Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2021; 13(9): 979-1002
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.979
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.979
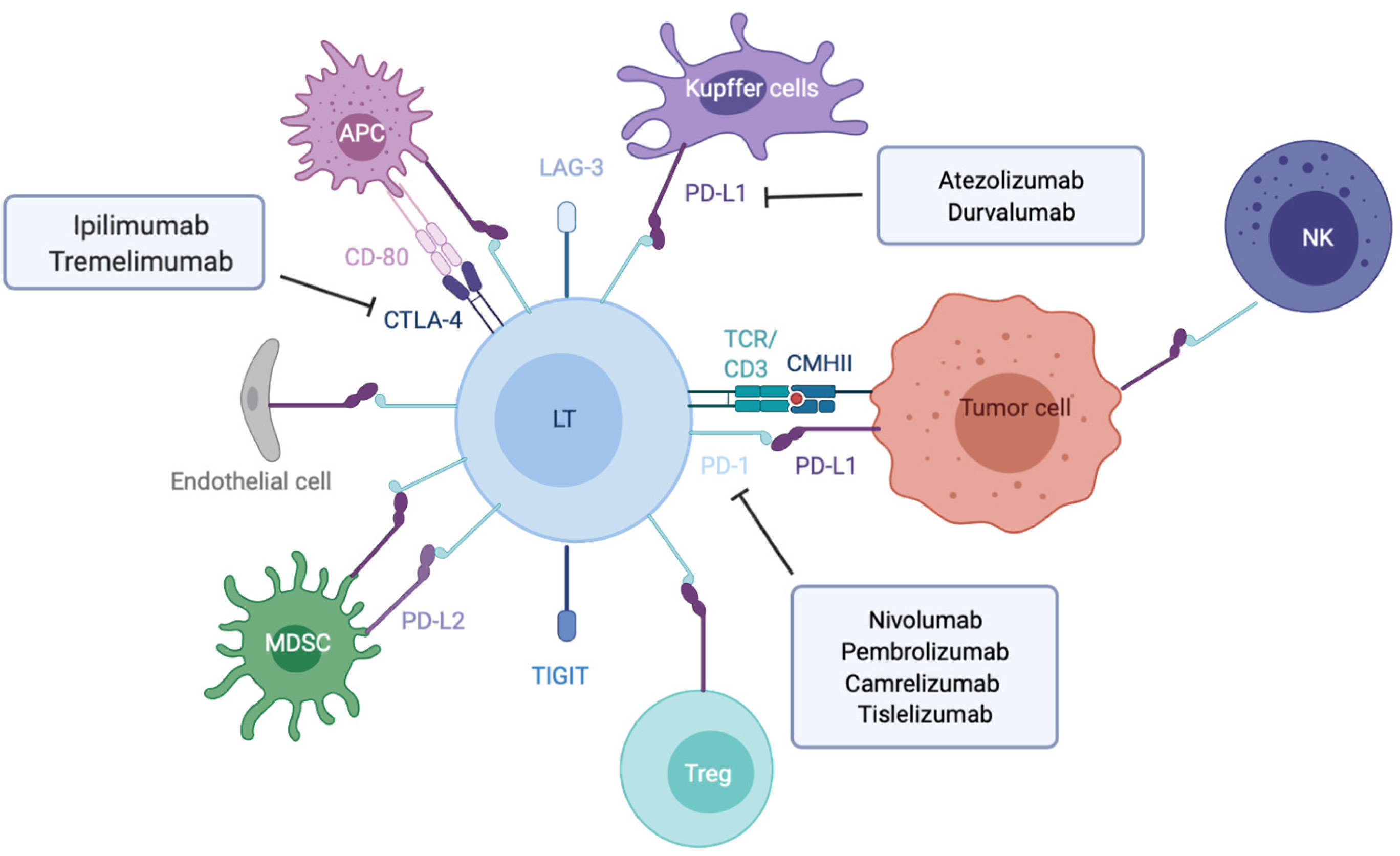
Figure 1 Overview of the main immune checkpoint and their respective targeted therapies.
Made with biorender.com. APC: Antigen presenting cell; LT: T lymphocyte; MDSC: Myeloid derived suppressive cell; NK: Natural killer; Treg: Lymphocyte T regulator; LAG-3: Lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-L1: Program cell death ligand 1; TCR: T cell receptor.
