Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2020; 12(11): 931-948
Published online Nov 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.931
Published online Nov 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.931
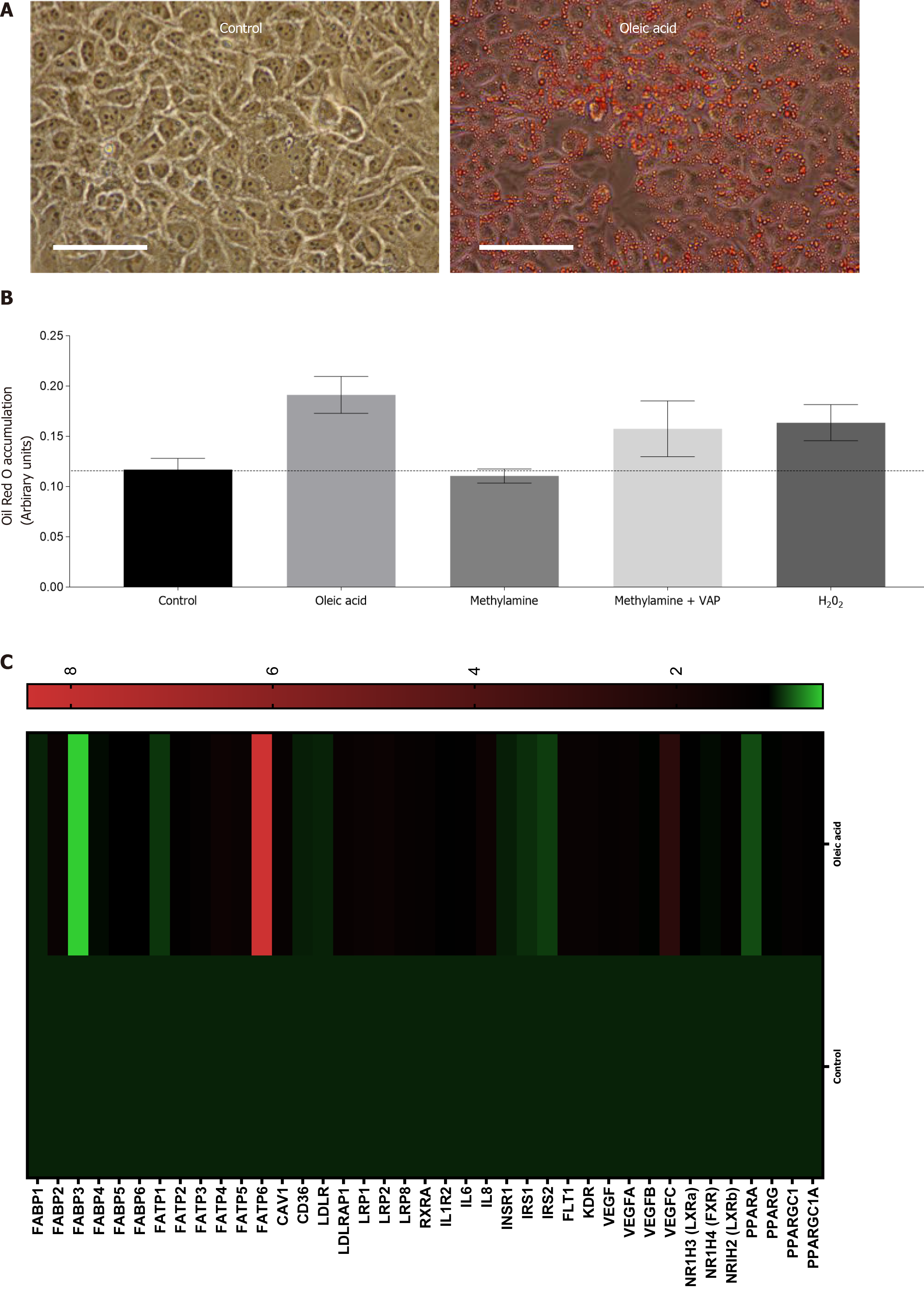
Figure 2 Exposure of Huh7.
5 cells to products of vascular adhesion protein-1 enzyme activity leads to lipid accumulation and gene expression changes. A: Representative phase contrast images of confluent control Huh7.5 (left) or cells pretreated with 250 μm Oleic Acid for 6 h. All wells were fixed and stained with Oil Red O, and images were captured at 40 × original magnification (representative of n = 3 samples per condition). Bar is 50 mm; B: Quantification of oleic acid accumulation after vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) stimulation. Huh7.5 were pretreated with either methylamine (200 μm) alone, or in combination with recombinant VAP-1 (500 ng/mL) or H2O2 (10 μmol/L), for approximately 18 h. This was followed by incubation for 6 h with 250 μm OA. Cells were fixed and stained with Oil Red O and solubilized. Signal is expressed in arbitrary units. Data are mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments; C: Analysis of mRNA expression in HuH7.5 cells after exposure to oleic acid by quantitative qPCR analysis. mRNA expression for indicated genes was assessed using fluidigm qPCR array® according to manufacturer’s instructions. Data is expressed as fold changes in relative gene expression compared to pooled housekeeping genes in control (untreated cells). Data are representative of triplicate conditions run on triplicate gene array plates.
- Citation: Shepherd EL, Karim S, Newsome PN, Lalor PF. Inhibition of vascular adhesion protein-1 modifies hepatic steatosis in vitro and in vivo. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(11): 931-948
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i11/931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.931