Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2018; 10(3): 352-370
Published online Mar 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i3.352
Published online Mar 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i3.352
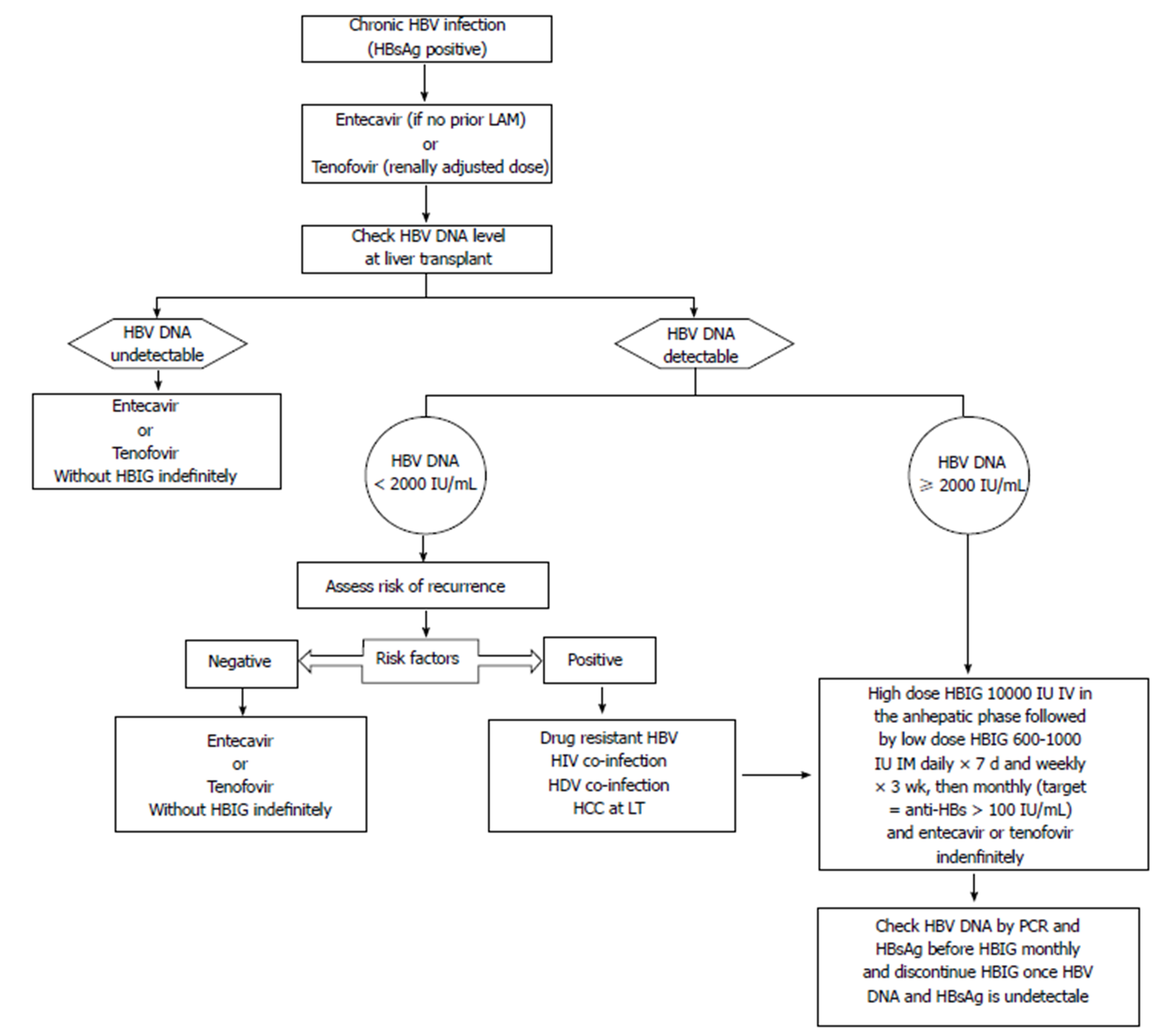
Figure 3 Proposed algorithm for hepatitis B prophylaxis in liver transplant patients.
In chronic hepatitis B patients Entecavir (if no prior Lamivudine therapy) or Tenofovir (adjusted to renal function) is recommended as the first line therapy. Based on HBV DNA level at the time of transplant and risk factors, HIBG should be initiated, if associated risk factors for HBV recurrence post LT. High risk patients include drug resistant HBV, HIV co-infection, HDV co-infection, HCC. This group of patients receive high dose IV HBIG 10000 IU given during the anhepatic phase followed by low dose HBIG to achieve target anti HBs > 100 IU/mL along with NAs. HBIG is discontinued once HBV DNA is undetectable and loss of HBsAg is achieved. HBIG: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; HDV: Hepatitis delta virus; LAM: Lamivudine; LT: Liver transplantation.
- Citation: Chauhan R, Lingala S, Gadiparthi C, Lahiri N, Mohanty SR, Wu J, Michalak TI, Satapathy SK. Reactivation of hepatitis B after liver transplantation: Current knowledge, molecular mechanisms and implications in management. World J Hepatol 2018; 10(3): 352-370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i3/352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i3.352