Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2015; 7(1): 223-234
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.223
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.223
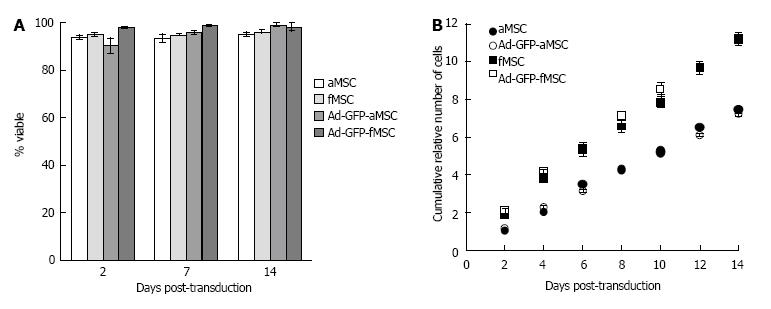
Figure 5 Mesenchymal stem cells viability and proliferation post-transduction.
A: Mean ± SD percent of viable cells as determined by 7-AAD positivity in flow cytometry at the indicated days post-transduction with Ad-GFP; B: Cumulative relative number of cells of Ad-GFP-MSCs and control MSCs. An estimated cell proliferation rate of 45 h and 29 h for aMSC or fMSCs, respectively, was determined from the slope of the curves; not significantly different between treated and control cells. Ad-GFP: E1-A-deleted-green fluorescent protein; fMSCs: Fetal mesenchymal stem cells; aMSCs: Adult mesenchymal stem cells.
-
Citation: Santiago-Torres JE, Lovasz R, Bertone AL. Fetal
vs adult mesenchymal stem cells achieve greater gene expression, but less osteoinduction. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(1): 223-234 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i1/223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.223