Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2020; 12(7): 332-349
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332
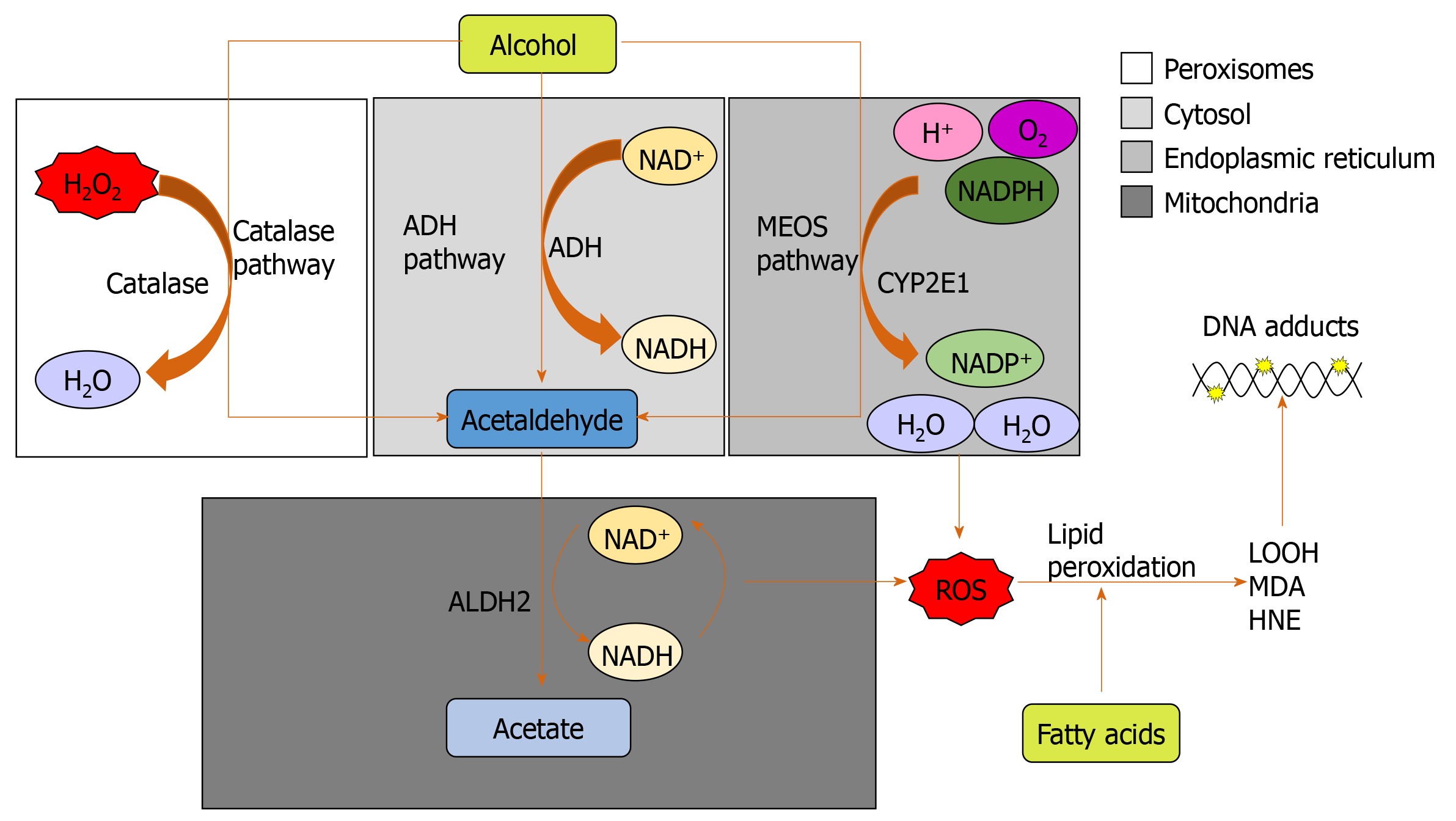
Figure 1 The three major pathways of alcohol metabolism.
The primary pathway is initiated by alcohol dehydrogenase, a NAD+ requiring enzyme expressed at high levels in hepatocytes, which oxidizes ethanol to acetaldehyde. The second major pathway, the microsomal ethanol oxidizing system pathway, involves the NADPH-requiring enzyme cytochrome P450 enzyme 2E1, which is induced by chronic alcohol exposure. The third pathway for ethanol metabolism is carried out by catalase, a peroxisomal enzyme. ADH: Alcohol dehydrogenase; ALDH2: Aldehyde dehydrogenase; CYP2E1: Cytochrome P450 enzyme 2E1; HNE: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; LOOH: Lipid hydroperoxides; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MEOS: Microsomal ethanol oxidizing system; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Tan HK, Yates E, Lilly K, Dhanda AD. Oxidative stress in alcohol-related liver disease. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(7): 332-349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i7/332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.332