Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2018; 10(2): 231-245
Published online Feb 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.231
Published online Feb 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.231
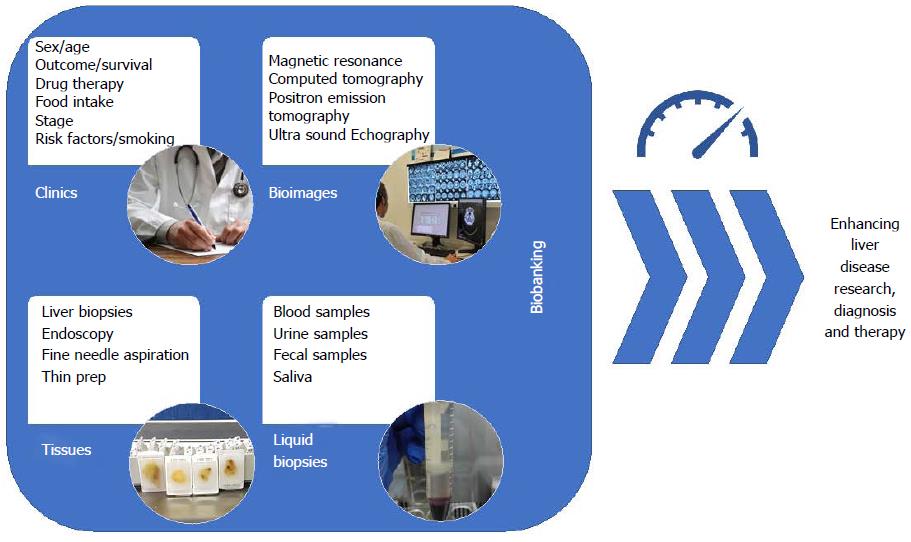
Figure 4 Modern vision of bio-banking.
The collection of patient clinical data, tissue samples, liquid biopsies as well as bio-images, in organized datasets is defined as “bio-banking”. With the advent of omics sciences (i.e., proteomics and genomics) where a large number of biological specimens and associated data are needed for making a precision medicine approach to the patients collaborative studies across centers are essential to maximizing patient recruitment. Equally, accessible well-structures data stores permit re-use and re-examination of data reducing the cost of subsequent studies. In this context, the field of bio-banking has the possibility to enhance research on liver disease as well as improve diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Citation: Mancini M, Summers P, Faita F, Brunetto MR, Callea F, De Nicola A, Di Lascio N, Farinati F, Gastaldelli A, Gridelli B, Mirabelli P, Neri E, Salvadori PA, Rebelos E, Tiribelli C, Valenti L, Salvatore M, Bonino F. Digital liver biopsy: Bio-imaging of fatty liver for translational and clinical research. World J Hepatol 2018; 10(2): 231-245
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i2/231.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.231