Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2023; 15(9): 1060-1083
Published online Sep 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1060
Published online Sep 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1060
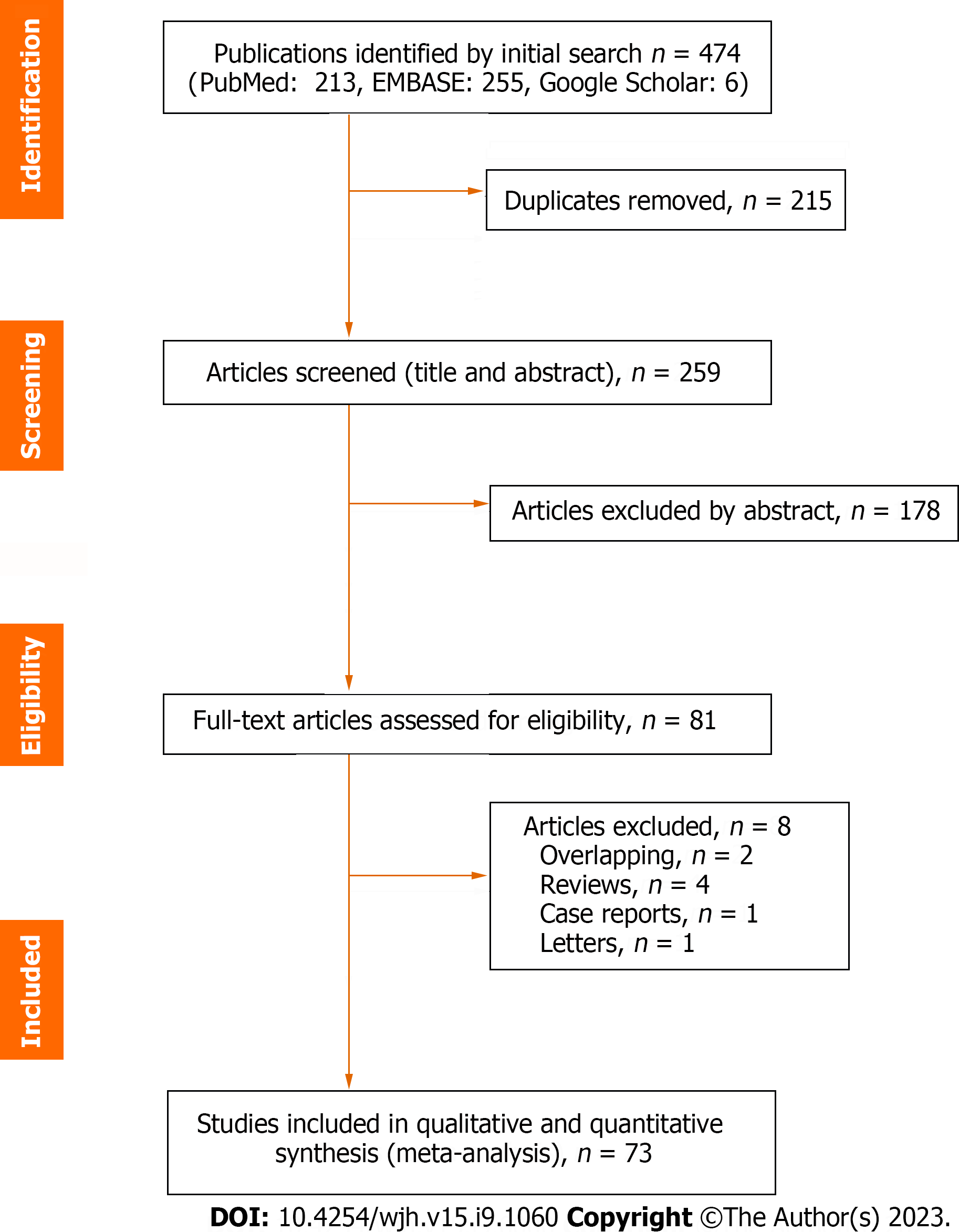
Figure 1
Study selection.
