Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2017; 9(8): 118-126
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118
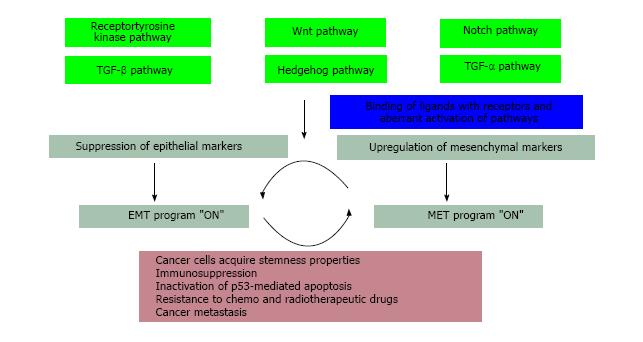
Figure 2 Signaling pathways regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-epithelial transition: Aberrant activation of signaling pathways including Notch, Wnt, Hedgehog, receptor tyrosine kinase, Transforming growth factor-beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulate the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-activating transcription factors.
EMT-ATFs induce EMT by repressing and activating the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal genes respectively. Epithelial plasticity confers long term survival advantages to the disseminated cancer stem cells at distant sites, makes them resistant to conventional therapies and allows the cancer to relapse. EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; MET: Mesenchymal-epithelial transition; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; EMT-ATFs: EMT-activating transcription factors.
- Citation: Garg M. Epithelial plasticity and cancer stem cells: Major mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis and therapy resistance. World J Stem Cells 2017; 9(8): 118-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v9/i8/118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v9.i8.118