Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Jun 28, 2015; 7(12): 1685-1693
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1685
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1685
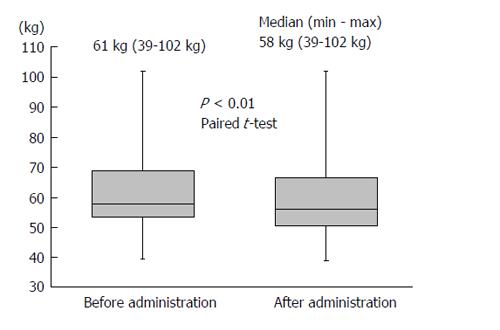
Figure 1 The median reduction in body weight was 3 kg (P < 0.
01) during the tolvaptan treatment period.
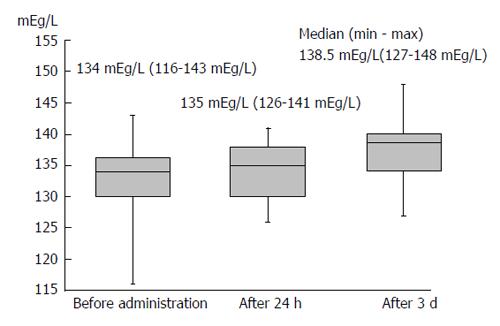
Figure 2 The serum sodium concentration peaked 3 d after administration of tolvaptan.
The median elevated serum sodium concentration was 4.5 mEq/L.
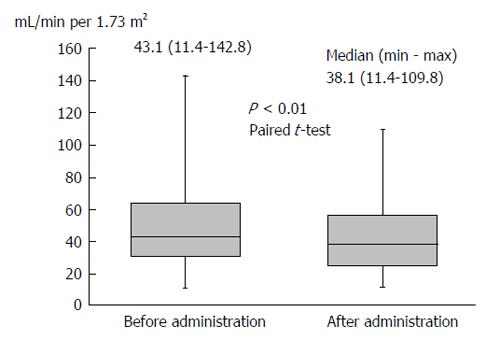
Figure 3 The estimated glomerular filtration rate significantly decreased after administration of tolvaptan from 43.
1 to 38.1 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
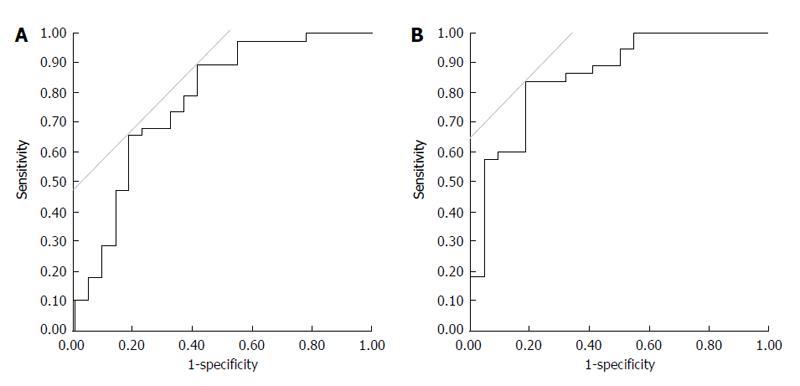
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic analysis.
A: A reduction in urine osmolality > 25% was the single best cut-off level for improvement of refractory ascites with 89.5% sensitivity and 59.1% specificity; B: A combination of urine output > 1800 mL within the first 24 h and a 30% reduction in urine osmolality were the best cut-off levels for improvement of refractory ascites with 84.2% sensitivity and 81.8% specificity.
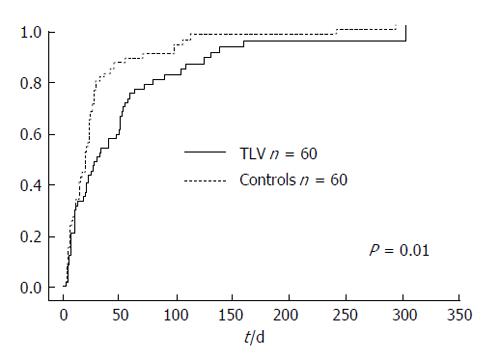
Figure 5 The cumulative incidence rate was significantly higher in the control group, with a median incidence time of 30 d in the tolvaptan group and 20 d in the control group.
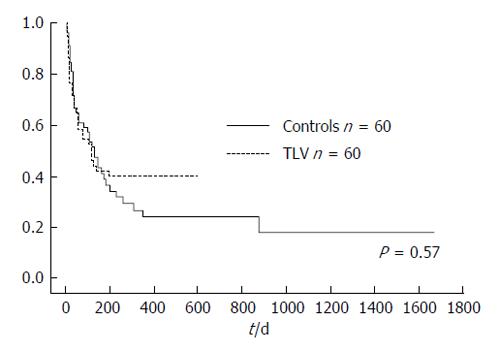
Figure 6 There was no significant difference in cumulative survival rate between the groups, with a median survival time of 121 d in the tolvaptan group and 123 d in the control group.
- Citation: Ohki T, Sato K, Yamada T, Yamagami M, Ito D, Kawanishi K, Kojima K, Seki M, Toda N, Tagawa K. Efficacy of tolvaptan in patients with refractory ascites in a clinical setting. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(12): 1685-1693
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i12/1685.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1685