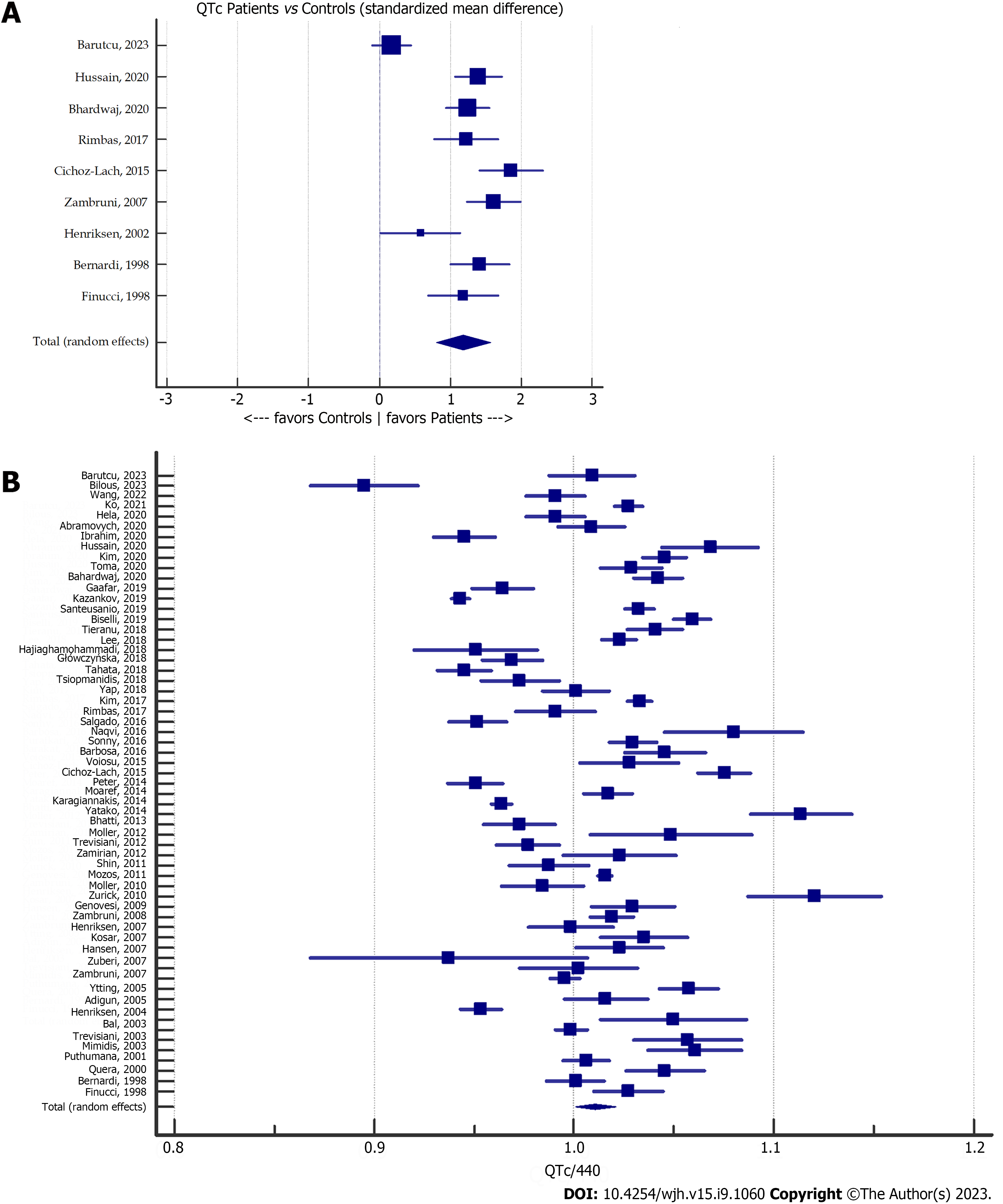
Figure 2 Meta-analysis forest plot.
A: Corrected QT (QTc) in patients with cirrhosis vs controls; B: QTc compared with the upper normal limit (440 ms) ratio in patients with cirrhosis. QTc: Corrected QT.
