Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2020; 12(10): 754-765
Published online Oct 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754
Published online Oct 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754
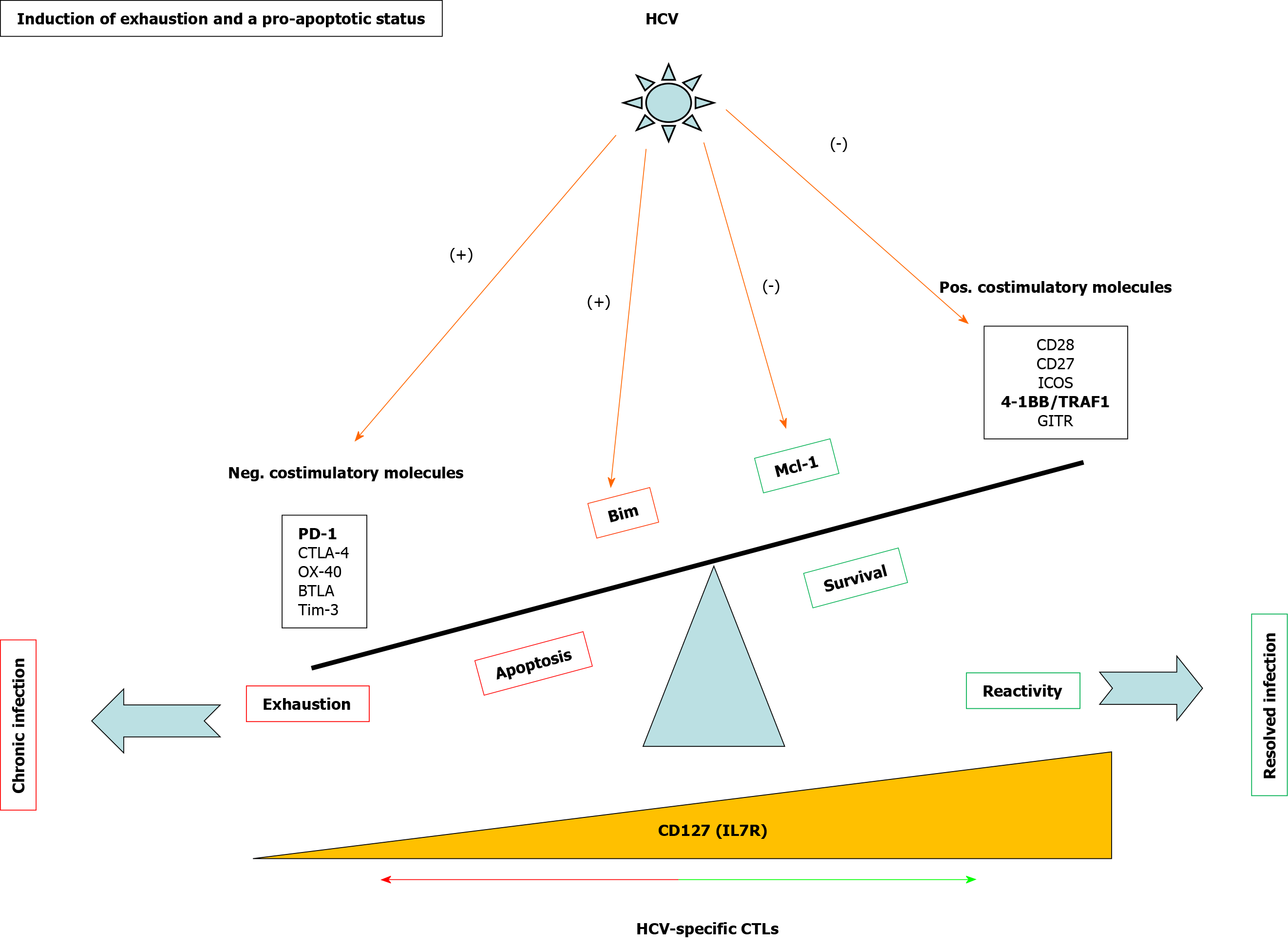
Figure 3 Mechanisms involved in T cell exhaustion and apoptosis during persistent hepatitis C virus infection.
Scheme showing positive and negative checkpoints and proteins involved in CD8 T cell reactivity and apoptosis during hepatitis C virus infection. In bold are highlighted the pathways discussed in the current review. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; 4-1BB: Tumor necrosis family receptor superfamily member 9; TRAF: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; GITR: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein; CTL: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Neg: Negative; Pos: Positive; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein-1; Mcl-1: Myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Peña-Asensio J, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Miquel J, Larrubia JR. Tumor necrosis family receptor superfamily member 9/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 pathway on hepatitis C viral persistence and natural history. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(10): 754-765
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i10/754.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i10.754