Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2015; 7(1): 11-26
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.11
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.11
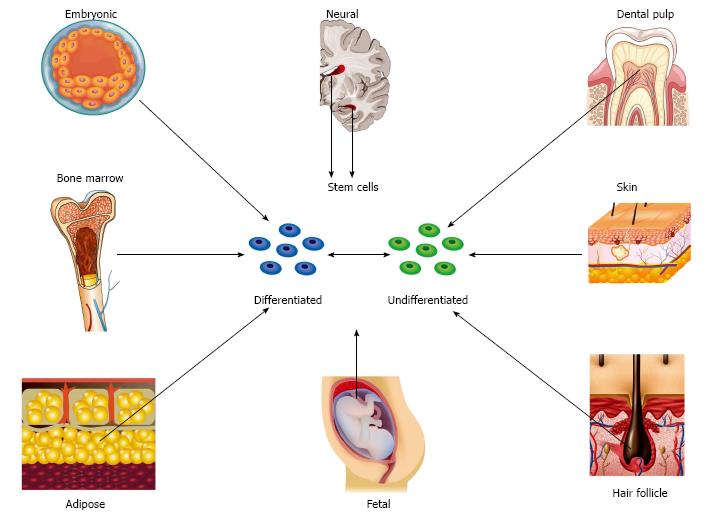
Figure 1 Different stem cell sources.
Embryonic stem cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst and therefore require destruction of the embryo. Nerve stem cells are harvested from the subventricular layer of the lateral ventricle and the subgranular layer of the hippocampus. Bone marrow derived stem cells are harvested from the marrow cavity of long bones. Adipose derived stem cells are derived from subcutaneous fat and are abundantly available following commonly performed procedures such as liposuction. Skin derived precursors are harvested from the dermis and represent a related population of cells harvested from hair follicles. Fetal tissue provides populations of cells from amniotic membrane, amniotic fluid, umbilical cord blood, umbilical cord tissue and Wharton’s jelly. Dental pulp stem cells can be harvested from deciduous teeth.
- Citation: Fairbairn NG, Meppelink AM, Ng-Glazier J, Randolph MA, Winograd JM. Augmenting peripheral nerve regeneration using stem cells: A review of current opinion. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(1): 11-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i1/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.11