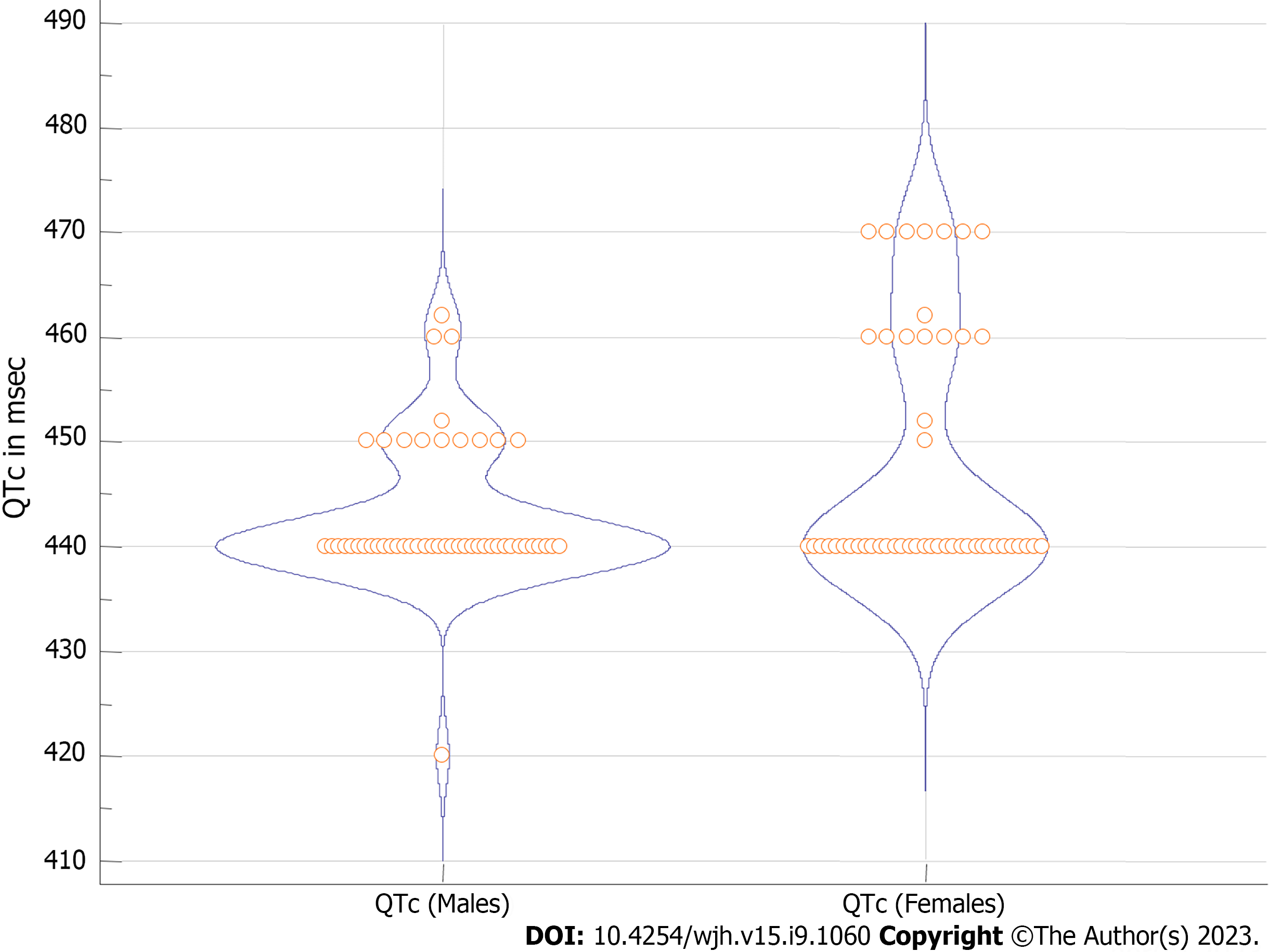
Figure 3 Violi plot for corrected QT upper normal limit used in the included studies.
QTc: Corrected QT.
