Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2017; 9(8): 118-126
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118
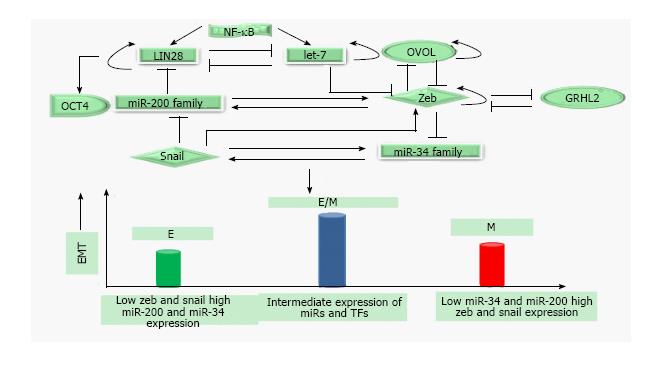
Figure 3 Epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory network: Mutually exclusive inhibitory loops including miR-200family/Zeb; miR-34family/Snail; LIN28/let-7 bring about bistable switch between epithelial (E) and mesenchymal (M) phenotypes, control Epithelial-mesenchymal transition/mesenchymal-epithelial transition and stemness.
Phenotypic stability factors like OVOL and GRHL2 couple to core-EMT decision making circuits and stabilize hybrid E/M phenotype. NF-κB controls LIN28/let-7 regulation and elevates the likelihood of hybrid E/M phenotype. Solid arrows represent the activation; solid lines represent the repression and circular loops represent the self-activation. Hybrid E/M: Hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; miR: MicroRNA; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
- Citation: Garg M. Epithelial plasticity and cancer stem cells: Major mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis and therapy resistance. World J Stem Cells 2017; 9(8): 118-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v9/i8/118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118