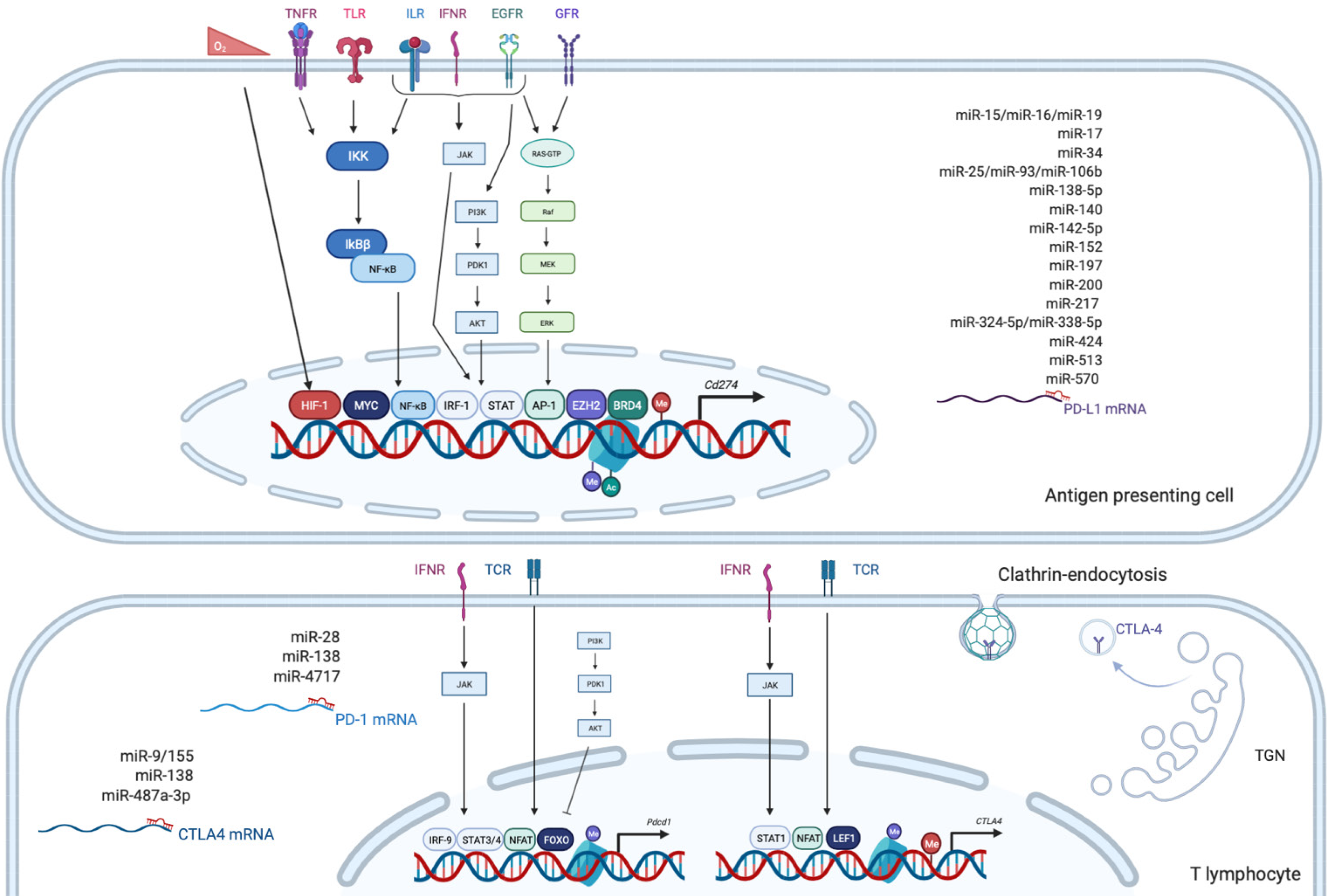
Figure 2 Overview of the main epigenetic and transcriptional regulations of program cell death 1, program cell death ligand 1 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4.
Made with biorender.com. Ac: Acetylation; Me: Methylation of DNA or histone; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GFR: Growth factor receptor; ILR: Interleukin receptor; IFNR: Interferon receptor; TCR: T cell receptor; TGN: Trans-Golgi Network; TLR: Toll like receptor; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor.