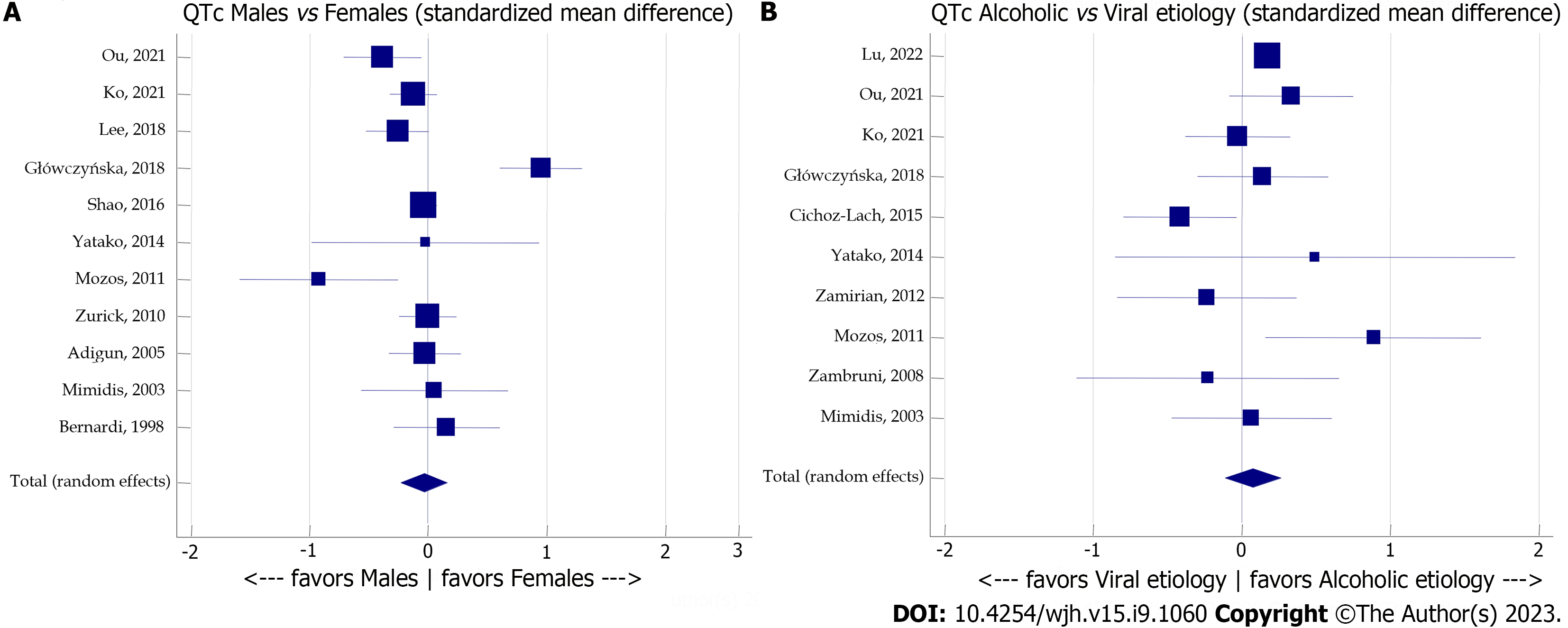
Figure 4 Meta-analysis forest plot concerning the effect of sex and etiology of cirrhosis on corrected QT.
A: The effect of sex on corrected QT (QTc) in patients with cirrhosis; B: The effect of etiology of cirrhosis on QTc. QTc: Corrected QT.
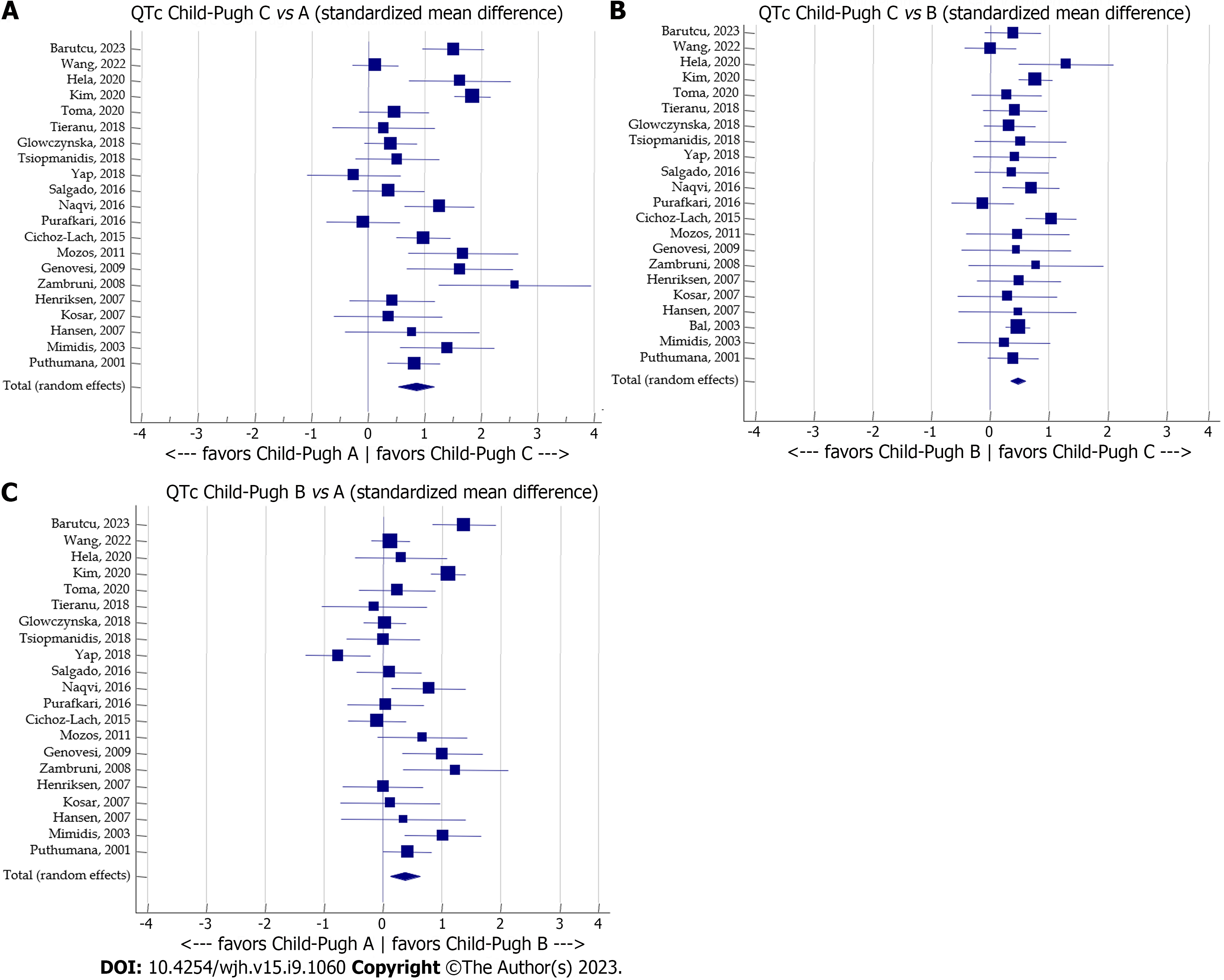
