Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2020; 12(12): 1198-1210
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198
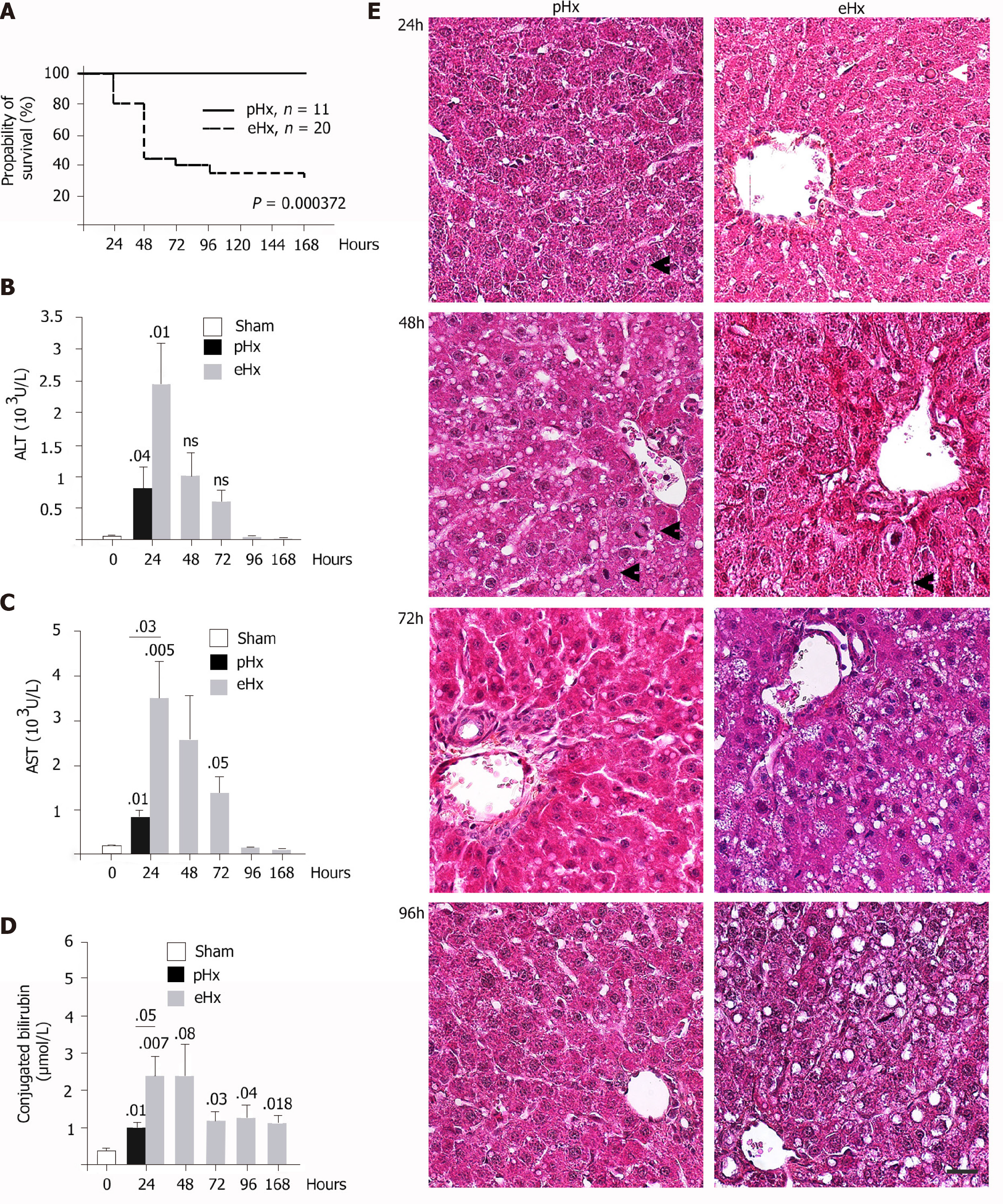
Figure 1 Survival rates and post-operative liver injury after enlarged liver resection.
Male Wistar rats were subjected to 70% [hepatectomy (pHx)] or 90% [extended hepatectomy (eHx)] followed by harvest of blood samples and the remnant liver tissues at the indicated time points after surgery. A: Kaplan-Meier survival plots; B: Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT); C: Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST); D: Conjugated bilirubin from hours 24 to 168 post-eHx (n = 45); E: Representative liver images stained with hematoxylin, eosin, and alcian blue at the indicated time points post-eHx; black arrowheads indicate mitotic figures, and white arrowheads point to globular red hyaline material. Scale bar: 50 μM. Sham: Laparotomy control group.
- Citation: Moniaux N, Lacaze L, Gothland A, Deshayes A, Samuel D, Faivre J. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27 function as critical regulators of liver regeneration following 90% hepatectomy in the rat. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(12): 1198-1210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i12/1198.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1198