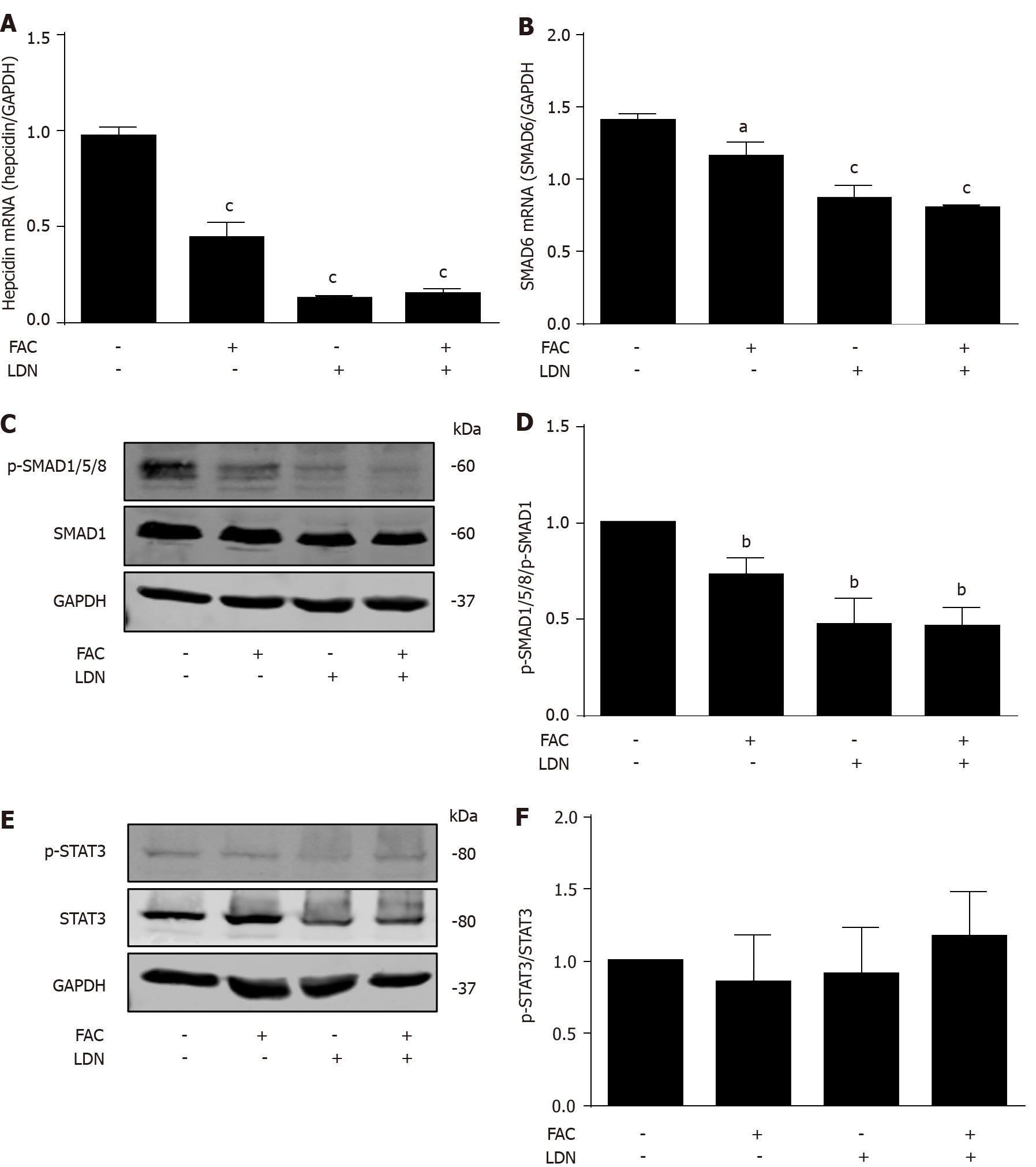
Figure 5 Inhibition of hepatocellular hepcidin by ferric ammonium citrate requires bone morphogenetic protein/small mothers against decapentaplegic signaling.
Huh7 cells were treated with or without ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) (50 μmol/L) in the presence or absence of LDN193189 Hydrochloride (LDN) (20 nmol/L) for 24 h. Total RNA and protein were extracted from Huh7 cells. A: FAC or LDN decreased the basal hepcidin mRNA expression, but FAC in combination with LDN did not further suppress hepcidin mRNA expression compared with LDN alone; B-D: FAC or LDN decreased the basal small mothers against decapentaplegic (SMAD)6 mRNA and p-SMAD1/5/8 protein expression, but FAC in combination with LDN did not further suppress SMAD6 and p-SMAD1/5/8 expression compared with LDN alone; E, F: Both FAC and LDN had no significant effect on phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3) protein expression. SMAD1, p-SMAD1/5/8, STAT3, p-STAT3 and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) protein levels were determined by Western blotting. Hepcidin and SMAD6 mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR, normalized to GAPDH. Western Blots are representatives of three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control. FAC: Ferric ammonium citrate; LDN: LDN193189 Hydrochloride; p-: Phospho-; SMAD: Small mothers against decapentaplegic; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Yu LN, Wang SJ, Chen C, Rausch V, Elshaarawy O, Mueller S. Direct modulation of hepatocyte hepcidin signaling by iron. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(10): 1378-1393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i10/1378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1378