Figure 5 Meta-analysis forest plots concerning the effect of the Child-Pugh stage on corrected QT.
A: Child-Pugh stage C vs A; B: Child-Pugh stage C vs B; C: Child-Pugh stage B vs A. QTc: Corrected QT.
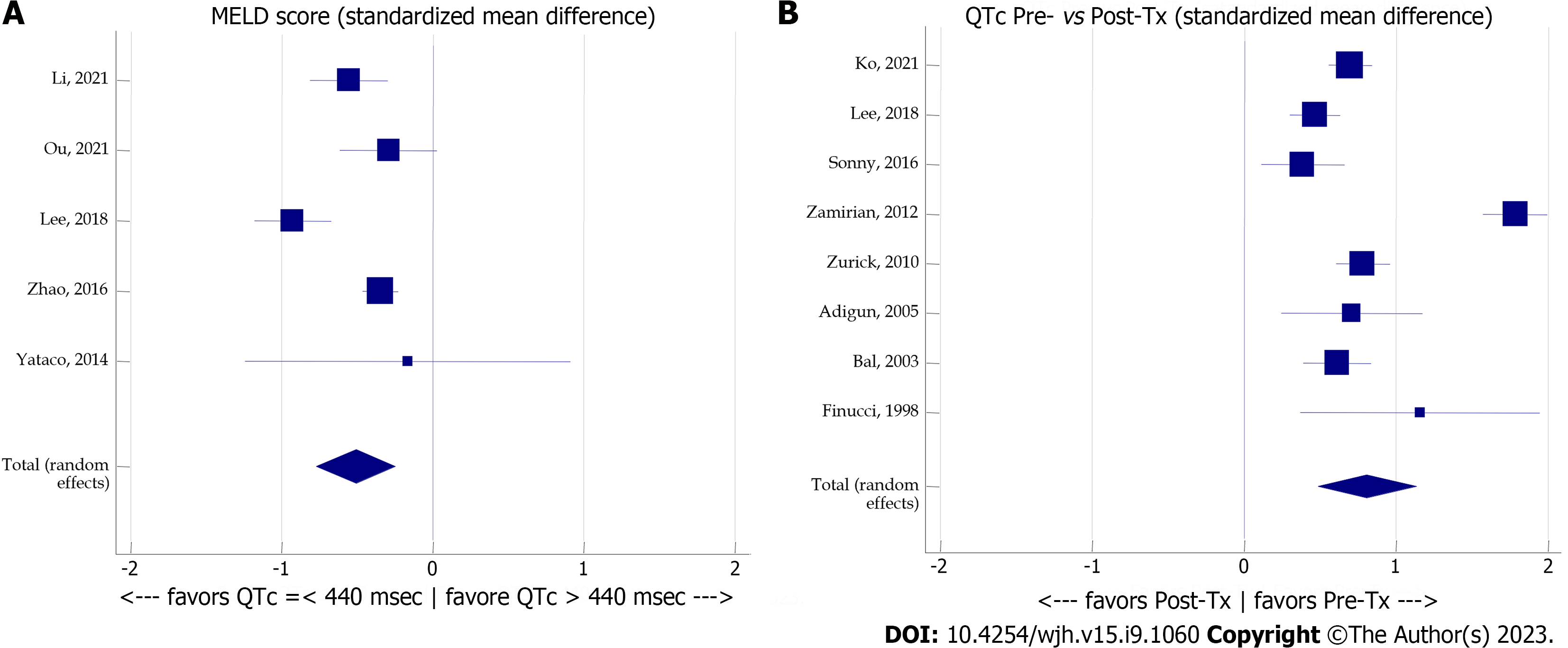
Figure 6 Meta-analysis forest plot concerning the effect of the model for end-stage liver disease score and liver transplantation on corrected QT.
