Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2015; 7(2): 495-501
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.495
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.495
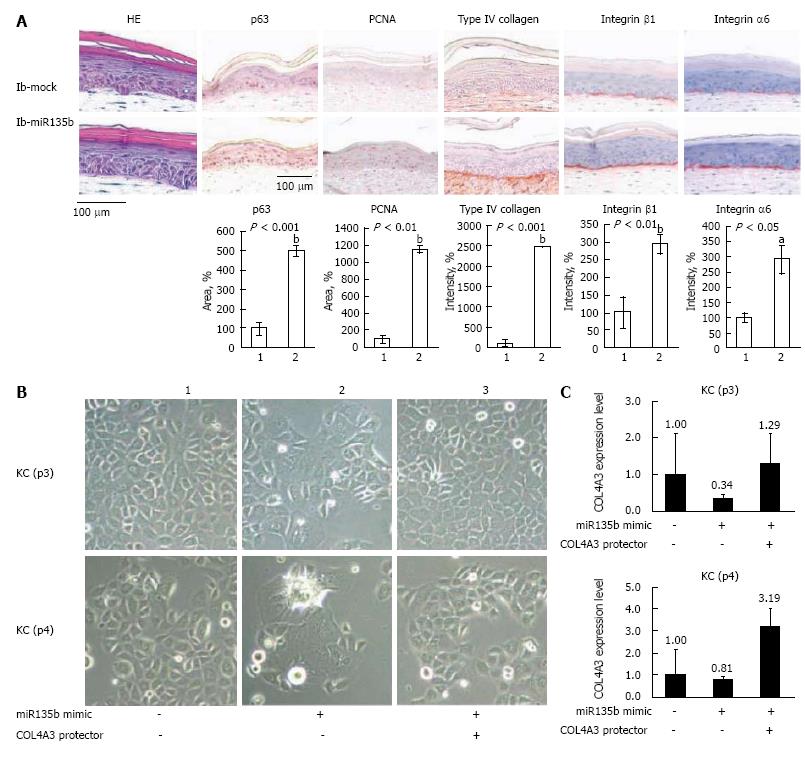
Figure 2 The inhibition of miR135b prolongs the stemness and proliferative potential of epidermal keratinocytes in skin equivalents models.
A: Histology of skin equivalent (SE) models constructed with ib-mock-transfected or ib-miR135b-transfected keratinocytes, and immunohistochemical staining of these models for p63, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, type IV collagen, and integrin β1, and integrin α6. Expression levels of p63, PCNA, type IV collagen, integrin β1, and integrin α6 were increased in SEs generated from ib-miR135b-transfected cells; 1: ib-mock; 2: ib-miR135b; B: Fast-forward co-transfection of keratinocytes with ‘‘miRNA mimic’’ and ‘‘target protector’’. 1: Negative control of miRNA mimic (10 nmol/L) and negative control of target protector (500 nmol/L); 2: miRNA mimic (10 nmol/L) and negative control of target protector (500 nmol/L); 3: MiRNA mimic and target protector (500 nmol/L). The inhibition of miR135b increases proliferation of keratinocyte via targeting type IV collagen; C: Real-time PCR analysis of gene expression in co-transfected keratinocytes. The housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an endogenous control. The result was same as (B). HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
- Citation: Choi HR, Byun SY, Kwon SH, Park KC. Niche interactions in epidermal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(2): 495-501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i2/495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.495