Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2020; 12(12): 1198-1210
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198
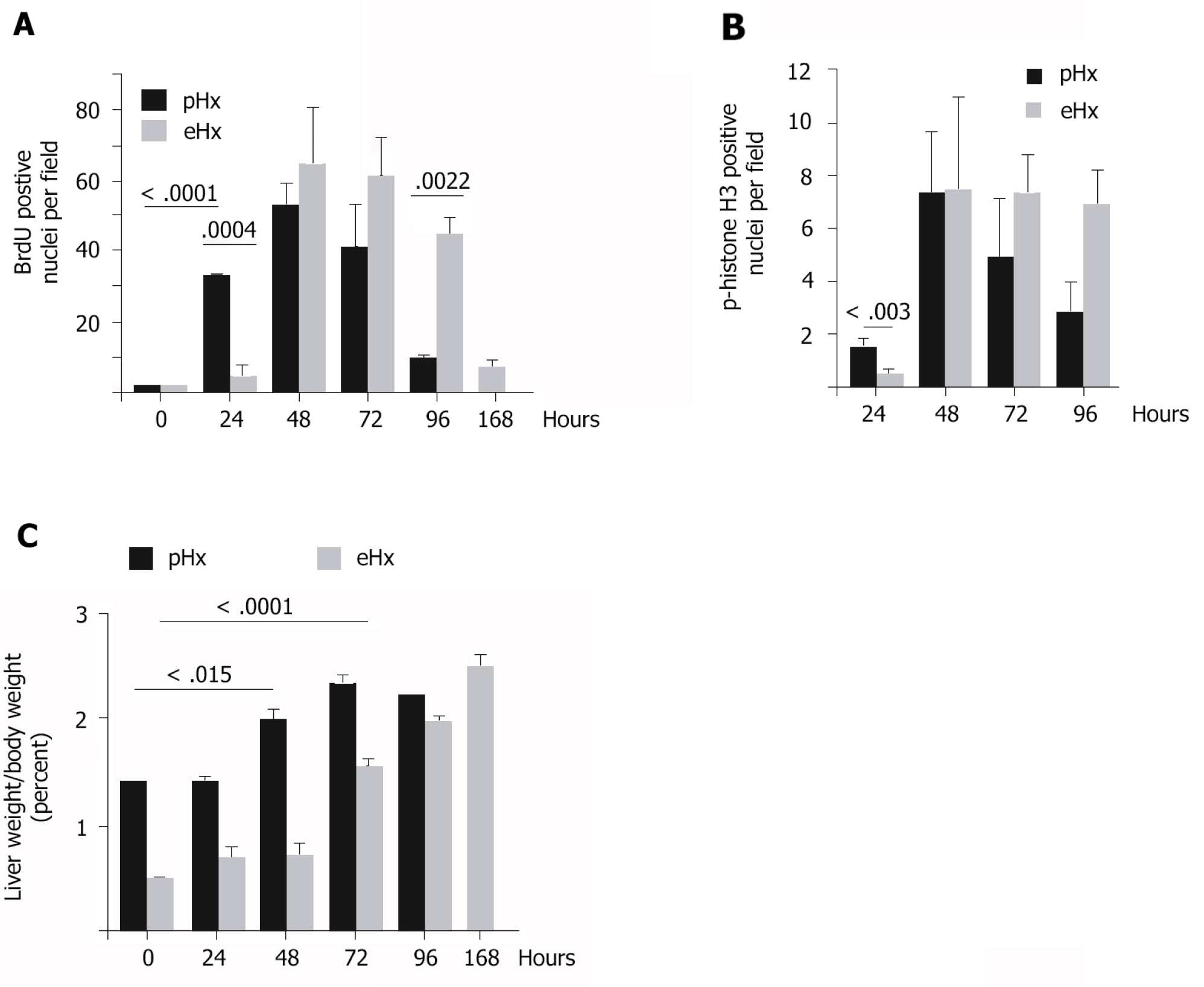
Figure 3 S-phase progression is markedly delayed after extended hepatectomy.
Animals were sacrificed at the indicated time points after 70% [hepatectomy (pHx)] or 90% [extended hepatectomy (eHx)], and remnant liver tissues were harvested for immunofluorescence analysis. A: Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation; B: Phospho-histone H3 Labeling of mitotic cells. Cell counting was performed in 10 random microscopic fields on 6 rats in the eHx group and 3 rats in pHx; C: Mean liver to body weight ratios after pHx and eHx. eHx: Extended hepatectomy; pHx: 70% hepatectomy.
- Citation: Moniaux N, Lacaze L, Gothland A, Deshayes A, Samuel D, Faivre J. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27 function as critical regulators of liver regeneration following 90% hepatectomy in the rat. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(12): 1198-1210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i12/1198.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198