A: The effect of the model for end-stage liver disease score on corrected QT (QTc); B: The effect of liver transplantation on QTc. Tx: Transplantation; MELD: Model for end-stage liver disease; QTc: Corrected QT.
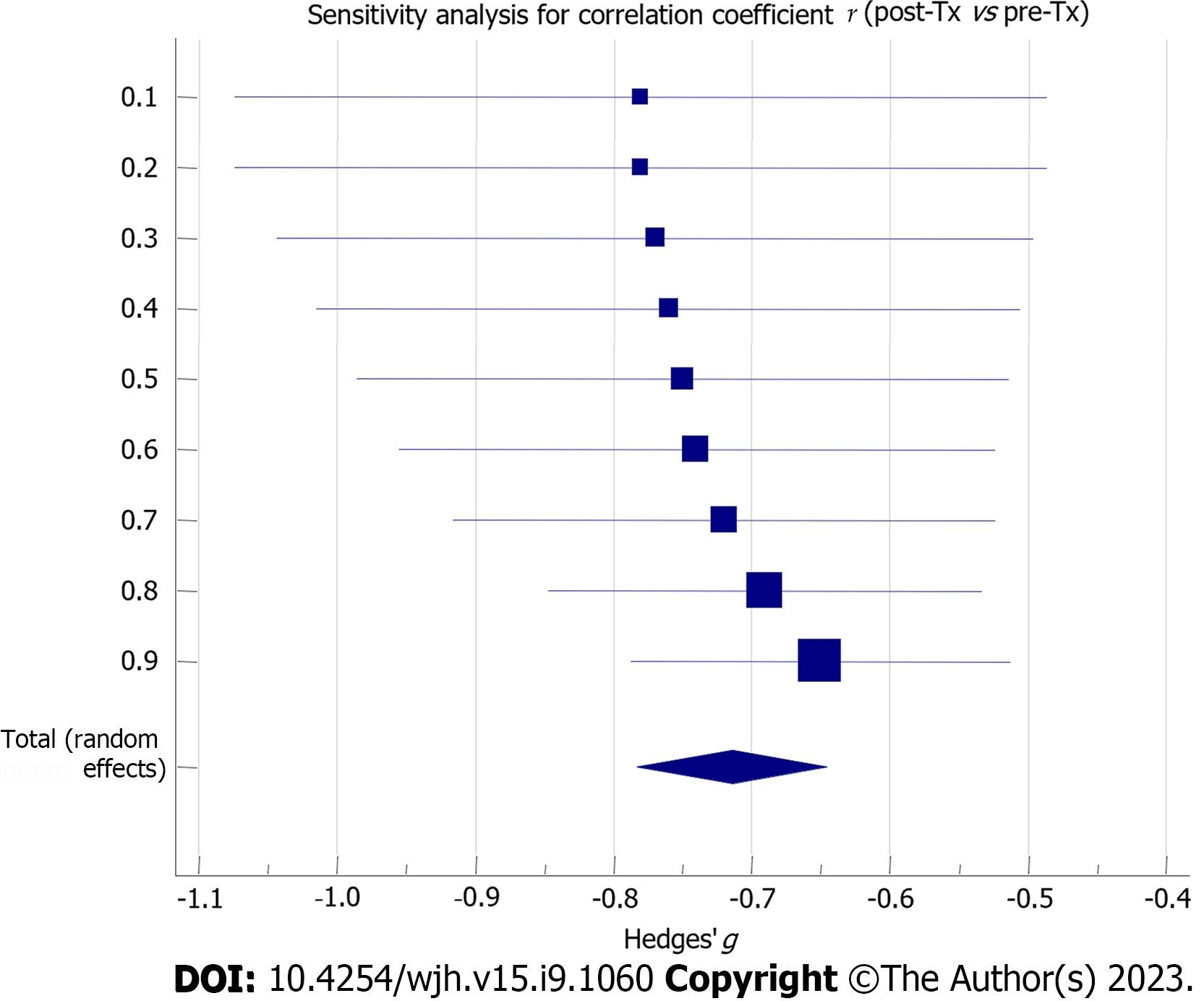
Figure 7 Sensitivity analysis forest plot concerning