Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2019; 11(1): 74-85
Published online Jan 27, 2019. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i1.74
Published online Jan 27, 2019. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i1.74
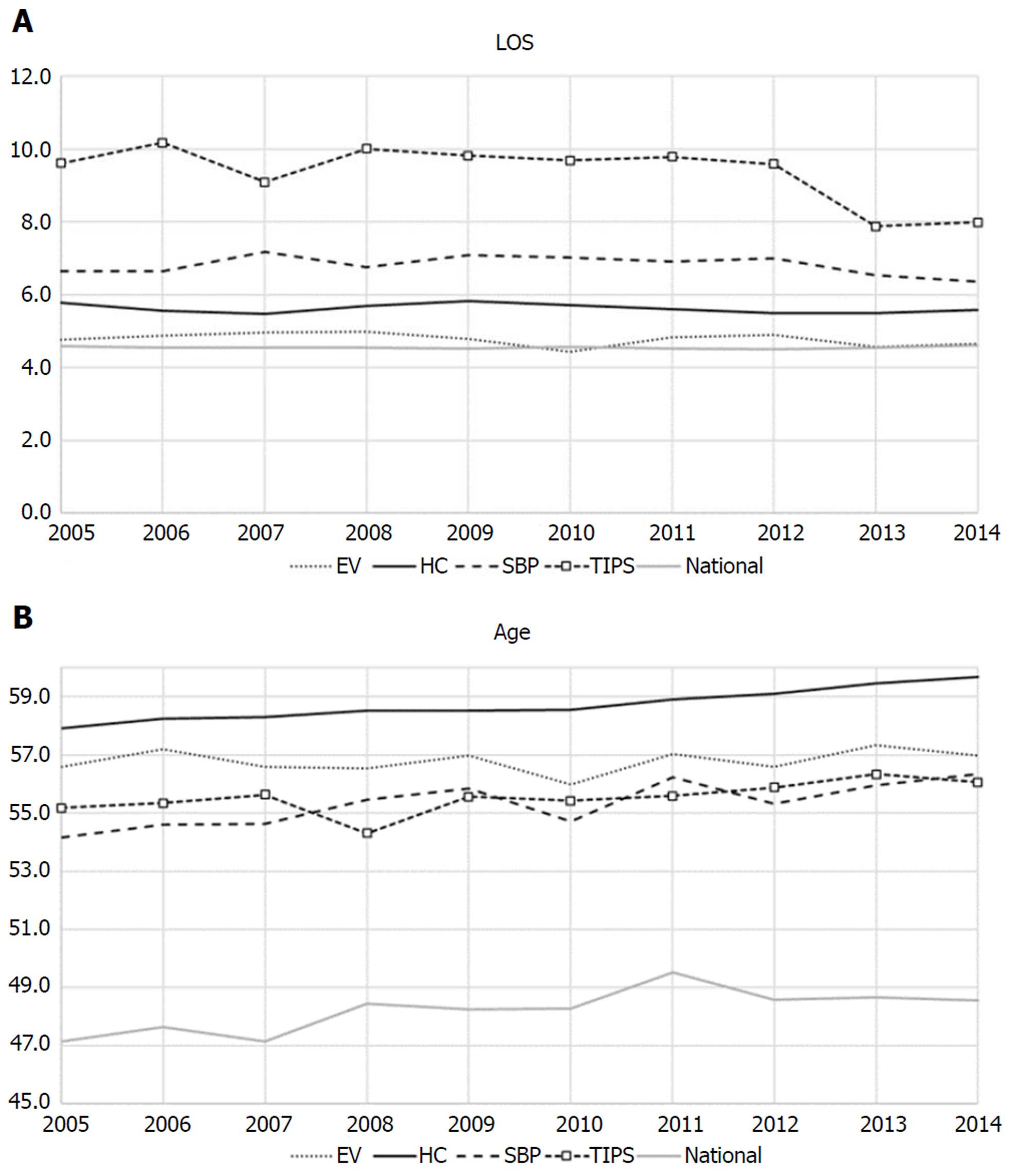
Figure 3 10-year temporal trends of mean length of stay and mean ages.
A: 10-year temporal trends of mean length of stay (LOS); B: 10-year temporal trends of mean ages. Mean LOS for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) decreased from 9.6 d in 2005 to 8.0 in 2014 with 17%. However, other cirrhosis related conditions and national LOS did not show any significant changes. TIPS had persistently higher LOS as compared to other conditions. Mean ages of cirrhosis-associated conditions were consistently higher than national average, and HC persistently had the highest mean age. EV: Esophageal varices with bleeding; HC: Hepatic encephalopathy/coma; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
- Citation: Sempokuya T, Zhang G, Nakagawa K. Temporal trends of cirrhosis associated conditions. World J Hepatol 2019; 11(1): 74-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v11/i1/74.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v11.i1.74