Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2014; 6(5): 526-539
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
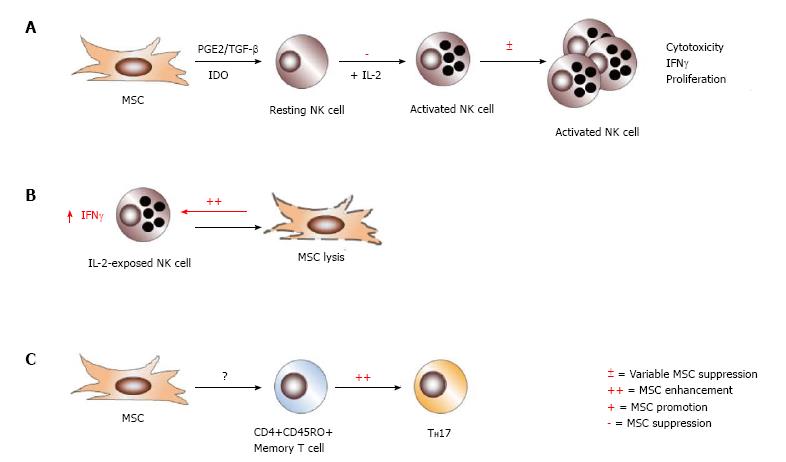
Figure 7 Effects of immune cell activation state on mesenchymal stem cell immune-modulation.
The differentiation state of immune cells can render them susceptible or refractory to mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) action. Though MSCs efficiently inhibit the activation and downstream cytotoxicity of resting NK cells, they exert variable suppression on IL-2-activated NK cells, which is partially ratio dependent (A). MSCs themselves may become targets of activated NK cells for lysis, and enhance NK cell production of IFNγ in the process (B). Interestingly, MSCs promote TH17 differentiation from CD4+CD45RO+ memory T cells, but no other CD4+ or CD8+ T cell population (C).
- Citation: Glenn JD, Whartenby KA. Mesenchymal stem cells: Emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation and therapy. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(5): 526-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i5/526.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526