the estimation of the correlation coefficient between post-transplantation and pre-transplantation corrected QT values.
Tx: Transplantation.
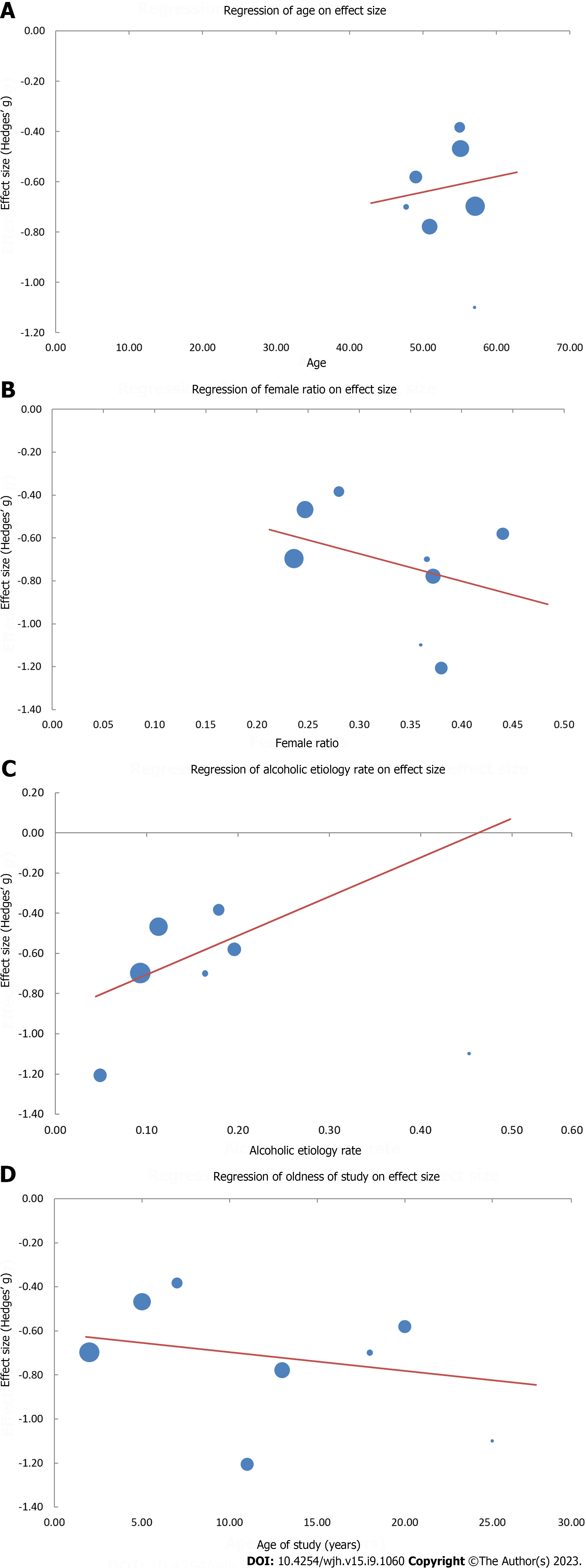
Figure 8 Plot points and regression lines on effect size, namely Hedges’ g, reflecting correlations of pre-transplantation vs post-transplantation corrected QT.
