Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2016; 8(4): 136-157
Published online Apr 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136
Published online Apr 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136
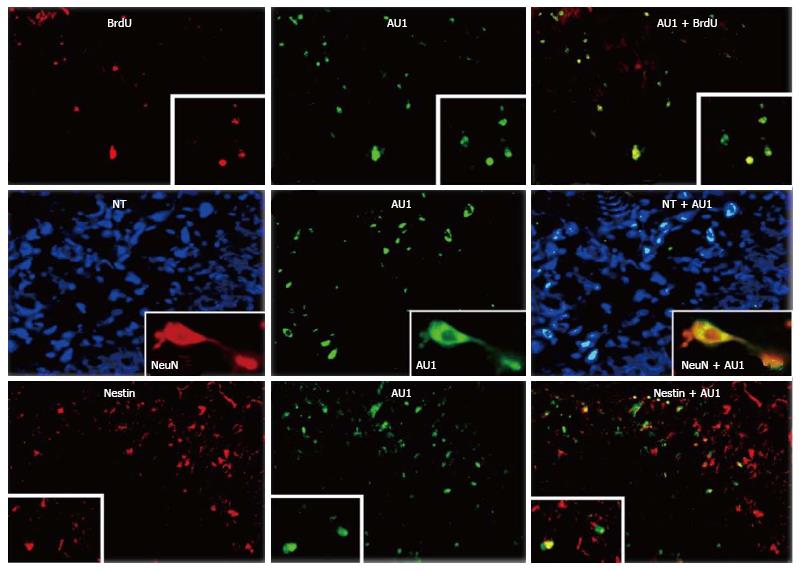
Figure 8 RNAiR5 gene delivery to the bone marrow increases numbers of bone marrow-derived cells in the hippocampus and neuroproliferative activity in the hippocampus, in the resting state and in response to kainic acid treatment.
Bone marrow-derived cells in the hippocampus (HC) were all neurons, and most proliferating cells in the HC were bone marrow-derived. Double immunostaining for AU1 plus BrdU (upper row) and nestin (lower row), and neuron identification using Neurotrace (NT) and NeuN (middle row) was performed. Shown are HC sections from kainic acid-treated rats, transduced with SV (RNAiR5-RevM10.AU1). Most of the AU1+ cells were also positive for BrdU (79.8%, ± 6.9%) as a marker of cell proliferation, and most BrdU+ cells were also AU1+ (72.2%, ± 7.4%). Numerous AU1+ cells were also positive for nestin, a marker of proliferating and migrating neurons, although there were as well many nestin-positive cells that did not express AU1. The equivalence of NT identification of neurons and NeuN immunostaining of neurons is illustrated in the insets in the middle row. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments (modified from Ref. [132]).
- Citation: Dennie D, Louboutin JP, Strayer DS. Migration of bone marrow progenitor cells in the adult brain of rats and rabbits. World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(4): 136-157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i4/136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136