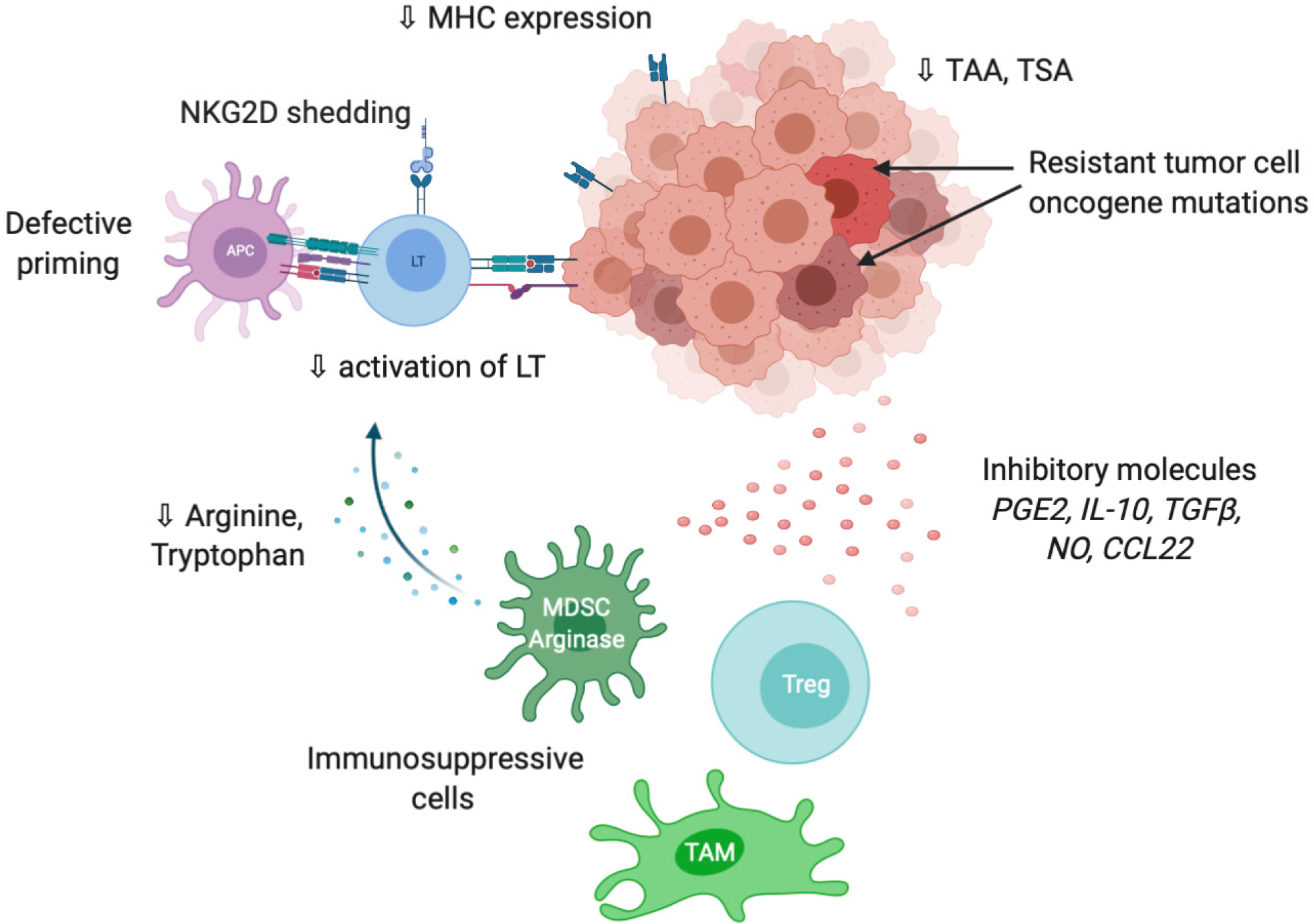
Figure 3 Overview of the main mechanisms involved in tumor evasion to immune response.
Made with biorender.com. APC: Antigen presenting cell; ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitors; LT: T lymphocyte; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; MDSC: Myeloid derived suppressive cell; NK: Natural killer; NKG2D: Natural killer group 2D; NO: Nitric oxide; TAA: Tumor-associated antigens; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; TSA: Tumor-specific antigen; Treg: Lymphocyte T regulator.
