Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2020; 12(10): 754-765
Published online Oct 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754
Published online Oct 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754
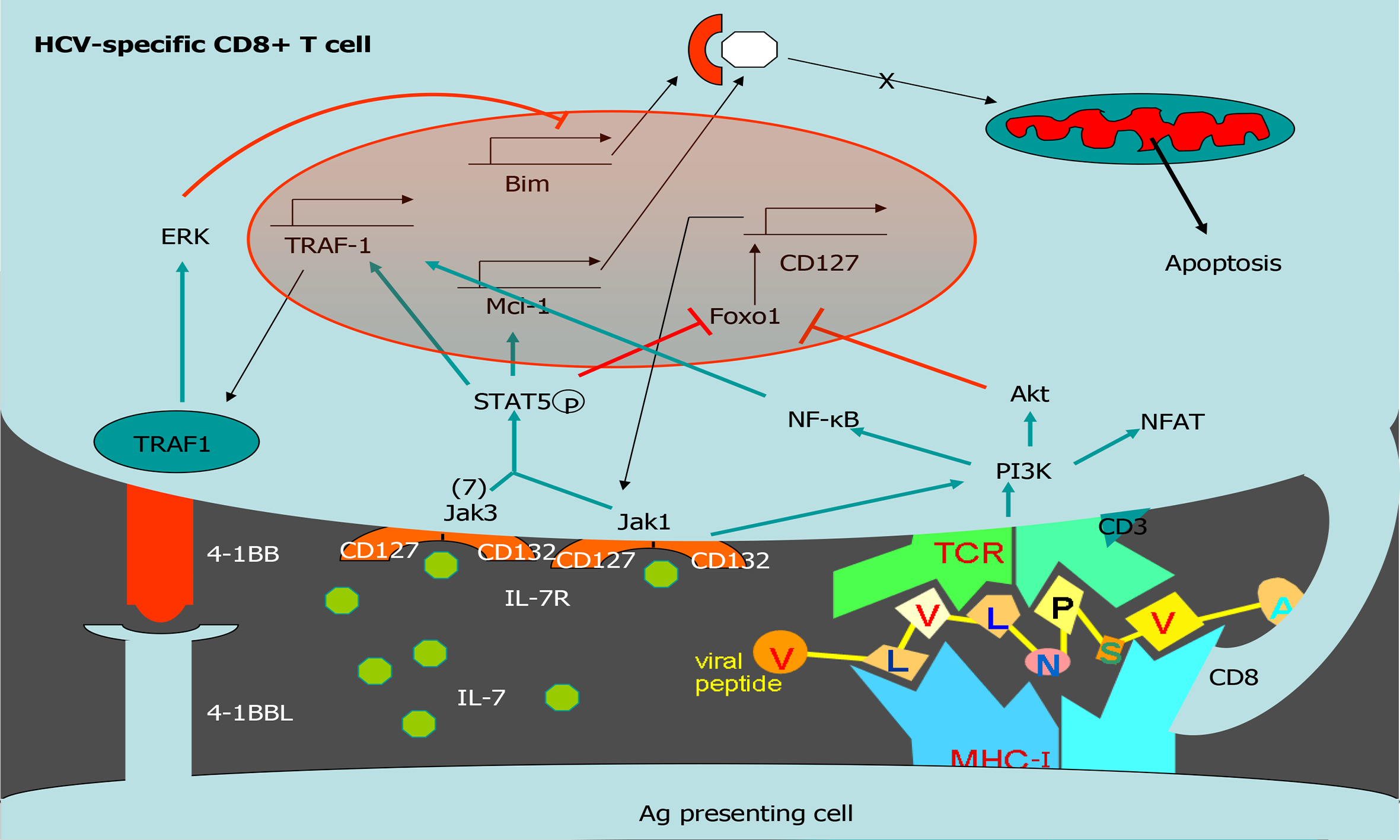
Figure 4 Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 pathways involved in T cell survival.
Scheme of T cell survival pathways. Interleukin (IL)-7/IL-7 receptor (CD127) increases the level of the anti-apoptotic molecule myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (Mcl-1) via signal transducer and activator of transcription 5. After T cell receptor activation, tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) level is upregulated via nuclear factor-kappa B. TRAF1 is the signal transducer of the positive checkpoint TNFR superfamily member 9 (4-1BB). 4-1BB stimulation downregulates Bim via extracellular signal-related kinase. IL-7 induces TRAF1 expression, increasing its anti-apoptotic effect by improving 4-1BB signaling. Together, 4-1BB and CD127 balance Bim and Mcl-1. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; 4-1BB: Tumor necrosis family receptor superfamily member 9; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; TRAF1: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1; Mcl-1: Myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein; IL: Interleukin; NF-Κb: Nuclear factor kappa B; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor.
- Citation: Peña-Asensio J, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Miquel J, Larrubia JR. Tumor necrosis family receptor superfamily member 9/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 pathway on hepatitis C viral persistence and natural history. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(10): 754-765
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i10/754.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754