Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2015; 7(6): 922-944
Published online Jul 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.922
Published online Jul 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.922
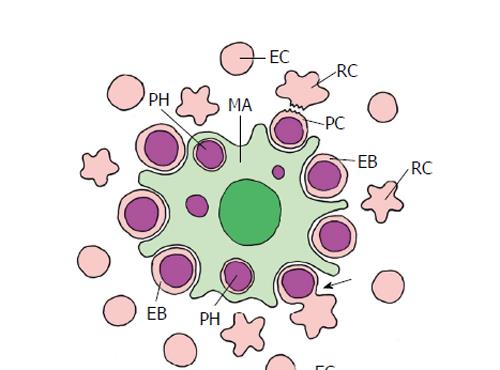
Figure 9 Erythropoiesis in mammal bone marrow (schematized).
The erythroblastic island consists of a central macrophage (MA) that functions as the niche, and the peripheral erythroblasts (EB), that represent stem/progenitor cells. Erythroblasts undergo an enucleation process (arrow) that results in the pyrenocyte (PC) that mainly consists of the erythroblast nucleus, and the nucleus-free reticulocyte (RC). The pyrenocyte is phagocytized by the macrophage (PH, phagosome), whereas the reticulocyte develops to the erythrocyte (EC) (adapted from Chasis et al[4]; Keerthivasan et al[98]).
- Citation: Dorn DC, Dorn A. Stem cell autotomy and niche interaction in different systems. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(6): 922-944
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i6/922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.922