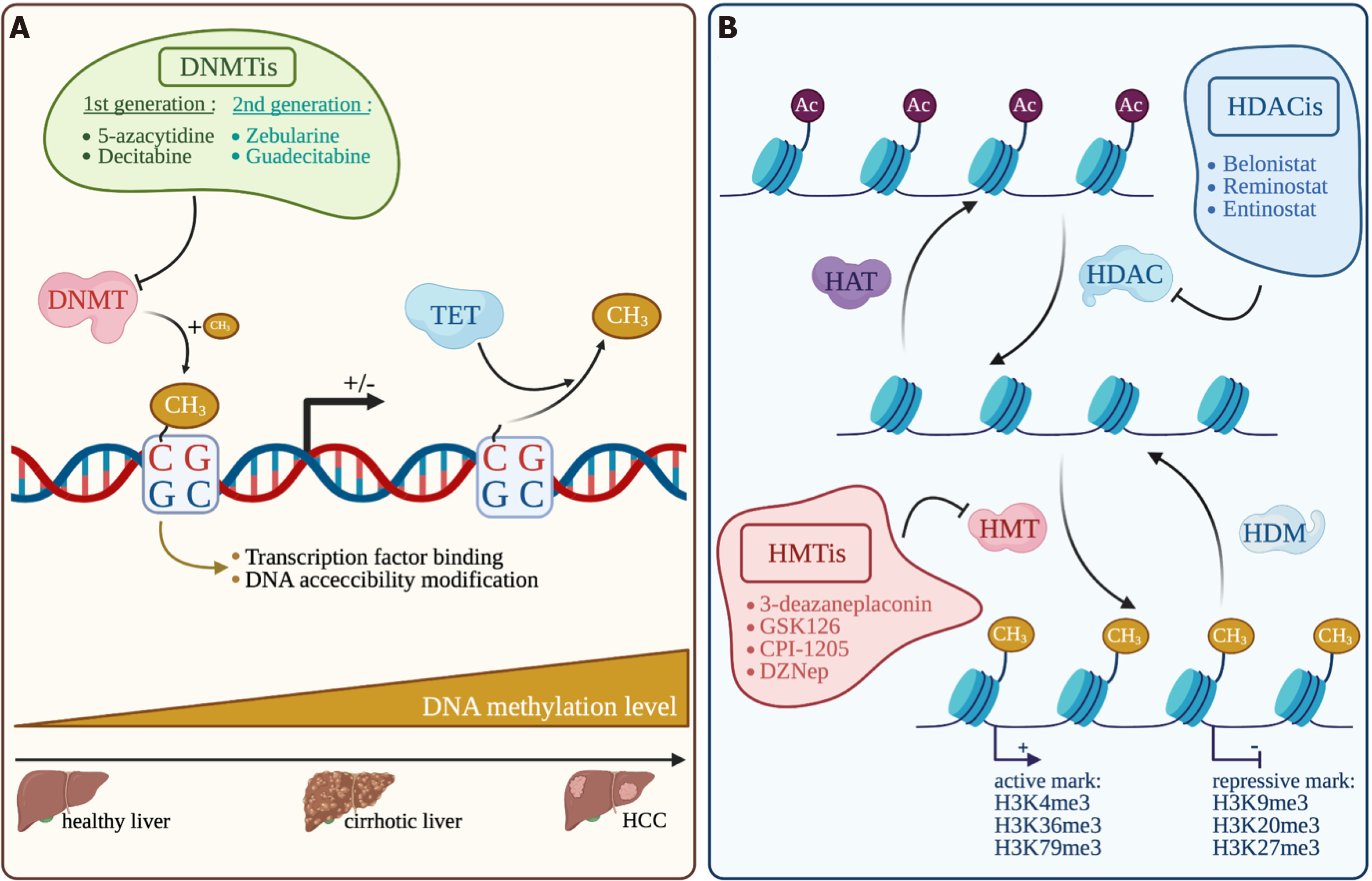
Figure 4 Overview of the main epigenetic mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma and their inhibitors.
Made with biorender.com. A: DNA methylation; B: Histone modification. DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; TET: Ten-eleven translocation; DNMTis: DNA methyltransferase inhibitors; HAT: Histone acetyl transferase; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; HDACis: Histone deacetylase inhibitors; HMT: Histone methyl transferase; HDM: Histone demethylase; HMTis: Histone methyl transferase inhibitors; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Sanceau J, Gougelet A. Epigenetic mechanisms of liver tumor resistance to immunotherapy. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(9): 979-1002
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i9/979.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.979