A: Age [Hg = -0.95 + 0.01 (yr); P = 0.417]; B: Female ratio [Hg = -0.29 - 1.28 (female ratio); P < 0.001]; C: Alcoholic etiology rate [Hg = -0.90 - 1.95 (alcoholic etiology rate); P < 0.001]; D: Age of study [Hg = -0.61 - 0.01 (age of study); P = 0.019]. Hg refers to Hedges’g.
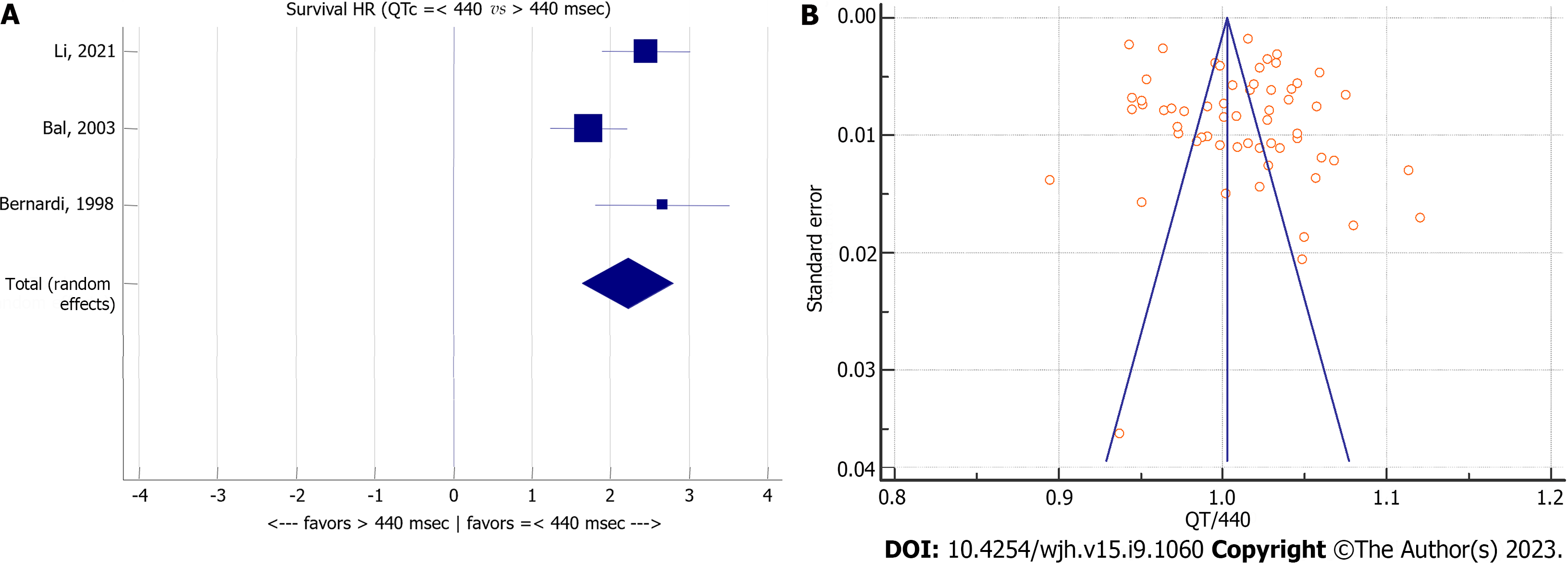
Figure 9 Meta-analysis forest plot concerning overall survival of patients with cirrhosis relating to corrected QT and corrected QT to upper normal limit (440 ms) ratio in patients with cirrhosis.
A: Overall survival of patients with cirrhosis relating to corrected QT (QTc); B: QTc to upper normal limit (440 ms) ratio in patients with cirrhosis. QTc: Corrected QT; HR: Hazard ratio.
- Citation: Papadopoulos VP, Mimidis K. Corrected QT interval in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(9): 1060-1083
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i9/1060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1060