Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2020; 12(12): 1211-1227
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1211
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1211
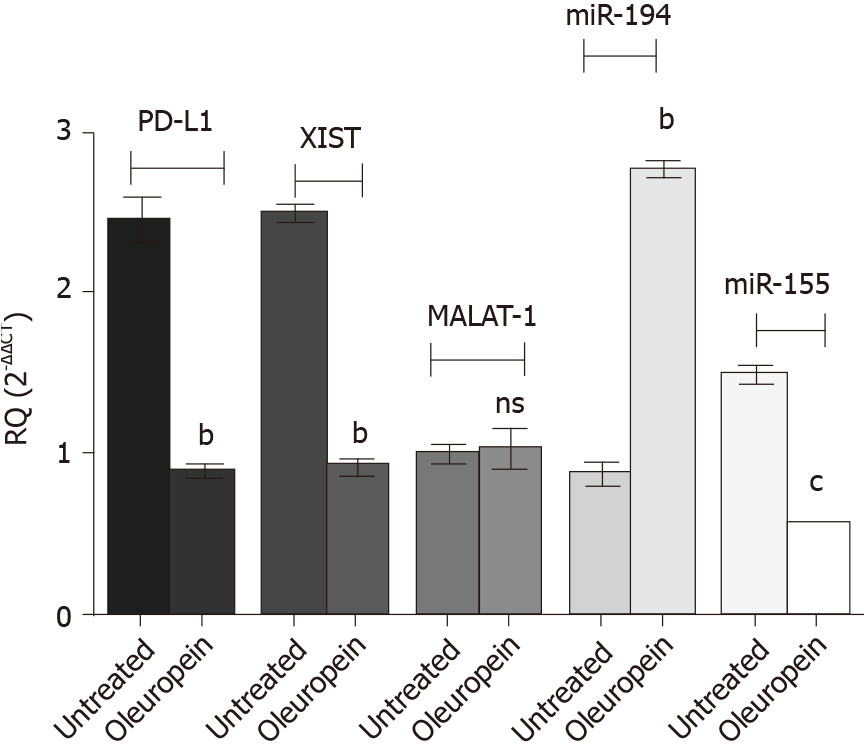
Figure 8 Impact of oleuropein on the expression profile of the study key players.
The expression pattern of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), micro ribonucleic acids 194-5p and 155-5p as well as long non-coding ribonucleic acids X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) and MALAT-1 were assessed following oleuropein treatment. Values for micro ribonucleic acids were normalized to RNU6B while that for PD-L1, XIST and MALAT-1 were normalized to B2M. Enhanced expression of miR-194-5p was observed following oleuropein treatment (P = 0.0022). However, PD-L1, XIST and miR-155-5p expression pattern were down regulated, (P = 0.0011), (P = 0.0020) and (P = 0.0001), respectively. Oleuropein did not show any significant impact on MALAT-1 expression profile. bP < 0.01 and cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Atwa SM, Handoussa H, Hosny KM, Odenthal M, El Tayebi HM. Pivotal role of long non-coding ribonucleic acid-X-inactive specific transcript in regulating immune checkpoint programmed death ligand 1 through a shared pathway between miR-194-5p and miR-155-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(12): 1211-1227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i12/1211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1211