Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2016; 8(4): 136-157
Published online Apr 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136
Published online Apr 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136
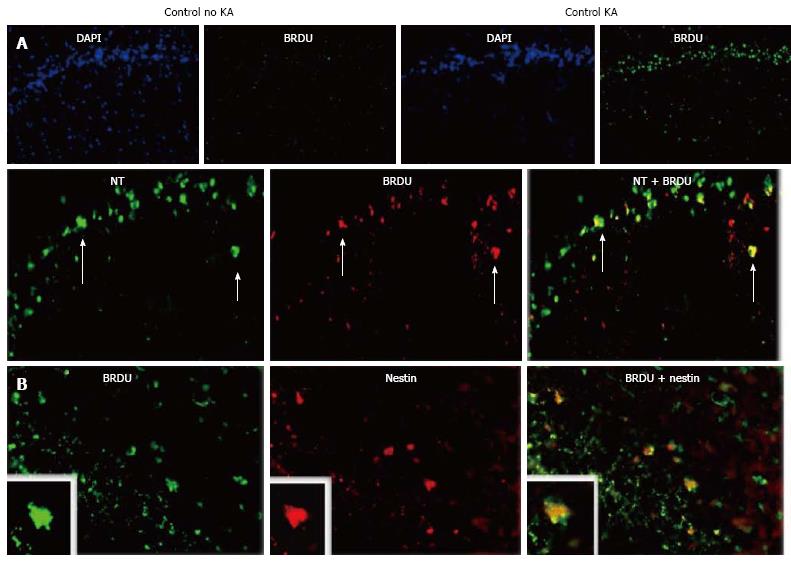
Figure 7 Kainic acid-induced regeneration in the hippocampus.
Rats were injected with kainic acid (KA) intraperitoneally (i.p.), 10 mg/kg, and their hippocampi (HCs) analyzed by immunomicroscopy 7 d thereafter. A: Neurogenesis following KA treatment. Rats given KA or saline were injected with BrdU. Then, at 7 d post-KA, their DGs were immunostained for BrdU to visualize proliferating cells. DAPI counterstain is shown to facilitate interpretation. Arrows show neurons positive for BrDU. Double staining with Neurotrace (NT) for neurons is shown below; B: Double staining for nestin, a marker of proliferating and migrating neural cells (modified from Ref. [132]).
- Citation: Dennie D, Louboutin JP, Strayer DS. Migration of bone marrow progenitor cells in the adult brain of rats and rabbits. World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(4): 136-157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i4/136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i4.136